EQUIVALENCE RELATION
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
As we have rules for reflexive, symmetric and transitive relations, we don't have any specific rule for equivalence relation.
Let R be a relation defined on a set A.
If the three relations reflexive, symmetric and transitive hold in R, then R is equivalence relation.
To verify equivalence, we have to check whether the three relations reflexive, symmetric and transitive hold.
To know the three relations reflexive, symmetric and transitive in detail, please click on the following links.
Example :
Let A = {1, 2, 3} and R be a relation defined on set A as
R = {(1, 1), (2, 2), (3, 3), (1, 2), (2, 1)}
Verify R is equivalence.
Solution :
We have to check whether the three relations reflexive, symmetric and transitive hold in R.
Reflexive :
In the set A, we find three elements. They are 1, 2 and 3.
When we look at the ordered pairs of R, we find the following associations.
(1, 1) -----> 1 is related to 1
(2, 2) -----> 2 is related to 2
(3, 3) -----> 3 is related to 3
In R, it is clear that every element of A is related to itself.
So, R is reflexive relation.
Symmetric :
To verify whether R is transitive, we have to check the condition given below for each ordered pair in R.
That is,
(a, b) -----> (b, a)
Let's check the above condition for each ordered pair in R.
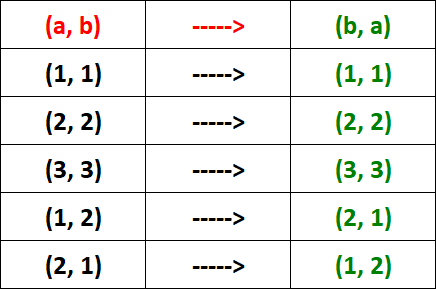
From the table above, it is clear that R is symmetric.
Transitive :
To verify whether R is transitive, we have to check the condition given below for each ordered pair in R.
That is,
(a, b), (b, c) -----> (a, c)
Let's check the above condition for each ordered pair in R.
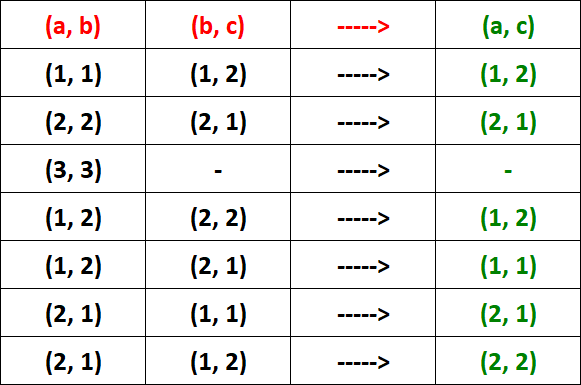
From the table above, it is clear that R is transitive.
Note :
For the ordered pair (3, 3), we don't find the ordered pair (b, c). So, we don't have to check the condition of transitive relation for that ordered pair.
Conclusion :
For the given relation R, all the three relations reflexive, symmetric and transitive hold.
Hence, R is equivalence.
Related Topics
Difference between reflexive and identity relation
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 47)
Mar 05, 26 09:19 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 47) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 46)
Mar 05, 26 08:37 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 46) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 45)
Mar 05, 26 08:02 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 45)