INTERIOR ANGLES OF A QUADRILATERAL
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Like triangles, quadrilaterals have both interior and exterior angles. If we draw a diagonal in a quadrilateral, you divide it into two triangles as shown below.
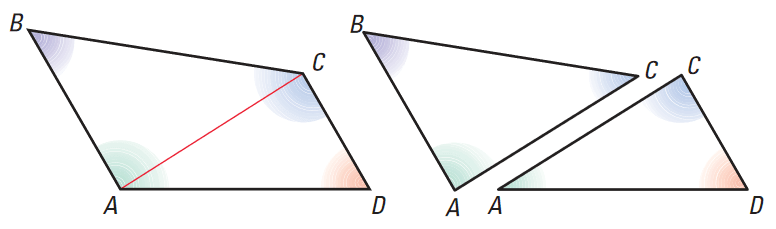
Each of the triangle above has interior angles with measures that add up to 180°.
So we can conclude that the sum of the measures of the interior angles of a quadrilateral is 2(180°), or 360°.
Theorem
The sum of the measures of the interior angles of a quadrilateral is 360°.
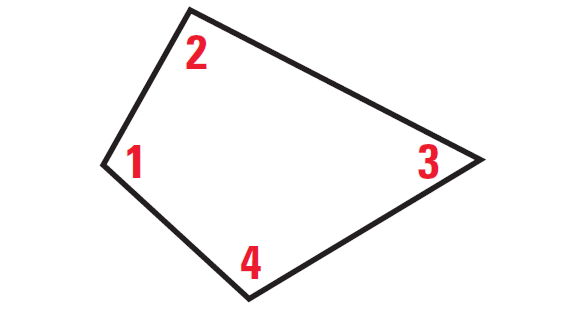
In the quadrilateral above, according to the theorem,
m∠1 + m∠2 + m∠3 + m∠4 = 360°
Solved Problems
Problem 1 :
In the diagram shown below, find m∠A.
Solution :
Because the figure ABCD is a closed figure and it is covered by four segments, it is quadrilateral.
By Internal Angles of a Quadrilateral Theorem, we have
m∠A + m∠B + m∠C + m∠D = 360°
Substitute m∠B = 105°, m∠C = 113°, m∠D = 75°.
m∠A + 105° + 113° + 75° = 360°
Simplify.
m∠A + 293° = 360°
Subtract 293° from both sides.
m∠A = 67°
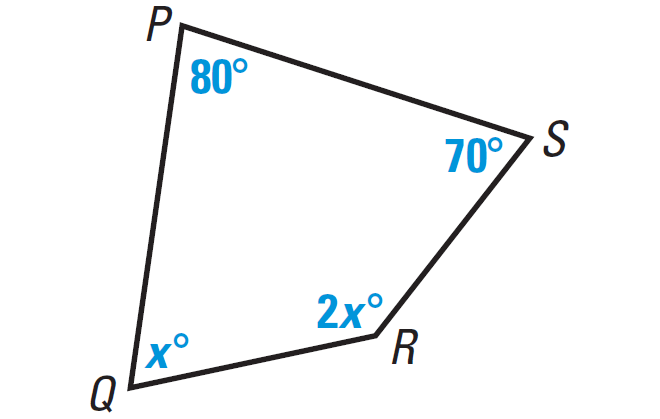
Problem 2 :
In the diagram shown below, find the value of x.

Solution :
Because the figure PQRS is a closed figure and it is covered by four segments, it is quadrilateral.
By Internal Angles of a Quadrilateral Theorem, we have
m∠P + m∠Q + m∠R + m∠S = 360°
Substitute m∠P = 80°, m∠Q = x°, m∠R = 2x°, m∠S = 70°.
80° + x° + 2x° + 70° = 360°
Simplify.
3x° + 150° = 360°
Subtract 150° from both sides.
3x° = 210°
3x = 210
Divide both sides by 3.
x = 70
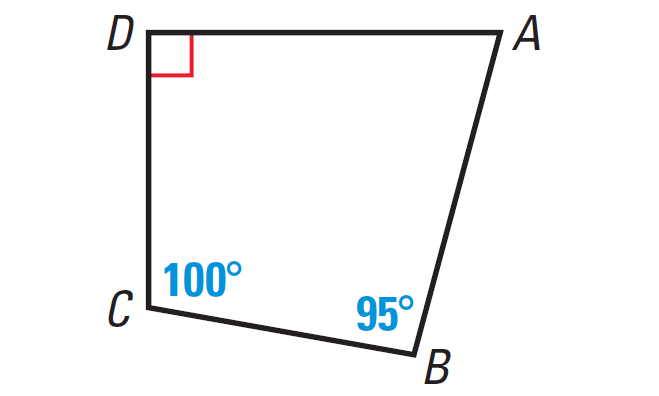
Problem 3 :
In the diagram shown below, find m∠A.
