THREE-DIMENSIONAL FIGURES
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Essential Question :
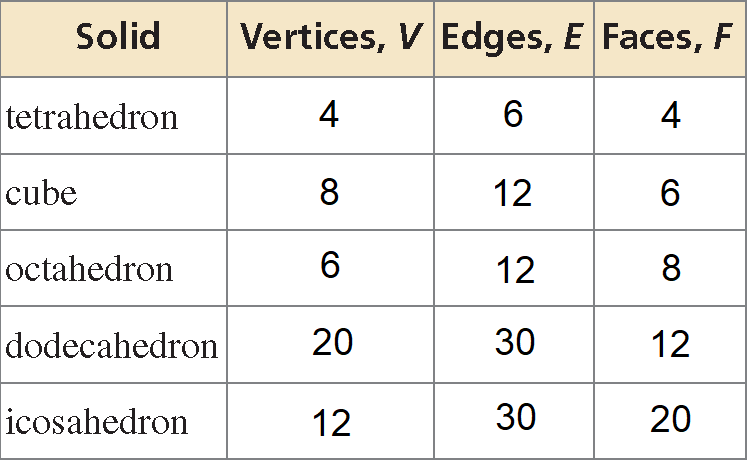
What is the relationship between the numbers of vertices V, edges E, and faces F of a polyhedron ?
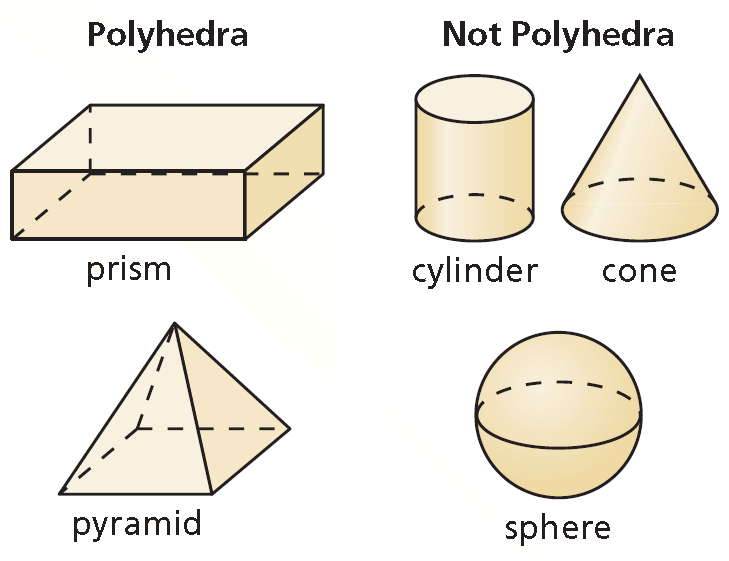
A polyhedron is a solid that is bounded by polygons, called faces.
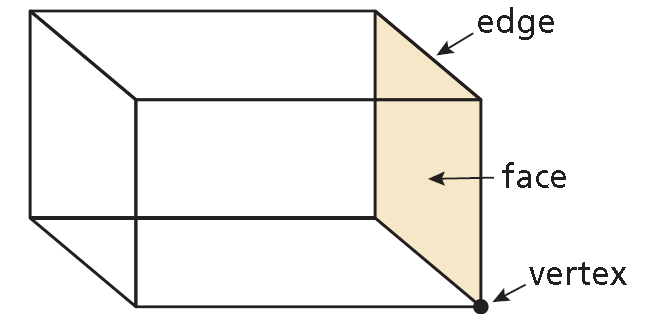
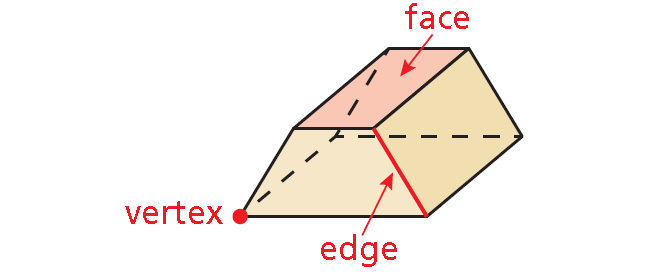
• Each vertex is a point.
• Each edge is a segment of a line.
• Each face is a portion of a plane.
