OVERLAPPING ARCS WORKSHEET
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
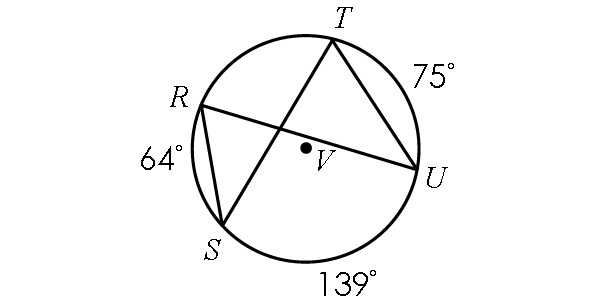
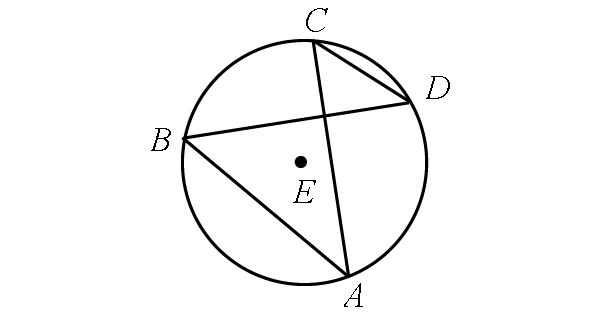
Problem 1 :
Find m∠RST and m∠RUT.
Problem 2 :
If m∠ABD = (6x + 26)° and m∠ACD = (13x - 9)°, find m∠arc AD.
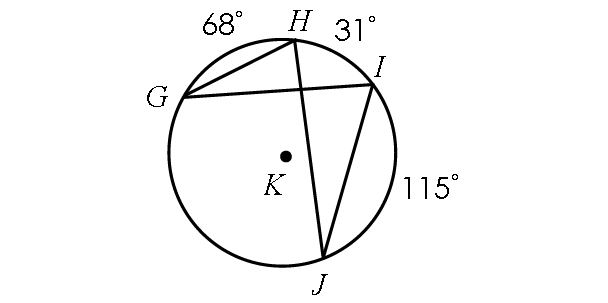
Problem 3 :
Find m∠GHJ and m∠GIJ.
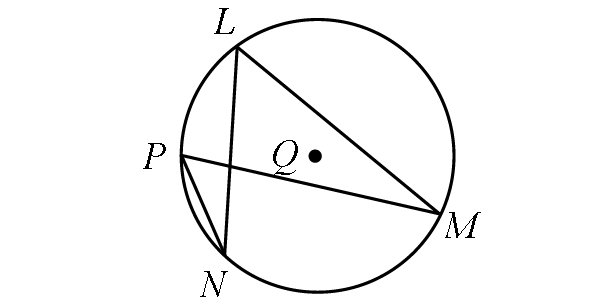
Problem 4 :
If m∠LMP = (5x - 19)° and m∠LNP = (2x + 11)°, find m∠arc PL.
Problem 5 :
Find m∠arc WX.
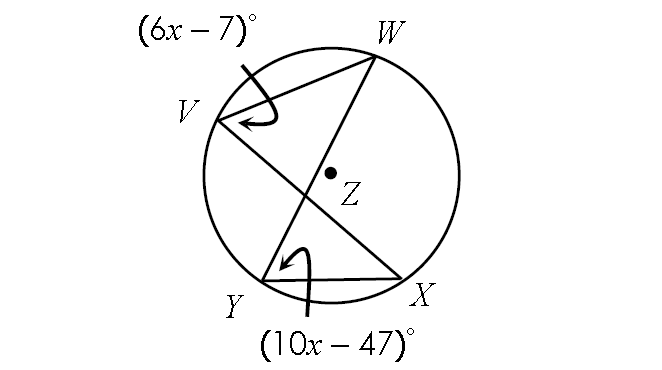
Problem 6 :
In circle P, if m∠arc QR = 110°, m∠arc RS = 94° and m∠QRT = 27°, find the following measures :
(i) m∠QTR, (ii) m∠QSR, (iii) m∠arc QT,
(iv) m∠arc TS, (v) m∠TRS, (vi) m∠RQS

Detailed Answer Key
Problem 1 :
Find m∠RST and m∠RUT.

