ANGLES FORMED BY PARALLEL LINES AND TRANSVERSAL
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
A transversal is a line that intersects two lines in the same plane at two different points.
In the diagram shown below, let the lines l1 and l2 be parallel. Because the line m cuts the lines l1 and l2, the line m is transversal.
So, the two parallel lines l1 and l2 cut by the transversal m.
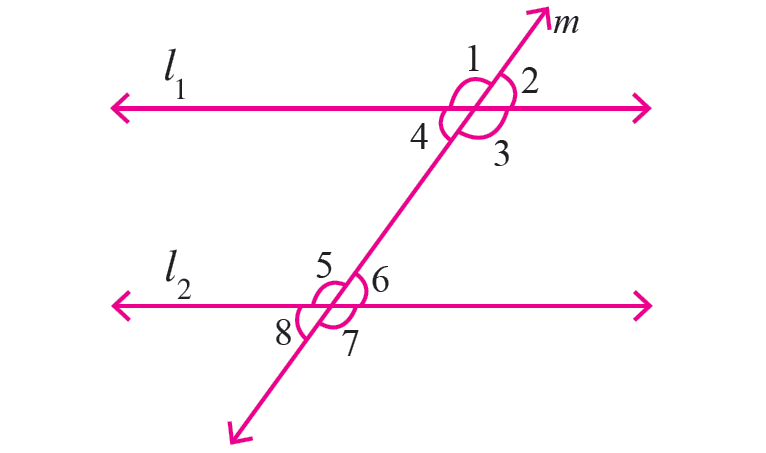
The angles formed by the two parallel lines l1 and l2 and the transversal min the above diagram will be as follows.
|
Vertically opposite angles are equal. |
m∠1 = m∠3 m∠2 = m∠4 m∠5 = m∠7 m∠6 = m∠8 |
|
Corresponding angles are equal. |
m∠1 = m∠5 m∠2 = m∠6 m∠3 = m∠7 m∠4 = m∠8 |
|
Alternate interior angles are equal. |
m∠3 = m∠5 m∠4 = m∠6 |
|
Alternate exterior angles are equal. |
m∠1 = m∠7 m∠2 = m∠8 |
|
Consecutive interior angles are supplementary. |
m∠3 + m∠6 = 180° m∠4 + m∠5 = 180° |
|
Same side exterior angles are supplementary. |
m∠1 + m∠8 = 180° m∠2 + m∠7 = 180° |
Example 1 :
In the figure given below, let the lines l1 and l2 be parallel and m is transversal. If m∠F = 65°, find the measure of each of the remaining angles.
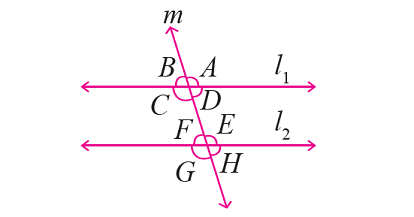
Solution :
In the figure above, ∠F and ∠H are vertically opposite angles and they are equal.
m∠H = m∠F
m∠H = 65°
∠H and ∠D are corresponding angles and they are equal.
m∠D = m∠H
m∠D = 65°
∠D and ∠B are vertically opposite angles and they are equal.
m∠B = m∠D
m∠B = 65°
∠F and ∠E form a linear pair and they are supplementary.
m∠F + m∠E = 180°
Substitute m∠F = 65°.
65° + m∠E = 180°
m∠E = 115°
∠E and ∠G are vertically opposite angles and they are equal.
m∠G = m∠E
m∠G = 115°
∠G and ∠C are corresponding angles and they are equal.
m∠C = m∠G
m∠C = 115°
∠C and ∠A are vertically opposite angles and they are equal.
m∠A = m∠C
m∠A = 115°
Therefore,
m∠A = m∠C = m∠E = m∠G = 115°
m∠B = m∠D = m∠F = m∠H = 65°
Example 2 :
In the figure given below, let the lines l1 and l2 be parallel and t is transversal. Find the value of x.
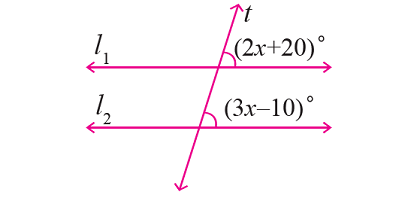
Solution :
In the figure above, (2x + 20)° and (3x - 10)° are corresponding angles and they are equal.
(2x + 20)° = (3x - 10)°
2x + 20 = 3x - 10
30 = x
Example 3 :
In the figure given below, let the lines l1 and l2 be parallel and t is transversal. Find the value of x.
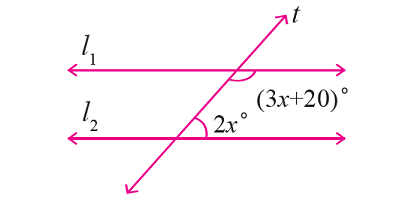
Solution :
In the figure above, (3x + 20)° and 2x° are consecutive interior angles and they are supplementary.
(3x + 20)° + 2x° = 180°
3x + 20 + 2x = 180
5x + 20 = 180
5x = 160
x = 32
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 50)
Mar 06, 26 07:48 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 50) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 49)
Mar 06, 26 06:47 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 49) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 48)
Mar 06, 26 05:24 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 48)


