LATERAL SURFACE AREA
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Lateral surface area of a solid is the measurement of outer area,where the extension of top and bottom portion wont be included.
Lateral surface area of cylinder
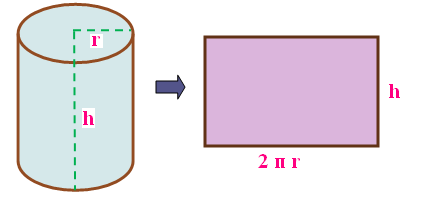
If a rectangle revolves about one side and completes one full rotation, the solid thus formed is called a right circular cylinder. The above picture shows that how rectangle forms a right circular cylinder. In other words lateral surface area can be represented as LSA
LSA of cylinder = 2⋅ π ⋅ r ⋅ h
"r" and "h" stands for radius and height of cylinder.
Lateral surface area of Sphere
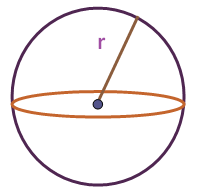
If we consider the shapes like sphere, both total surface area and LSA would be same.
Because in the shape sphere, we don't need any specific top portion or bottom portion (circles or any other shapes) as we have for cylinder
LSA of Sphere = 4 ⋅ π ⋅ r²
Here "r" represents radius of the sphere.
Lateral surface area of hemisphere
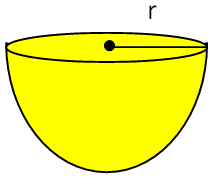
LSA of Hemisphere = 2 ⋅ π ⋅ r²
Total Surface Area of Sphere
Surface area or total surface area of the sphere is
= Lateral surface area + Area of the base
= 2 ⋅ π ⋅ r² + π ⋅ r²
= 3 ⋅ π ⋅ r²
Lateral surface area of cone
And for the shapes like cone, we don't have any specific shape at the top portion. But we have the circle at the base (bottom). So when we want to find the LSA of a cone, we need to find the area that exclude the extension of the bottom portion or base.In the top portion.
We don't need to exclude anything. Because there will be only one vertex at the top.So we don't have to exclude any thing at the top when we want to find LSA of cone.
LSA of cone = π ⋅ r ⋅ l
Here "r" represents radius and "L" represents slant height of the cone.
Example problems of LSA
Question 1
A solid right circular cylinder has radius of 14 cm and height of 8 cm. Find its LSA
Solution:
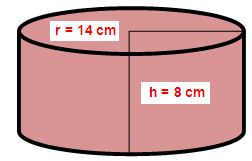
Radius of the cylinder (r) = 14 cm
Height of the cylinder (h) = 8 cm
LSA of cylinder = 2 Π r h
= 2 x (22/7) x 14 x 8
= 704 sq.cm
LSA of cylinder = 704 sq.cm
Hence, LSA of cylinder is 704 sq.cm
Question 2:
Lateral surface area and circumference at the base of a solid right circular cylinder are 4400 sq.cm and 110 cm respectively. Find its height and diameter.
Solution:
LSA of cylinder = 4400 sq.cm
Circumference of the base = 110 cm
2 Π r = 110 ==> 2 x (22/7) x r = 110
r = 110 x (1/2) x (7/22) ==> r = 17.5 cm
diameter = 2 r
= 2 (17.5) ==> 35 cm
2 Π r h = 4400 ==> 110 x h = 4400 ==> h = 4400/110
h = 40 cm
Height = 40 cm
Diameter of the cylinder = 35 cm
Hence, height and diameter of cylinder are 40 cm and 35 cm respectively.
Question 3:
A mansion has 12 right cylindrical pillars each having radius 50 cm and height 3.5 m. Find the cost to paint the lateral surface of pillars at $ 20 per square meter.
Solution:
The pillars of the mansion are in the shape of cylinder
Radius = 50 cm ==> 0.5 m
Height = 3.5 m
LSA of one pillar = 2 x (22/7) x 0.5 x 3.5
= 2 x 22 x 0.5 x 0.5 ==> 11 m²
LSA of 12 pillars = 12 x 11 ==> 132 m²
Cost to paint per m² = $ 20
Total cost = 20 x 132
= $ 2640
Hence, total cost of painting 12 pillars is $ 2640
Question 4:
If the circumference of the base of the solid right circular cone is 236 and its slant height is 12 cm, find its LSA.