Solution :
Because the figure ABCD is a closed figure and it is covered by four segments, it is quadrilateral.
In quadrilateral ABCD above, angle A is a right angle.
So, we have
m∠D = 90°
By Internal Angles of a Quadrilateral Theorem, we have
m∠A + m∠B + m∠C + m∠D = 360°
Substitute m∠B = 95°, m∠C = 100°, m∠D = 90°.
m∠A + 95° + 100° + 90° = 360°
Simplify.
m∠A + 285° = 360°
Subtract 285° from both sides.
m∠A = 75°
Problem 4 :
In the diagram shown below, find the value of x.
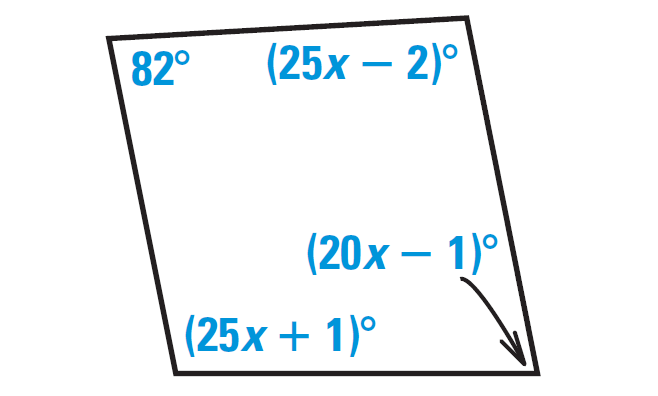
Solution :
Because the figure shown above is a closed figure and it is covered by four segments, it is quadrilateral.
By Internal Angles of a Quadrilateral Theorem,
"The sum of the measures of the interior angles of a quadrilateral is 360°"
So, we have
82° + (25x - 2)° + (20x - 1)° + (25x + 1)° = 360°
82 + 25x - 2 + 20x - 1 + 25x + 1 = 360
Simplify.
70x + 80 = 360
Subtract 80 from both sides.
70x = 280
Divide both sides by 70.
x = 4
Problem 5 :
In the diagram shown below, find the value of x.
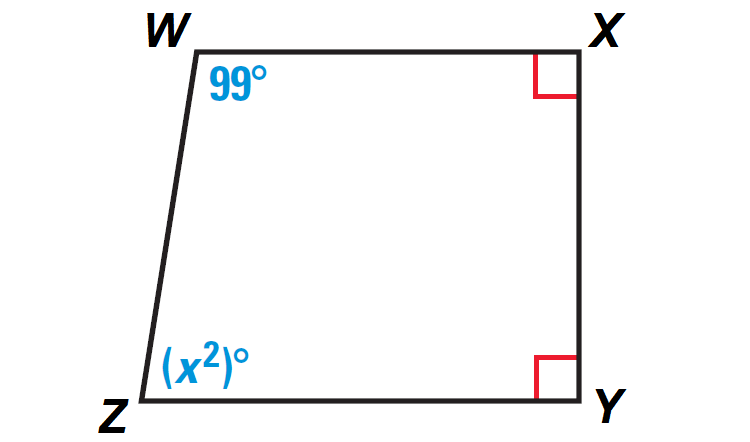
Solution :
Because the figure WXYZ is a closed figure and it is covered by four segments, it is quadrilateral.
In quadrilateral WXYZ above, angles X and Y are right angles.
So, we have
m∠X = 90°
m∠Y = 90°
By Internal Angles of a Quadrilateral Theorem,
m∠W + m∠X + m∠Y + m∠Z = 360°
Substitute m∠W = 99°, m∠X = 90°, m∠Y = 90°, m∠Z = (x2)°.
99° + 90° + 90° + (x2)° = 360°
99 + 90 + 90 + x2 = 360
Simplify.
279 + x2 = 360
Subtract 279 from both sides.
x2 = 81
x2 = 92
x = 9
Problem 6 :
In the diagram shown below, find the value of x.
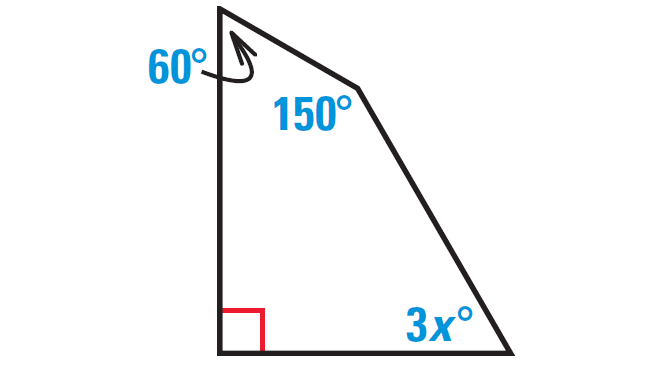
Solution :
Because the figure shown above is a closed figure and it is covered by four segments, it is quadrilateral.
