TRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS OF SPECIAL ANGLES
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
In trigonometry, 0°, 30°, 45°, 60° and 90° are called as special angles and they always lie in the first quadrant.
These special angles 0°, 30°, 45° and 60° are frequently seen in applications and we can use geometry to determine the trigonometric ratios of these angles.
Let us see, how to determine trigonometric ratios of these special angles using geometry.
Trigonometric Ratios of 30° and 60°
Let ABC be an equilateral triangle whose sides have length a (see the figure given below). Draw AD perpendicular to BC, then D bisects the side BC.
Then,
BD = DC = a/2
∠BAD = ∠DAC = 30°
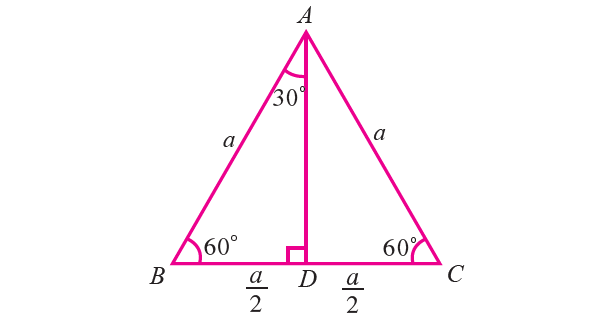
Now, in right triangle ADB, ∠BAD = 30° and BD = a/2.
In right triangle ADB, by Pythagorean theorem,
AB2 = AD2 + BD2
a2 = AD2 + (a/2)2
a2 - (a2/4) = AD2
3a²/4 = AD2
√(3a2/4) = AD
√3 ⋅ a/2 = m AD
Hence, we can find the trigonometric ratios of angle 30° from the right triangle ADB.
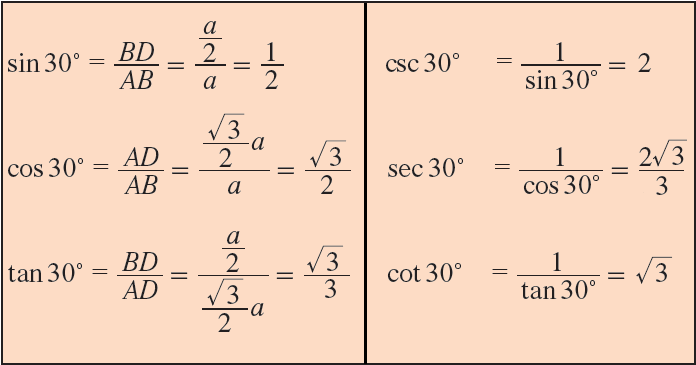
In right triangle ADB, ∠ABD = 60°.
So, we can determine the trigonometric ratios of angle 60°.
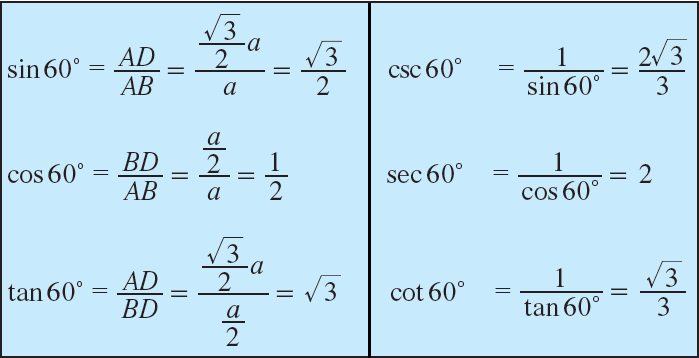
Trigonometric Ratio of 45°
If an acute angle of a right triangle is 45°, then the other acute angle is also 45°.
Thus the triangle is isosceles. Let us consider the triangle ABC with
∠B = 90°
∠A = ∠C = 45°
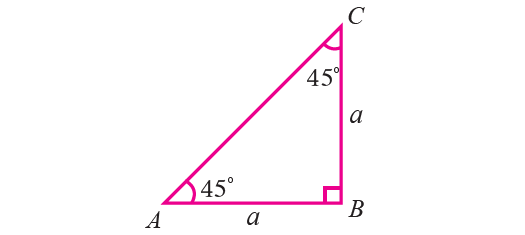
Then AB = BC.
Let AB = BC = a.
By Pythagorean theorem,
AC2 = AB2 + BC2
AC2 = a2 + a2
AC2 = 2a2
Take square root on each side.
AC = a√2
Hence, we can find the trigonometric ratios of angle 45° from the right triangle ABC.
