PROBABILITY QUESTIONS INVOLVING RELATIVE FREQUENCY
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
If we are given a table of frequencies then we use relative frequencies to estimate the probabilities of the events.
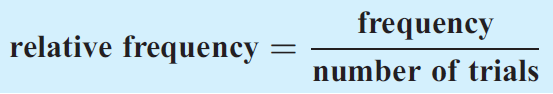
Example 1 :
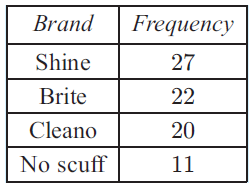
A marketing company surveys 80 randomly selected people to discover what brand of shoe cleaner they use. The results are shown in the table alongside :
a) Based on these results, what is the experimental probability of a community member using :
i) Brite ii) Cleano?
Solution :
For brite = 22/80 = 0.275
For cleano = 20/80 = 0.25
Example 2 :
A marketing company was commissioned to investigate brands of products usually found in the bathroom. The results of a soap survey are given below:
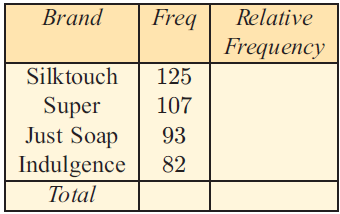
a) How many people were randomly selected in this survey?
b) Calculate the relative frequency of use of each brand of soap.
c) Using the results obtained by the marketing company, what is the experimental probability that the soap used by a randomly selected person is:
i) Just Soap ii) Indulgence iii) Silk touch?
Solution :
(a) Total number of people selected randomly
= 125+107+93+82
= 407 people
(b) Relative frequency :
|
Brand Silk touch Super Just soap Indulgence Total |
Frequency 125 107 93 82 407 |
Relative frequency 0.307 0.263 0.229 0.201 |
(c)
i) Just Soap = 0.229
ii) Indulgence = 0.201
iii) Silk touch = 0.307
Example 3 :
Two coins were tossed 489 times and the number of heads occurring at each toss was recorded. The results are shown below :

a) Copy and complete the table given.
b) Estimate the chance of the following events occurring :
i) 0 heads ii) 1 head iii) 2 heads
Solution :
(a) Number of times coins tossed = 489
121 + number of times coin shows 1 head + 109 = 489
number of times coin shows 1 head = 489 - 230
= 259
|
Outcome 0 head 1 head 2 heads Total |
Frequency 121 259 109 489 |
Relative frequency 0.247 0.530 0.223 1 |
b)
(i) The chance of occurring 0 heads = 0.247
(ii) The chance of occurring 1 head = 0.530
(iii) The chance of occurring 2 heads = 0.223
Example 4 :
At the Annual Show the toffee apple vendor estimated that three times as many people preferred red toffee apples to green toffee apples.
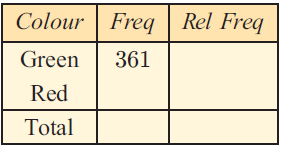
a) If 361 people wanted green toffee apples, estimate how many wanted red.
b) Copy and complete the table given.
c) Estimate the probability that the next customer will ask for:
i) a green toffee apple ii) a red toffee apple.
Solution :
(a) Number of people wanted red = 3(361)
= 1083
(b)
|
Colour Green Red Total |
Frequency 361 1083 1444 |
Relative frequency 0.25 0.75 1 |
c) (i) Probability of green apple = 0.25
(ii) Probability of red apple = 0.75
Example 5 :
The tickets sold for a tennis match were recorded as people entered the stadium. The results are shown:
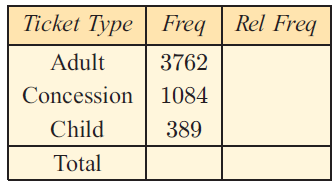
a) How many tickets were sold in total?
b) Copy and complete the table given.
c) If a person in the stadium is selected at random, what is the probability that the person bought a Concession ticket?
Solution :
(a) Total number of tickets sold = 3762+1084+389
= 5235
(b)
|
Ticket type Adult Concession Child Total |
Frequency 3762 1084 389 5235 |
Relative frequency 0.718 0.207 0.074 1 |
(c) The probability of a person busying concession ticket = 0.207
Example 6 :
Some men and women were surveyed at a football game. They were asked which team they supported. The results are shown in the two way table.
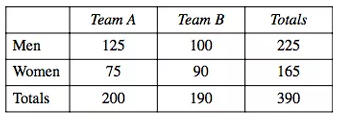
What percentage of the women surveyed supported Team B, correct to the nearest percent?
(A) 23% (B) 45% (C) 47% (D) 55%
Solution :
Probability of getting women in team B = 90/190
Converting into percentage = (90/190) x 100%
= 47.3 %
Approximately 47%.
Example 7 :
At the opening of the ski season, there has been sufficient snow for skiing for 37 out of the past 50 years. Calculate the relative frequency of sufficient snow at the beginning of the ski season.
Solution :
Identify the number of years with sufficient snow: 37 years.
Identify the total number of years: 50 years.
Calculate the relative frequency:
Relative frequency = (Number of years with sufficient snow) / (Total number of years)
= 37/50
= 0.74
Example 8 :
A biased coin has been tossed 100 times with the result of 79 Heads. Calculate the relative frequency of the coin landing Heads.
Solution :
Probability of landing on heads = 79/100
= 0.79
Example 9 :
Of eight Maths tests done by a class during a year, Peter has topped the class three times. Calculate the relative frequency of Peter topping the class.
Solution :
Number of maths test = 8
Number of tests he topped = 3
required probability = 3/8
= 0.375
Example 10 :
A survey of 25000 new car buyers found that 750 had a major mechanical problem in the first year of operation. Calculate the relative frequency of:
a) having mechanical problems in the first year
b) not having mechanical problems in the first year.
Solution :
a) Probability of having mechanical problems
= 750/25000
= 0.03
b) Probability of not having mechanical problems
= (25000 - 750)/25000
= 24250/25000
= 0.97
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
US Common Core K-12 Curricum Algebra Solving Simple Equations
Jan 07, 26 01:53 PM
US Common Core K-12 Curricum Algebra Solving Simple Equations -
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 4)
Jan 05, 26 06:56 PM
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 4) -
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 3)
Jan 05, 26 06:34 PM
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 3)