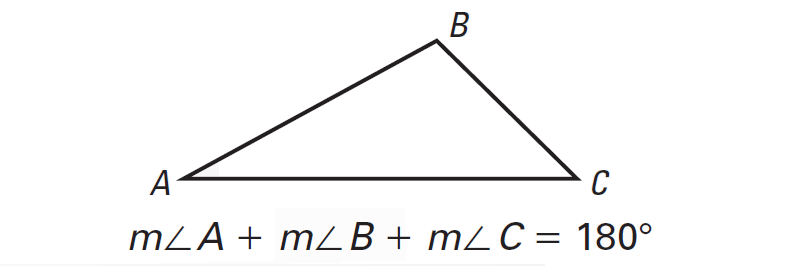WRITE DIRECT VARIATION EQUATIONS
Two quantities are said to be in direct variation if an increase (or decrease) in one quantity results in increase (or decrease) in the other quantity.
(i.e.) If two quantities vary always in the same ratio then they are in direct variation.
Direct variation can be represented by the equation
y = kx
Here the variable 'k' is known as the constant of variation, and it cannot be equal to zero.
Example 1 :
In a direct variation y = 12 when x = 2. Write the direct variation equation that shows the relationship between x and y.
Solution :
Equation of direct variation :
y = kx -----(1)
Substitute x = 2 and y = 12.
12 = k(2)
12 = 2k
Divide each side by 2.
6 = k
Substitute k = 1 in (1)
y = 6x
Example 2 :
In a direct variation y = 300 when x = 5. Write the direct variation equation that shows the relationship between x and y .
Solution :
Equation of direct variation :
y = kx -----(1)
Substitute x = 5 and y = 300.
300 = k(5)
300 = 5k
Divide each side by 5.
60 = k
Substitute k = 60 in (1).
y = 60x
Example 3 :
In a direct variation y = 12 when x = 40. Write the direct variation equation that shows the relationship between x and y .
Solution :
Equation of direct variation :
y = kx -----(1)
Substitute x = 40 and y = 12.
40 = k(12)
40 = 12k
Divide each side by 12.
10/3 = k
Substitute k = 10/3 in (1).
y = (10/3)x
Example 4 :
In a direct variation y = 4 when x = 15. Write the direct variation equation that shows the relationship between x and y .
Solution :
Equation of direct variation :
y = kx -----(1)
Substitute x = 15 and y = 4.
4 = k(15)
4 = 15k
Divide each side by 15.
4/15 = k
Substitute k = 4/15 in (1).
y = (4/15)x
Example 5 :
In a direct variation y = 48 when x = 16. Write the direct variation equation that shows the relationship between x and y .
Solution :
Equation of direct variation :
y = kx -----(1)
Substitute x = 16 and y = 48.
48 = k(16)
48 = 16k
Divide each side by 16.
3 = k
Substitute k = 3 in (1).
y = 3x
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com
Recent Articles
-
Sum of the Three Angles of a Triangle
Apr 26, 24 09:20 PM
Sum of the Three Angles of a Triangle - Concept - Solved Examples -
Writing Quadratic Functions in Standard Form
Apr 26, 24 12:39 PM
Writing Quadratic Functions in Standard Form or Vertex Form -
Factoring Quadratic Trinomials
Apr 26, 24 01:51 AM
Factoring Quadratic Trinomials - Key Concepts - Solved Problems