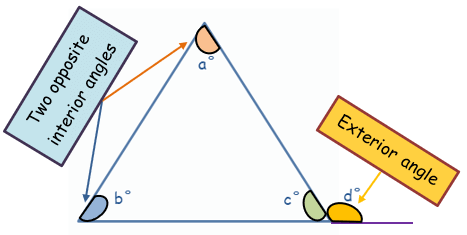
EXTERIOR ANGLE PROPERTY OF A TRIANGLE
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
The exterior angle is equal to the sum of the
two opposite interior angles.
Find a in the following, giving brief reasons :
Example 1 :
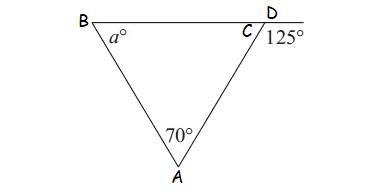
Solution :
The exterior angle is equal to the sum of the two opposite
interior angles.
m∠A = 70°, m∠B = a° (interior angles)
m∠D = 125° (exterior angle)
m∠A + m∠B = m∠D
70° + a° = 125°
Subtract 70° from both sides.
a° = 55°
Example 2 :
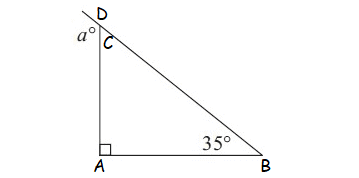
Solution
:
m ∠A = 90°, m∠B = 45° (interior angles)
m∠D = a° (exterior angle)
m∠D = m∠A + m∠B
a° = 90° + 45°
a° = 135°
Example 3 :
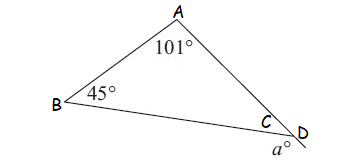
Solution
:
m ∠A = 101°, m∠B = 45° (interior angles)
m∠D = a° (exterior angle)
m∠D = m∠A + m∠B
a° = 101° + 45°
a = 146°
Example 4 :
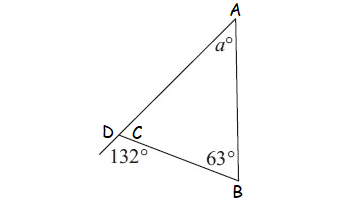
Solution :
m ∠A = a°, m∠B = 63° (interior angles)
m∠D = 132° (exterior angle)
m∠A + m∠B = m∠D
a° + 63° = 132°
Subtract 63° from both sides.
a° = 69°
Example 5 :
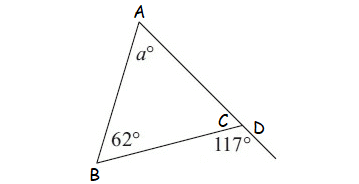
Solution :
m ∠A = a°, m∠B = 62° (interior angles)
m∠D = 117° (exterior angle)
m∠A + m∠B = m∠D
a° + 62° = 117°
Subtract 62° from both sides.
a° = 55°
Example 6 :
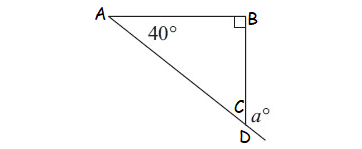
Solution :
m ∠A = 40°, m∠B = 90° (interior angles)
m∠D = a° (exterior angle)
m∠D = m∠A + m∠B
a° = 40° + 90°
a° = 130°
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 1)
Feb 05, 26 09:37 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 1) -
AP Precalculus Problems and Solutions
Feb 05, 26 06:41 AM
AP Precalculus Problems and Solutions -
SAT Math Preparation with Hard Questions
Feb 05, 26 05:30 AM
SAT Math Preparation with Hard Questions