PROBLEMS ON EXPERIMENTAL PROBABILITY
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
The estimated experimental probability is the relative frequency of the outcome.
Example 1 :
Find the experimental probability of
(a) Tossing a head with one toss of a coin if it falls heads 96 times in 200 tosses.
(b) Rolling a six with a die given that when it was rolled 300 times, a six occurred 54 times
Solution :
(a) Number of times it tosses = 200
Number of times the coin shows head = 96
P(getting a head) = 96/200
(b) Number of times the die was rolled = 300
Number of times 6 appears = 54
P(getting six) = 54/300
Example 2 :
Find the experimental probability of rolling an odd number with a die if an odd number occurred 33 times when the die was rolled 60 times.
Solution :
Number of times die rolled = 60
Number of times odd number occurred = 33
P(getting odd number) = 33/60
= 11/20
Example 3 :
Clem fired 200 arrows at a target and hit the target 168 times. Find the experimental probability of Clem hitting the target.
Solution :
Number of arrows fired at a target = 200
Number of arrows reached the target = 168
P(hitting the target) = 168/200
Example 4 :
Ivy has free-range hens. Out of the first 123 eggs that they laid she found that 11 had double-yolks. Calculate the experimental probability of getting a double-yolk egg from her hens.
Solution :
Total number of eggs = 123
Number of double yolk eggs = 11
P(getting double yolk eggs) = 11/123
Example 5 :
Jackson leaves for work at the same time each day. Over a period of 227 working days, on his way to work he had to wait for a train at the railway crossing on 58 days. Calculate the experimental probability that Jackson has to wait for a train on his way to work.
Solution :
Total number of working days = 227
Number of days he wait for a train at the railway crossing = 58
P(Jackson has to wait) = 58/227
Example 6 :
Ravi has a circular spinner marked P, Q and R on equal sectors. Find the experimental probability of getting a Q if the spinner was twirled 417 times and finished on Q on 138 occasions.
Solution :
Total number of times the spinner was twirled = 417
Number of times it is finished with Q = 138
P(getting Q) = 138/417
Example 7 :
Each time Claude shuffled a pack of cards before a game, he recorded the suit of the top card of the pack His results for 140 games were 34 Hearts, 36 Diamonds, 38 Spades and 32 Clubs.
Find the experimental probability that the top card of a shuffled pack is :
(a) a Heart (b) a Club or Diamond
Solution :
Total number of games played = 140
In which, number of times it shows the top card as
heart = 34
diamond = 36
spades = 38
clubs = 32
(i) P(getting heart at top) = 34/140
(ii) P(club or diamond) = (32+36)/140
= 68/140
Example 8 :
If a car factory checks 360 cars and 8 of them have defects, how many will have defects out of 1260?
Solution :
Let x be the defective number of cars out of 1260.
= (8/360) ⋅ 1260
= 28
So, 28 cars are defective out of 1260 cars.
Example 9 :
If a car factory checks 320 cars and 12 of them have defects, how many out of 560 will NOT have defects?
Solution :
Number of defective cars = (12/320) ⋅ 560
= 21
21 cars are defective out of 560 cars.
Number of cars which are not defective = 560 - 21
= 539
So, 539 cars are not defective.
Example 10 :
What is the theoretical probability that an even number will be rolled on a number cube?
Solution :
When we roll a cube, the possible outcomes are
= {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
Total number of outcomes = 6
Even numbers are = {2, 4, 6}
Total even numbers = 3
Required probability = 3/6
= 1/2
Example 11 :
What was the experimental probability of how many times an even number was actually rolled using the table?
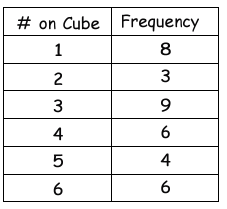
Solution :
Number of times we get even numbers are :
- getting 2, three times
- getting 4, six times
- getting 6, six times
= 3 + 6 + 6
= 15 times
Total number of outcomes = 8 + 3 + 9 + 6 + 4 + 6
= 36
Required probability = 15/36
After the simplification, we get 5/12.
Example 12 :
Martin has a bag of marbles. He removed one marble at random, recorded the color and then placed it back in the bag. He repeated this process several times and recorded his results in the table. Find the experimental probability of drawing each color.
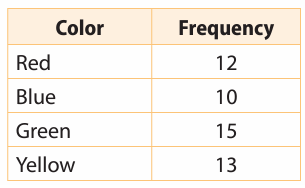
Solution :
Total number of trails = 12 + 10 + 15 + 13
= 50
Probability of drawing red color = 12/50
Probability of drawing blue = 10/50
Probability of drawing green color = 15/50
Probability of drawing yellow color = 13/50
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
SAT Math Problem Solving
Feb 16, 26 05:32 AM
SAT Math Problem Solving -
SAT Math Problems and Solutions
Feb 14, 26 06:05 AM
SAT Math Problems and Solutions -
SAT Math Practice Questions with Answers
Feb 14, 26 05:47 AM
SAT Math Practice Questions with Answers