HOW TO FIND ZERO OF A POLYNOMIAL FUNCTION
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
To find zeroes of a polynomial, we have to equate the polynomial to zero and solve for the variable.
To check whether 'k' is a zero of the polynomial f(x), we have to substitute the value 'k' for 'x' in f(x).
If f(k) = 0, then 'k' is a zero of the polynomial f(x).
Find the zeros of the following polynomials
Question 1 :
p(x) = 4x-1
Solution :
Let p(x) = 4x-1
4x-1 = 0
4x = 1
x = 1/4
So, 1/4 is the zero of the given polynomial 4x-1.
Question 2 :
p(x) = 3x+5
Solution :
Let p(x) = 3x+5
3x+5 = 0
3x = -5
x = -5/3
So, -5/3 is the zero of the given polynomial 3x+5.
Question 3 :
p(x) = 2x
Solution :
Let p(x) = 2x
2x = 0
x = 0/2
x = 0
So, 0 is the zero of the given polynomial 2x.
Question 4 :
p(x) = x+9
Solution :
Let p(x) = x+9
x+9 = 0
x = -9
So, -9 is the zero of the given polynomial x+9.
Verify whether the following are roots of the polynomial equations indicated against them.
Question 1 :
x2 - 5x +6 = 0 x = 2, 3
Solution :
Given that p(x) = x² - 5x +6
p(2) = 22 - 5(2) + 6
= 4 -10 + 6
p(2) = 0
Given that p(x) = x2 - 5x +6
p(3) = 32-5(3)+6
= 9 -15 + 6
p(3) = 0
So, 2 and 3 are zeroes or roots of the polynomial p(x).
Question 2 :
x2 +4x+3 = 0 : x = -1, 2
Solution :
Given that p(x) = x2 +4x+3
p(-1) = (-1)2+ 4(-1) +3
= 1-4+3
p(-1) = 0
p(2) = 22+4(2)+3
= 4+8+3
p(2) = 11 ≠ 0
So, -1 is a zero of the polynomial and 2 is not a zero.
Question 3 :
x3 -2x2-5x+6 = 0 : x = 1, -2, 3
Solution :
Given that p(x) = x3 -2x2-5x+6
p(-1) = x3 -2x2-5x+6
p(1) = (1)3 -2(1)2-5(1) +6
= 1-2-5+6
p(-1) = 0
p(-2) = (-2)3 -2(-2)2-5(-2) +6
= -8-8+10+6
= -16+16
p(-2) = 0
p(3) = 33 -2(3)2-5(3) +6
= 27-18-15+6
= 33-33
p(3) = 0
So, -1, -2 and 3 are zeroes or roots of the given polynomial.
Question 4 :
x3-2x2-x+2 = 0: x = -1, 2
Solution :
Given that p(x) = x3-2x2-x+2
p(-1) = x3-2x2-x+2
p(-1) = (-1)3 -2(-1)2-(-1)+2
= -1-2+1+2
= -3+3
p(-1) = 0
p(2) = 23 -2(2)2-2+2
= 8-2(4)-2+2
= 8-8-2+2
p(2) = 0
So, -1 and 2 are zeroes of the polynomial.
Question 5 :
A box with an open top is formed by cutting out of the corners of a rectangular piece of cardboard and then folding up the sides. If x represents the length of side of the square cut from each corner and if the original piece of cardboard is 16 inches by 9 inches, what size must be cut off if the volume of the box is 120 cubic inches ?
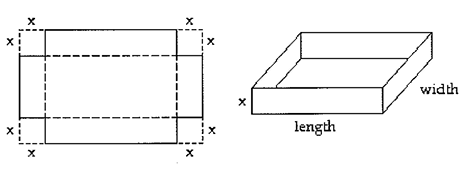
Solution :
Length of cardboard = 16 inches
After we cut x inches on both sides, the new length
= 16 - 2x
Width of the cardboard = 9 inches
After we cut x inches on both sides, the new width
= 9 - 2x
Volume of the box = length x width x height
= (16 - 2x) (9 - 2x) x
= x(144 - 18x - 32x + 4x2)
= x(144 - 50x + 4x2)
4x3 - 50x2 + 144x = 120
4x3 - 50x2 + 144x - 120 = 0
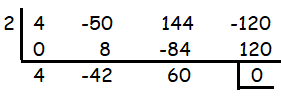
When x = 2, we get the remainder as 0. Then 2 is one of the zeroes of the polynomial.
So, length of side of square to cut from the box is 2 inches.
Find an nth degree polynomial function with real coefficients satisfying the given condition.
Question 6 :
Degree n = 3, 3 and i are zeroes of polynomial and f(2) = 25
Solution :
Zeroes of polynomial with highest exponent = 3.
Since i is one of the zeroes of the polynomial, then its conjugate -i will be other zero.
Let α = i and β = -i
Quadratic equation with the roots α and β is
x2 - (α+β)x + α β = 0
α+β = i - i ==> 0
αβ = i(i) = i2 ==> -1
x2 - 0x + (-1) = 0
x2 - 1 = 0
The required cubic polynomial will have other root which is given as 3. So, other factor is (x - 3)
Multiplying these factors, we get
(x2 - 1)(x - 3) = 0
x3 - 3x2 - x + 3 = 0
Question 7 :
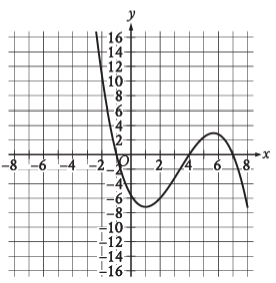
The graph y = f(x) is shown where the function f is defined b y f(x) = ax3 + bx2 + cx + d and a, b, c and d are constants. For how many values of x does f(x) = 0 ?
a) one b) two c) three d) four
Solution :
Every cubic polynomial will have 3 zeroes.
Another name of zeroes :
Solutions, roots, x-intercepts
By observing the graph, the curve is intersecting the graph at three different values -1, 4 and 7.
So, the answer is three, option c is correct.
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
The Hidden Patterns in Hard SAT Math Questions
Feb 09, 26 06:45 PM
The Hidden Patterns in Hard SAT Math Questions -
AP Precalculus Problems and Solutions
Feb 09, 26 08:43 AM
AP Precalculus Problems and Solutions -
Dilation Transformation
Feb 07, 26 08:30 PM
Dilation Transformation - Concept - Rule - Examples with step by step explanation