Analyzing a Property of Polyhedra
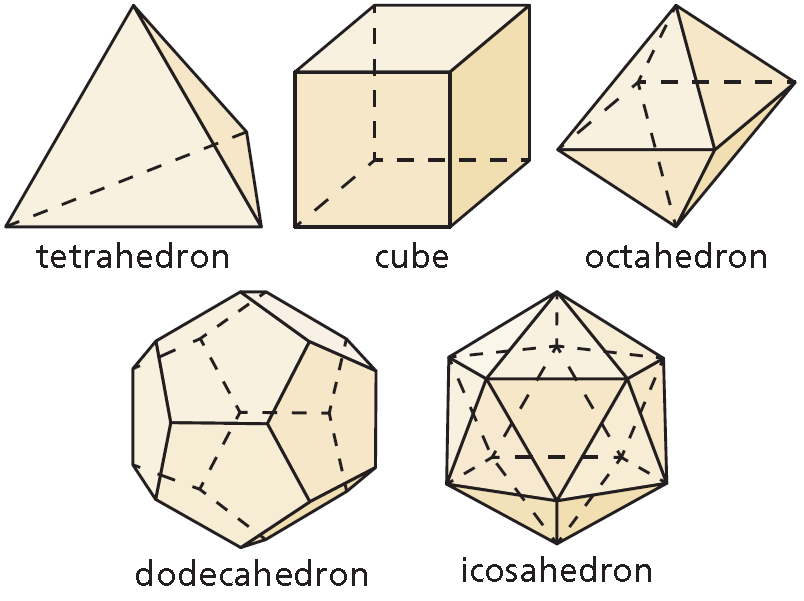
The five Platonic solids are shown below. Each of these solids has congruent regular polygons as faces. Complete the table by listing the numbers of vertices, edges, and faces of each Platonic solid.
Classifying Solids
A three-dimensional figure, or solid, is bounded by flat or curved surfaces that enclose a single region of space. A polyhedron is a solid that is bounded by polygons, called faces. An edge of a polyhedron is a line segment formed by the intersection of two faces. A vertex of a polyhedron is a point where three or more edges meet. The plural of polyhedron is polyhedra or polyhedrons.
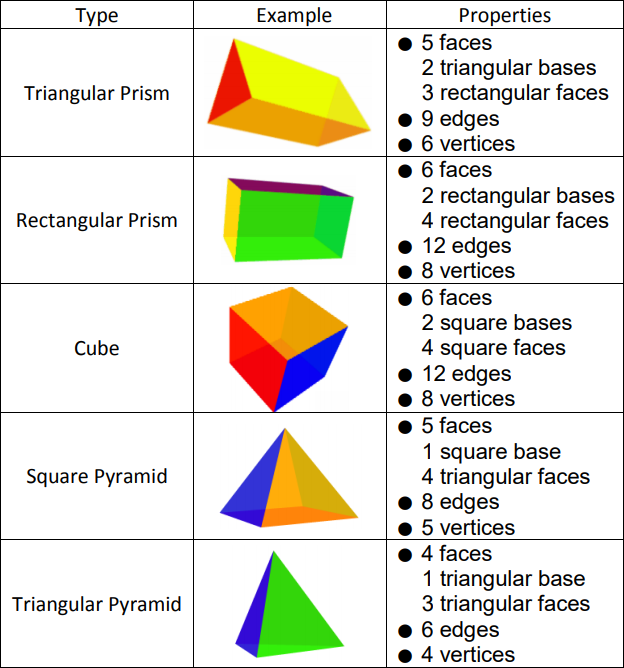
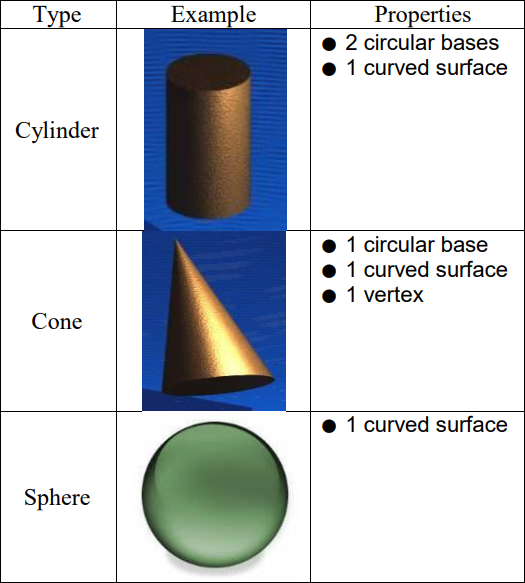
Core Concept - Types of Solids
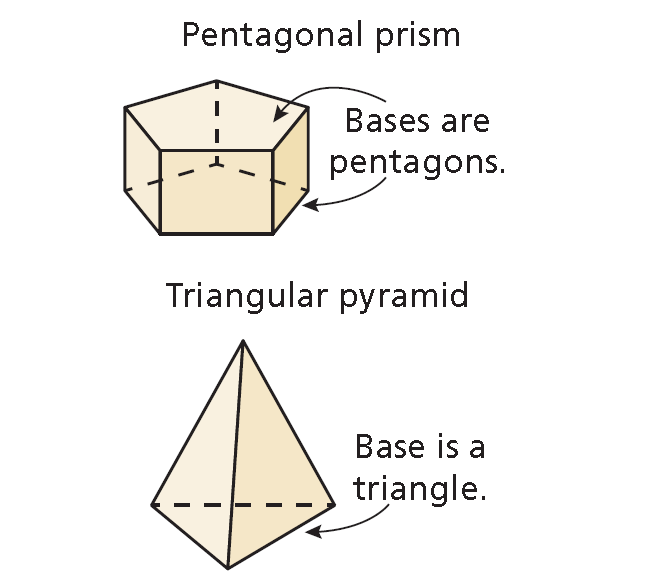
To name a prism or a pyramid, use the shape of the base. The two bases of a prism are congruent polygons in parallel planes. For example, the bases of a pentagonal prism are pentagons. The base of a pyramid is a polygon. For example, the base of a triangular pyramid is a triangle.