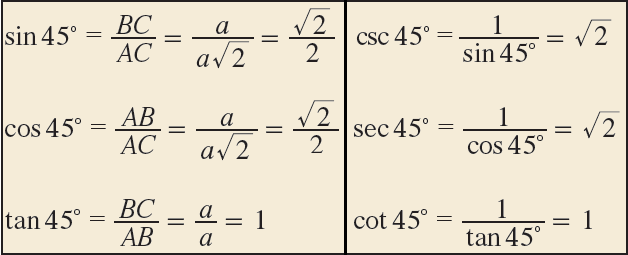
Trigonometric Ratios of 0° and 90°
Consider the figure given below which shows a circle of radius 1 unit centered at the origin.
Let P be a point on the circle in the first quadrant with coordinates (x, y).
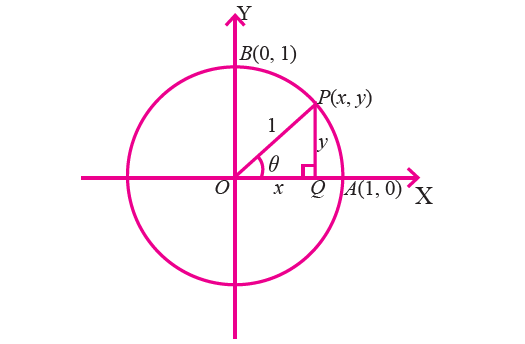
We drop a perpendicular PQ from P to the x-axis in order to form the right triangle OPQ.
Let ∠POQ = θ, then
sin θ = PQ / OP = y/1 = y (y coordinate of P)
cos θ = OQ / OP = x/1 = x (x coordinate of P)
tan θ = PQ / OQ = y/x
If OP coincides with OA, then angle θ = 0°.
Since, the coordinates of A are (1, 0), we have
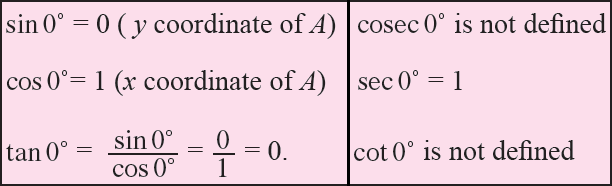
If OP coincides with OB, then angle θ = 90°.
Since, the coordinates of B are (0, 1), we have
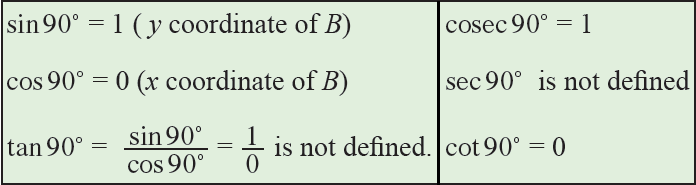
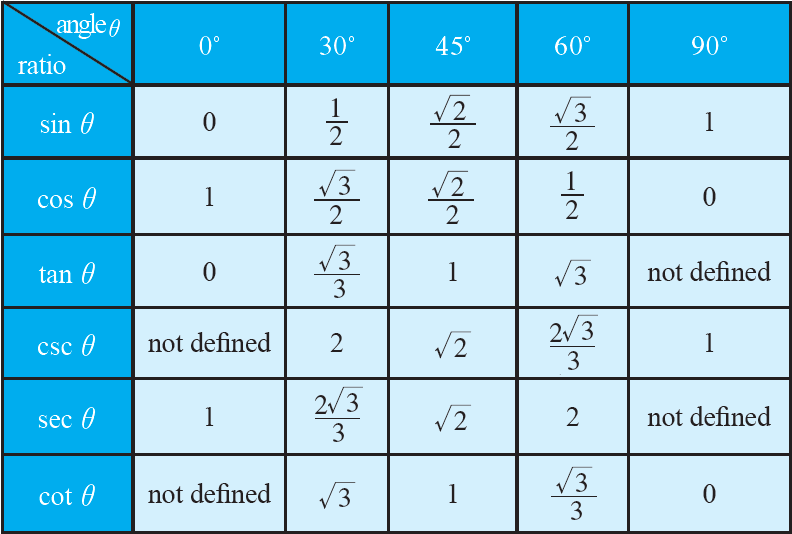
The six trigonometric ratios of angles 0°, 30°, 45°, 60° and 90° are provided in the following table.
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 40)
Mar 03, 26 06:53 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 40) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 39)
Mar 03, 26 04:59 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 39) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 38)
Mar 03, 26 10:05 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 38)