In the quadrilateral above, one of the angles marked in red color is right angle.
By Internal Angles of a Quadrilateral Theorem,
"The sum of the measures of the interior angles of a quadrilateral is 360°"
So, we have
60° + 150° + 3x° + 90° = 360°
60 + 150 + 3x + 90 = 360
Simplify.
3x + 300 = 360
Subtract 300 from both sides.
3x = 60
Divide both sides by 3.
x = 20
Problem 7 :
In the diagram shown below, find the value of x.
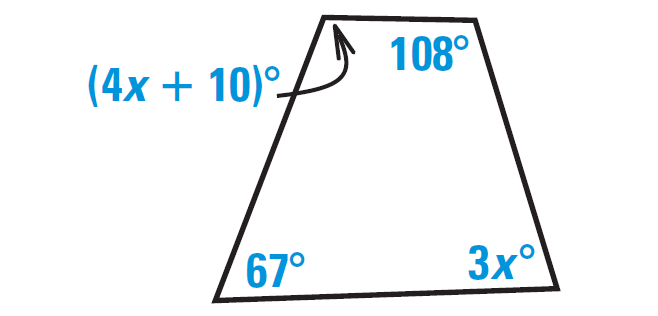
Solution :
Because the figure shown above is a closed figure and it is covered by four segments, it is quadrilateral.
By Internal Angles of a Quadrilateral Theorem,
"The sum of the measures of the interior angles of a quadrilateral is 360°"
So, we have
(4x + 10)° + 108° + 3x° + 67° = 360°
4x + 10 + 108 + 3x + 67 = 360
Simplify.
7x + 185 = 360
Subtract 185 from both sides.
7x = 175
Divide both sides by 7.
x = 25
Problem 8 :
In the diagram shown below, find the values of x and y.
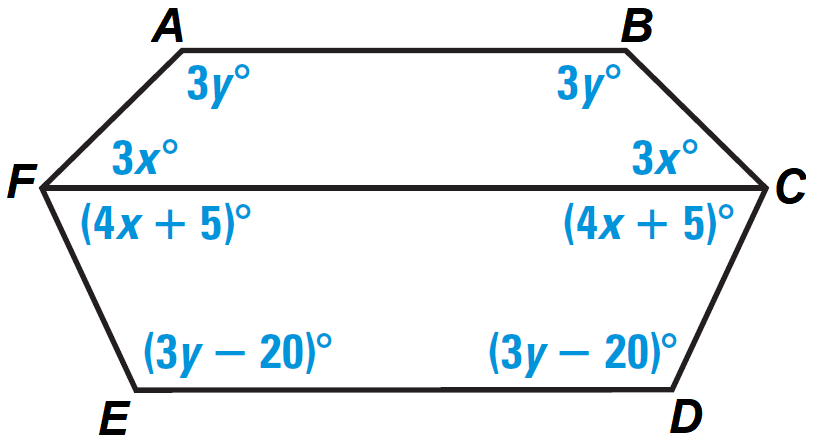
Solution :
In the diagram above, figure ABCF is a closed figure and it is covered by four segments, it is quadrilateral.
In quadrilateral ABCF, by Internal Angles of a Quadrilateral Theorem,
m∠A + m∠B + m∠C + m∠F = 360°
3y° + 3y° + 3x° + 3x° = 360°
Simplify.
6y° + 6x° = 360°
6x + 6y = 360
Divide both sides by 6.
x + y = 60 -------(1)
In the diagram above, figure FCDE is a closed figure and it is covered by four segments, it is quadrilateral.
In quadrilateral FCDE, by Internal Angles of a Quadrilateral Theorem,
m∠F + m∠C + m∠D + m∠E = 360°
(4x + 5)° + (4x + 5)° + (3y - 20)° + (3y - 20)° = 360°
4x + 5 + 4x + 5 + 3y - 20 + 3y - 20 = 360
Simplify.
8x + 6y - 30 = 360
8x + 6y = 390
Divide both sides by 2.
4x + 3y = 195 -------(2)
Solving (1) and (2), we get
x = 15
y = 45
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 50)
Mar 06, 26 07:48 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 50) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 49)
Mar 06, 26 06:47 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 49) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 48)
Mar 06, 26 05:24 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 48)