Example 1 :
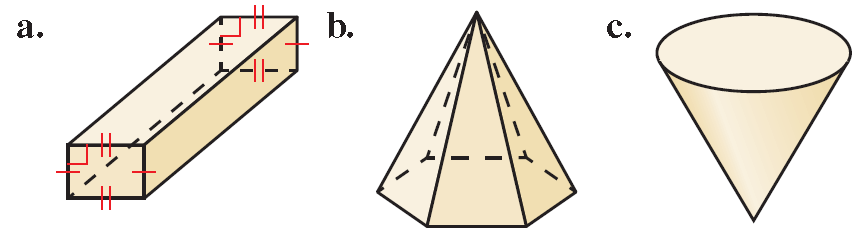
Tell whether each solid is a polyhedron. If it is, name the polyhedron.
Solution :
(a) The solid is formed by polygons, so it is a polyhedron. The two bases are congruent rectangles, so it is a rectangular prism.
(b) The solid is formed by polygons, so it is a polyhedron. The base is a hexagon, so it is a hexagonal pyramid.
(c) The cone has a curved surface, so it is not a polyhedron.
Describing Cross Sections
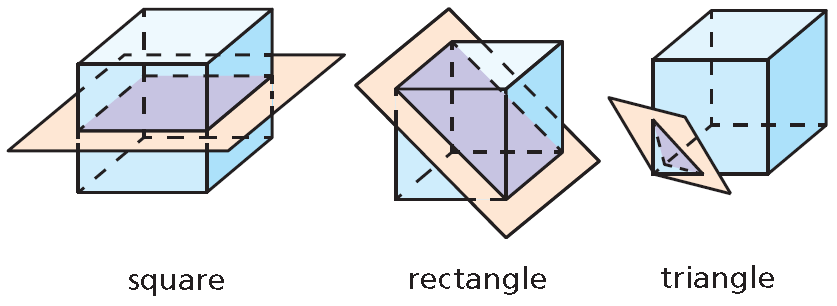
Imagine a plane slicing through a solid. The intersection of the plane and the solid is called a cross section. For example, three different cross sections of a cube are shown below.
Example 2 :
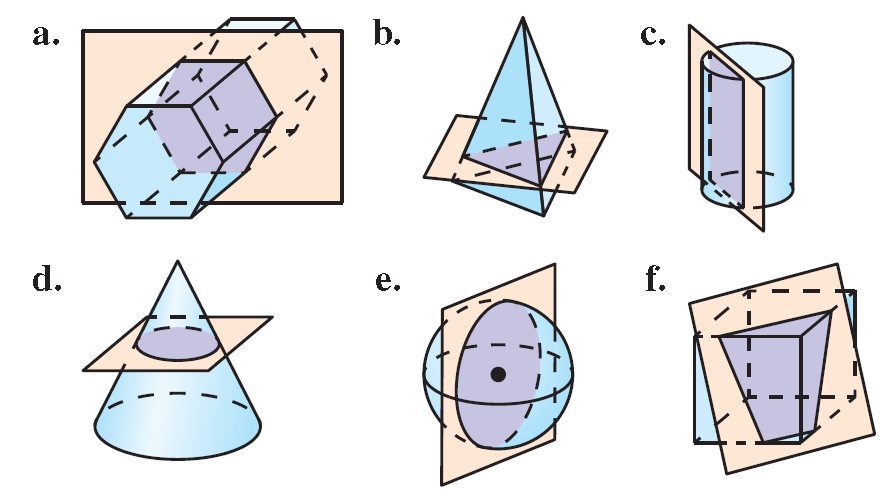
Describe the shape formed by the intersection of the plane and the solid.