Solution :
In the diagram above,
m∠arc RT + m∠arc TU + m∠arc US + m∠arc SR = 360°
m∠arc RT + 75° + 139° + 64° = 360°
m∠arc RT + 75° + 139° + 64° = 360°
m∠arc RT + 278° = 360°
Subtract 278° from each side.
m∠arc RT = 82°
By Inscribed Angle Theorem,
m∠RST = 1/2 ⋅ m∠arc RT
m∠RST = 1/2 ⋅ 82°
m∠RST = 41°
In the diagram above, two inscribed angles m∠RST and m∠RUT intercept the same arc RT. So, the angles are congruent.
m∠RUT = m∠RST
m∠RUT = 41°
Problem 2 :
If m∠ABD = (6x + 26)° and m∠ACD = (13x - 9)°, find m∠arc AD.

Solution :
In the diagram above, two inscribed angles m∠ABD and m∠ACD intercept the same arc AD. So, the angles are congruent.
m∠ABD = m∠ACD
(6x + 26)° = (13x - 9)°
6x + 26 = 13x - 9
Subtract 6x from each side.
26 = 7x - 9
Add 9 to each side.
35 = 7x
Divide each side by 7.
5 = x
Finding m∠ABD.
m∠ABD = (6x + 26)°
Substitute x = 5.
m∠ABD = [6(5) + 26]°
m∠ABD = [30 + 26]°
m∠ABD = 56°
By Inscribed Angle Theorem,
m∠arc AD = 2 ⋅ m∠ABD
m∠arc AD = 2 ⋅ 56°
m∠arc AD = 112°
Problem 3 :
Find m∠GHJ and m∠GIJ.

Solution :
In the diagram above,
m∠arc GJ + m∠arc JI + m∠arc IH + m∠arc HG = 360°
m∠arc GJ + 115° + 31° + 68° = 360°
m∠arc GJ + 214° = 360°
Subtract 214° from each side.
m∠arc GJ = 146°
By Inscribed Angle Theorem,
m∠GHJ = 1/2 ⋅ m∠arc GJ
m∠GHJ = 1/2 ⋅ 146°
m∠GHJ = 73°
In the diagram above, two inscribed angles m∠GHJ and m∠GIJ intercept the same arc GJ. So, the angles are congruent.
m∠GIJ = m∠GHJ
m∠GIJ = 73°
Problem 4 :
If m∠LMP = (5x - 19)° and m∠LNP = (2x + 11)°, find m∠arc PL.

