ROOTS AND REAL NUMBERS
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Roots
A number that is multiplied by itself to form a product is a square root of that product. The radical symbol √ is used to represent square roots. For nonnegative numbers, the operations of squaring and finding a square root are inverse operations. In other words, for x ≥ 0,
√x ⋅ √x = x
Positive real numbers have two square roots. The principal square root of a number is the positive square root and is represented by √ . A negative square root is represented by -√. The symbol ±√ is used to represent both square roots.
3 ⋅ 3 = 32 = 9 ---> √9 = 3 Positive square root of 9
(-3)(-3) = (-3)2 = 9 ---> -√9 = -3 Negative square root of 9
A perfect square is a number whose positive square root is a whole number. Some examples of perfect squares are shown below.
0
02
1
12
2
22
3
32
4
42
A number that is raised to the third power to form a product is a cube root of that product. The symbol 3√ indicates a cube root.
Since 23 = 8, 3√8 = 2. Similarly, the symbol 4√ indicates a fourth root : 24 = 16, so 4√16 = 2.
Finding Roots
Find each root.
Example 1 :
√36
Solution :
= √36
Think : What number squared equals 36?
= √62
= 6
Example 2 :
-√49
Solution :
= -√49
Think : What number squared equals 49?
= -√72
= -7
Example 3 :
3√-64
Solution :
= 3√-64
Think : What number cubed equals -125?
[(-4)(-4)(-4) = 16(-4) = -64]
= 3√(-4)3
= -4
Finding Roots of Fractions
Find each root.
Example 4 :
√(1/9)
Solution :
= √(1/9)
Think : What number squared equals 1/9?
= √(1/3)2
= 1/3
Example 5 :
√(16/25)
Solution :
= √(16/25)
Think : What number squared equals 16/25?
= √(4/5)2
= 4/5
Note :
Square roots of numbers that are not perfect squares, such as 15, are not whole numbers. A calculator can be used to approximate the value of √15 as 3.872983346…
Without a calculator, square roots of perfect squares can be used to estimate the square roots of other numbers.
Real Numbers
Real numbers can be classified according to their characteristics.
Natural numbers are the counting numbers :
1, 2, 3, …
Whole numbers are the natural numbers and zero :
0, 1, 2, 3, …
Integers are the whole numbers and their opposites :
…, -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, …
Rational numbers are numbers that can be expressed in the form a/b, where a and b are both integers and b ≠ 0. When expressed as a decimal, a rational number is either a terminating decimal or a repeating decimal.
• A terminating decimal has a finite number of digits after the decimal point (for example, 1.25, 2.75, and 4.0).
• A repeating decimal has a block of one or more digits after the decimal point that repeat continuously (where all digits are not zeros).
Irrational numbers are all real numbers that are not rational. They cannot be expressed in the form a/b where a and b are both integers and b ≠ 0. They are neither terminating decimals nor repeating decimals.
For example :
0.10100100010000100000…
After the decimal point, this number contains 1 followed by one 0, and then 1 followed by two 0’s, and then 1 followed by three 0’s, and so on.
This decimal neither terminates nor repeats, so it is an irrational number.
If a whole number is not a perfect square, then its square root is irrational.
For example, 2 is not a perfect square, and √2 is irrational.
The real numbers are made up of all rational and irrational numbers.
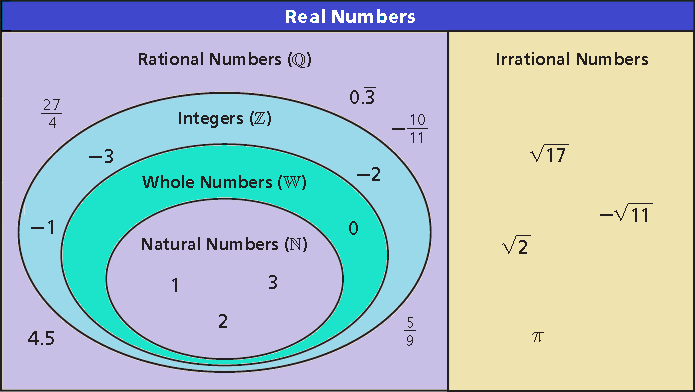
Classifying Real Numbers
Write all classifications that apply to each real number.
Example 6 :
8/9
Solution :
8/9 is in the form a/b, where a and b are integers (b ≠ 0).
8 ÷ 9 = 0.8888…
8/9 can be written as a repeating decimal.
So, the classification of 8/9 is rational, repeating decimal.
Example 7 :
15
Solution :
15 can be written in the form a/b.
15 = 15/1
15 can be written as a terminating decimal.
15 = 15.0
So, the classification of 15 is rational, terminating decimal, integer, whole, natural.
Example 8 :
√26
Solution :
26 is not a perfect square, so √26 is irrational.
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part -27)
Feb 28, 26 07:46 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part -27) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 26)
Feb 28, 26 06:28 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 26) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 25)
Feb 28, 26 07:21 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 25)