Solution:
Circumference of the base = 236 cm
Slant height (L) = 12 cm
2 Π r = 236 ==> Π r = 236/2 ==> 118
LSA of cone = Π r l
= 118 (12) ==> 1416 cm²
LSA of cone = 1416 cm²
Question 5:
A heap of paddy is in the form of a cone whose diameter is 4.2 m and height is 2.8 m. If the heap is to be covered exactly by a canvas to protect it from rain,then find the area of the canvas needed.
Solution:
Diameter of heap of paddy = 4.2 m
r = 4.2/2 ==> 2.1 m
height of paddy (h) = 2.8 m
L² = r² + h²
L = √(2.1)² + (2.8)² ==> √4.41 + 7.84 ==>√12.25 = 3.5
LSA of heap of paddy = Π r l
= (22/7) x (2.1) x (3.5) ==> 22 x (2.1) x (0.5) ==> 23.1 cm²
CSA of paddy = 23.1 cm²
Question 6:
The central angle and radius of a sector of a circular disc are 180 degree and 21 cm respectively. If the edges of the sector are joined together to make a hollow cone,then find the radius of the cone.
Solution:
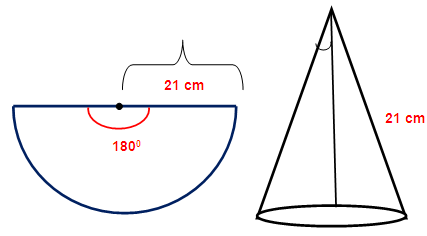
The cone is being created by joining the radius. So the radius of the sector is going to be the slant height of the cone.
Slant height (L) = 21 cm
Arc length of the sector = Circumference of the base of the cone
Length of arc = (θ/360) x 2Π R
Here R represents radius of the sector
= (180/360) x 2 x (22/7)x (21) ==> (1/2) x 2 x 22x 3 ==> 66 cm
So,circumference of the base of the cone = 66
2 Π r = 66 ==> 2 x (22/7) x r = 66 ==> r = 10.5 cm
Radius of the cone = 10.5 cm
Question 7 :
If the lateral surface area of solid sphere is 98.56 cm², then find the radius of the sphere.
Solution:
LSA of sphere = 98.56 cm²
4 Π r² = 98.56 ==> 4 x (22/7) x r² = 98.56
r² = 98.56 x (1/4) x (7/22) ==> r² = 7.84 ==> 2.8 cm
Radius of the sphere = 2.8 cm
Question 8 :
If the lateral surface area of the solid hemisphere is 2772 sq.cm, then find its radius.
Solution:
Lateral surface area of hemisphere = 2772 cm²
2 Π r² = 2772 ==> 2 x (22/7) x r² = 2772
r² = 2772 x (1/2) x (7/22) ==> r² = 441 ==> r = 21
Radius of hemisphere = 21 cm
Question 9 :
Radii of two solid hemispheres are in the ratio 3:5. Find the ratio of their lateral surface areas.
Let r₁ and r₂ are the radii of two hemispheres
r₁ : r₂ = 3 : 5
r₁/ r₂ = 3/5
r₁= 3 r₂/5
Lateral surface area of hemisphere = 2 Π r²
Ratio of LSA of two hemisphere
2 Π r₁² : 2 Π r₂²
(3 r₂/5)² : r₂² ==> 3²/5² : 1 ==> 9 : 25
Ratio of LSA is 9 : 25
Question 10 :
Find the LSA of a hollow hemisphere whose outer and inner radii are 4.2 cm and 2.1 cm respectively.
Solution:
Inner radius (r) = 2.1 cm
Outer radius (R) = 4.2 cm
LSA of hollow hemisphere = 2Π (R² + r²)
= 2 x Π x [(4.2)² + (2.1)²] ==> 2 x Π x (17.64 + 4.41)
= 2 x Π x (22.05) ==> 44.1 Π cm²
LSA of hollow hemisphere = 44.1 Π cm²
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Questions and Answers
Mar 10, 26 05:53 PM
Digital SAT Math Questions and Answers -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 50)
Mar 06, 26 07:48 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 50) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 49)
Mar 06, 26 06:47 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 49)