Solution :
In the diagram above, two inscribed angles m∠LMP and m∠LNP intercept the same arc LP. So, the angles are congruent.
m∠LMP = m∠LNP
(5x - 19)° = (2x + 11)°
5x - 19 = 2x + 11
Subtract 2x from each side.
3x - 19 = 11
Add 19 to each side.
3x = 30
Divide each side by 3.
x = 10
Finding m∠LMP.
m∠LMP = (5x - 19)°
Substitute x = 10.
m∠LMP = [5(10) - 19]°
m∠LMP = [50 - 19]°
m∠LMP = 31°
By Inscribed Angle Theorem,
m∠arc PL = 2 ⋅ m∠LMP
m∠arc PL = 2 ⋅ 31°
m∠arc PL = 62°
Problem 5 :
Find m∠arc WX.
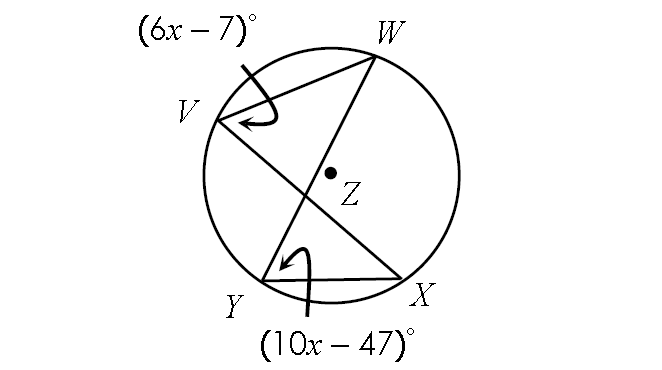
Solution :
In the diagram above, two inscribed angles m∠WVX and m∠WYX intercept the same arc WX. So, the angles are congruent.
m∠WVX = m∠WYX
(6x - 7)° = (10x - 47)°
6x - 7 = 10x - 47
Subtract 6x from each side.
-7 = 4x - 47
Add 47 to each side.
40 = 4x
Divide each side by 4.
10 = x
Finding m∠WVX.
m∠WVX = (6x - 7)°
Substitute x = 10.
m∠WVX = [6(10) - 7]°
m∠WVX = [60 - 7]°
m∠WVX = 53°
By Inscribed Angle Theorem,
m∠arc WX = 2 ⋅ m∠WVX
m∠arc WX = 2 ⋅ 53°
m∠arc WX = 106°
Problem 6 :
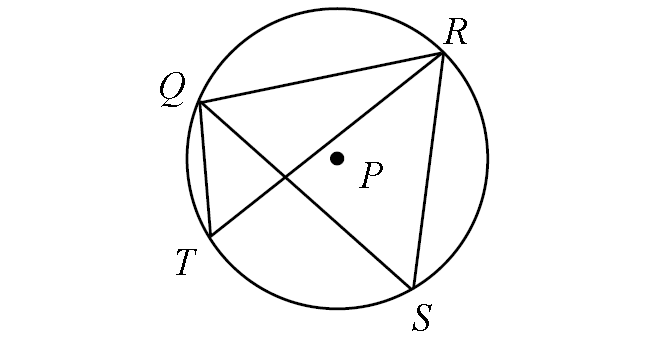
In circle P, if m∠arc QR = 110°, m∠arc RS = 94° and m∠QRT = 27°, find the following measures :
(i) m∠QTR, (ii) m∠QSR, (iii) m∠arc QT,
(iv) m∠arc TS, (v) m∠TRS, (vi) m∠RQS

Solution :
(i) m∠QTR :
By Inscribed Angle Theorem,
m∠QTR = 1/2 ⋅ m∠arc QR
Substitute m∠arc QR = 110°.
m∠QTR = 1/2 ⋅ 110°
m∠QTR = 55°
(ii) m∠QSR :
In the diagram above, two inscribed angles m∠QTR and m∠QSR intercept the same arc QR. So, the angles are congruent.
m∠QSR = m∠QTR
m∠QSR = 55°
(iii) m∠arc QT :
m∠arc QT = 2 ⋅ m∠QRT
Substitute m∠QRT = 27°.
m∠arc QT = 2 ⋅ 27°
m∠arc QT = 54°
(iv) m∠arc TS :
In the circle P above,
m∠arc TS + m∠arc RS + m∠arc QR + m∠arc QT = 360°
Substitute.
m∠arc TS + 94° + 110° + 54° = 360°
m∠arc TS + 258° = 360°
Subtract 258° from each side.
m∠arc TS = 102°
(v) m∠TRS :
By Inscribed Angle Theorem,
m∠TRS = 1/2 ⋅ m∠arc TS
Substitute m∠arc TS = 102°.
m∠TRS = 1/2 ⋅ 102°
m∠TRS = 51°
(vi) m∠RQS :
By Inscribed Angle Theorem,
m∠RQS = 1/2 ⋅ m∠arc RS
Substitute m∠arc RS = 94°.
m∠RQS = 1/2 ⋅ 94°
m∠RQS = 47°
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions
Feb 18, 26 03:01 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions -
Conquering the Hardest SAT Math Questions
Feb 18, 26 02:24 AM
Conquering the Hardest SAT Math Questions -
Problem Solving Strategies for SAT Math
Feb 17, 26 08:09 PM
Problem Solving Strategies for SAT Math