Solution :
(a) The cross section is a hexagon.
(b) The cross section is a triangle.
(c) The cross section is a rectangle.
(d) The cross section is a circle.
(e) The cross section is a circle.
(f) The cross section is a trapezoid.
Sketching and Describing Solids of Revolution
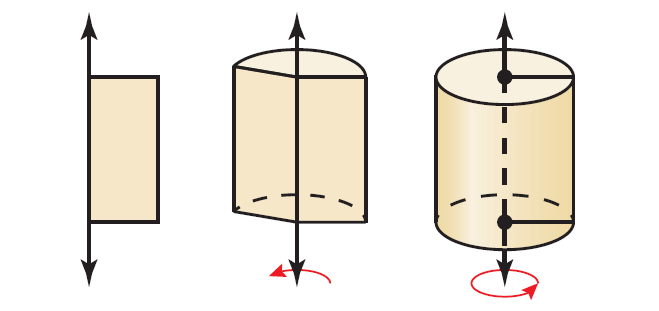
A solid of revolution is a three-dimensional figure that is formed by rotating a two-dimensional shape around an axis. The line around which the shape is rotated is called the axis of revolution.
For example, when you rotate a rectangle around a line that contains one of its sides, the solid of revolution that is produced is a cylinder.
Example 3 :
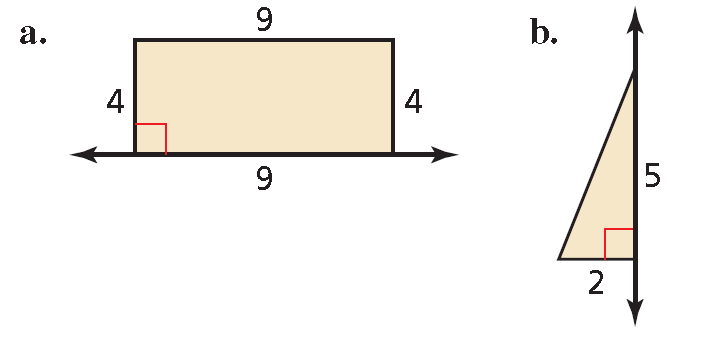
Sketch the solid produced by rotating the figure around the given axis. Then identify and describe the solid.
Solution :
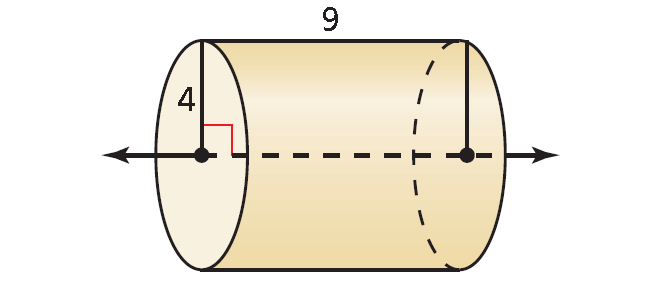
(a) The solid is a cylinder with a height of 9 and a base radius of 4.
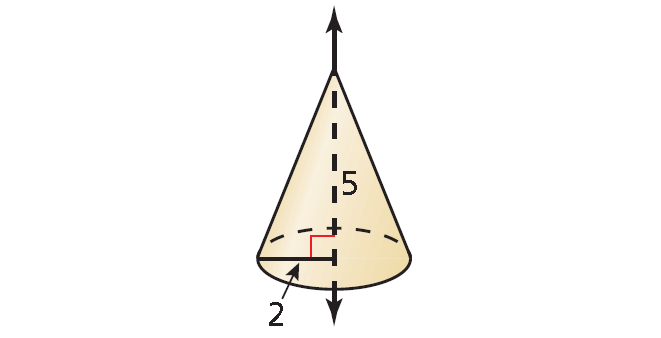
(b) The solid is a cone with a height of 5 and a base radius of 2.
Prisms and Pyramids
Three Dimensional Figures with Curved Surfaces
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 50)
Mar 06, 26 07:48 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 50) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 49)
Mar 06, 26 06:47 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 49) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 48)
Mar 06, 26 05:24 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 48)


