SIMILAR TRIANGLES IN GEOMETRY
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
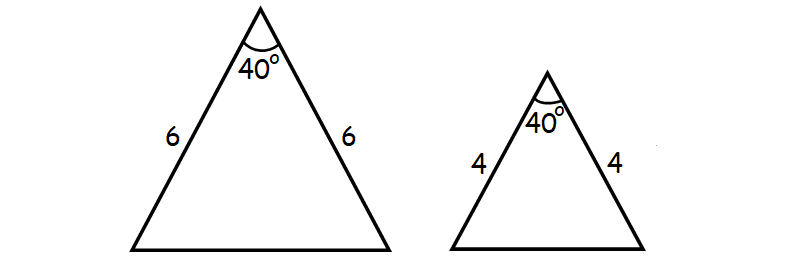
Identifying Similar Triangles
Triangles which are similar will have the same shape, but not necessarily the same size.
We can use the following postulates and theorems to identify similar triangles.
Triangle Similarity Postulates and Theorems
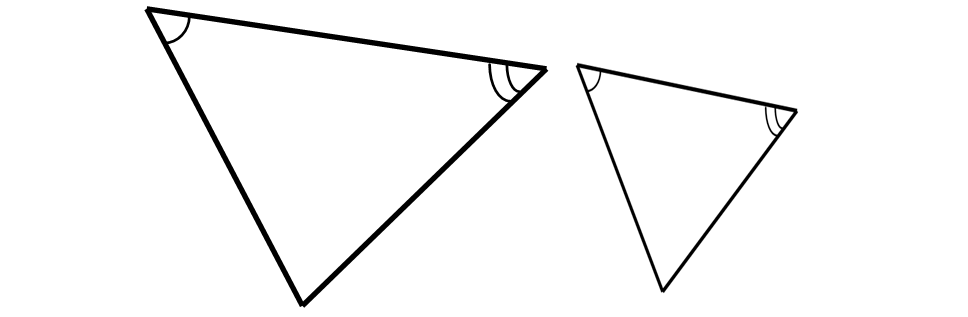
1. Angle-Angle (AA) Similarity Postulate :
If two angles of one triangle are congruent to two angles of another, then the triangles must be similar.
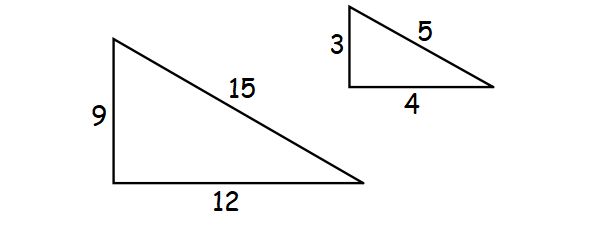
2. Side-Side-Side (SSS) Similarity Theorem :
If the lengths of the corresponding sides of two triangles are proportional, then the triangles must be similar.
3. Side-Angle-Side (SAS) Similarity Theorem :
If an angle of one triangle is congruent to an angle of a second triangle and the lengths of the sides including these angles are proportional, then the triangles must be similar.
Writing Proportionality Statements
Example :
In the diagram shown below ΔACB ∼ ΔDCE.
a. Write the statement of proportionality.
b. Find ∠CDE.
c. Find DC and AD.
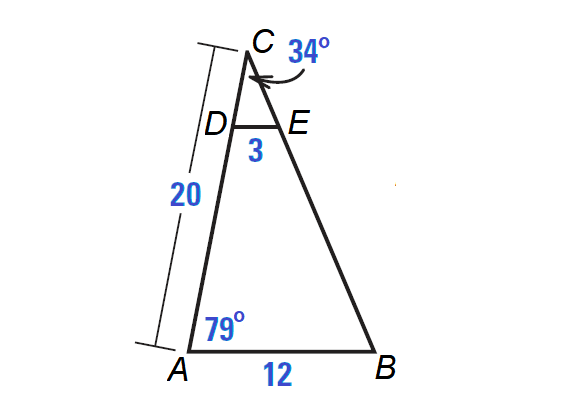
Solution (a) :
DC / AC = CE / CB = ED / BA
Solution (b) :
Because ΔACB ∼ ΔDCE,
∠A ≅ ∠CDE
Then, we have
∠CDE = ∠A = 79°
Solution (c) :
Write proportion.
ED / BA = DC / AC
Substitute.
3 / 12 = DC / 20
Multiply each side by 20.
20 ⋅ (3 / 12) = (DC / 20) ⋅ 20
Simplify.
5 = DC
Because AD = AC - DC,
AD = 20 - 5
AD = 15
So, DC is 5 units and AD is 15 units.
Investigating Similar Triangles - Activity
Use a protractor and a ruler to draw two noncongruent triangles so that each triangle has a 40° angle and a 60° angle. Check your drawing by measuring the third angle of each triangle—it should be 80°. Why? Measure the lengths of the sides of the triangles and compute the ratios of the lengths of corresponding sides. Are the triangles similar ?
Proving that Two Triangles are Similar
Example :
Color variations in the tourmaline crystal shown below lie along the sides of isosceles triangles. In the triangles each vertex angle measures 52°. Explain why the triangles are similar.
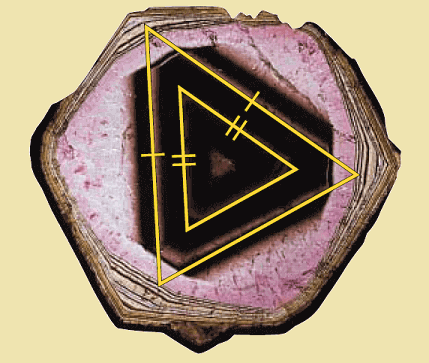
Solution :
Because the triangles are isosceles, you can determine that each base angle is 64°. Using the AA Similarity Postulate, we can conclude that the triangles are similar.
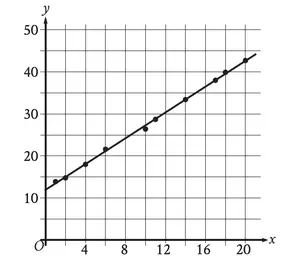
Why a Line Has Only One Slope
Example :
Use properties of similar triangles to explain why any two points on a line can be used to calculate the slope. Find the slope of the line using both pairs of points shown.
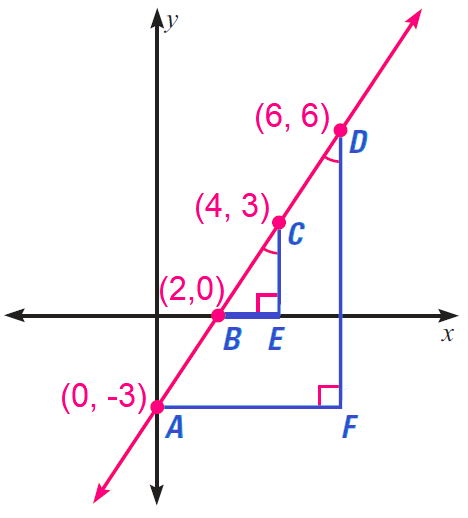
Solution :
By the AA Similarity Postulate ΔBEC ∼ ΔAFD, so the ratios of corresponding sides are the same.
In particular,
CE / DF = BE / AF
By a property of proportions, we have
CE / BE = DF / AF
The slope of a line is the ratio of the change in y to the corresponding change in x. The ratios CE/BE and DF/AF represent the slopes of BC and AD respectively.
Because the two slopes are equal, any two points on a line can be used to calculate its slope. We can verify this with specific values from the diagram.
Using slope formula,
Slope of BC = (3 - 0) / (4 - 2) = 3 / 2
Slope of AD = [6 - (-3)] / (4 - 2) = 9 / 6 = 3 / 2
Using Similar Triangles in Real LIfe
Example :
Low-level aerial photos can be taken using a remote-controlled camera suspended from a blimp. we want to take an aerial photo that covers a ground distance g of 50 meters. Use the proportion f/h = n/g to estimate the altitude h that the blimp should fly at to take the photo. In the proportion, use f = 8 cm and n = 3 cm. These two variables are determined by the type of camera used.
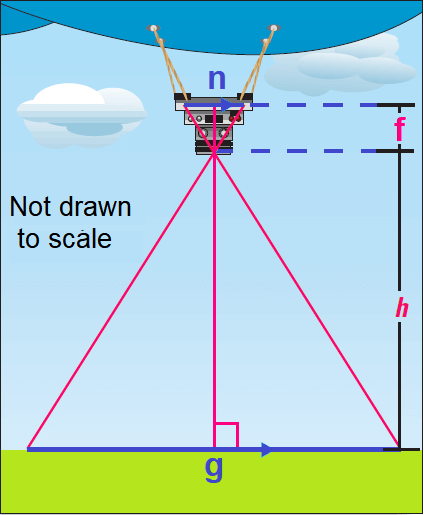
Solution :
Write proportion.
f / h = n / g
Substitute.
8 / h = 3 / 50
By reciprocal property of proportion,
h / 8 = 50 / 3
Multiply each side by 8.
8 ⋅ (h / 8) = 8 ⋅ (50 / 3)
Simplify.
h ≈ 133
So, the blimp should fly at an altitude of about 133 meters to take a photo that covers a ground distance of 50 meters.
Using Scale Factors
Example :
Find the length of the altitude DG in the diagram shown below.
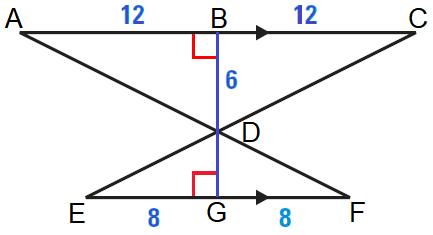
Solution :
Find the scale factor of ΔADC to ΔFDE.
AC / FE = (12 + 12) / (8 + 8)
AC / FE = 24 / 16
AC / FE = 3 / 2
Now, because the ratio of the lengths of the altitudes is equal to the scale factor, we can write the following equation.
DB / DG = 3 / 2
Substitute 6 for DB and and solve for DG.
6 / DG = 3 / 2
By reciprocal property of proportion,
DG / 6 = 2 / 3
Multiply each side by 6.
6 ⋅ (DG / 6) = (2 / 3) ⋅ 6
Simplify.
DG = 4
So, the length of the altitude DG is 4 units.
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
Problem Solving Strategies for SAT Math
Feb 17, 26 08:09 PM
Problem Solving Strategies for SAT Math -
SAT Math Challenge Problems
Feb 17, 26 07:01 PM
SAT Math Challenge Problems -
How to Solve Challenging Math Problems in SAT
Feb 17, 26 06:42 PM
How to Solve Challenging Math Problems in SAT