FIND GCD OF TWO POLYNOMIALS USING DIVISION METHOD
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Step 1 :
First, divide f(x) by g(x) to obtain.
f(x) = g(x)q(x)+ r(x)
where q(x) is the quotient and r(x) is remainder,
so, deg (g(x)) > deg (r(x))
If the remainder r(x) is 0, then g(x) is the GCD of f(x) and g(x).
Step 2 :
If the remainder r(x) is non-zero, divide g(x) by r(x) to obtain.
g(x) = r(x) q(x)+ r1(x)
where r1(x) is the remainder.
So, deg r(x) > deg r1(x)
If the remainder r1(x) is 0, then r(x) is the required GCD.
Step 3 :
If r1(x) is non-zero, then continue the process until we get zero as remainder.
The remainder in the last but one step is the GCD of f(x) and g(x).
We write GCD(f(x), g(x)) to denote the GCD of the polynomials f(x) and g(x).
Find the GCD of the following pairs of polynomials using division algorithm
Problem 1 :
x3 - 9x2 + 23x - 15 and 4x2 - 16x + 12
Solution :
x3 - 9x2 + 23x - 15 and 4x2 - 16x + 12
Let f(x) = x3 - 9x2 + 23x - 15 and
g(x) = 4x2 - 16x + 12
g(x) = 4(x2 - 4x + 3)
Here, degree of f(x) > degree of g(x)
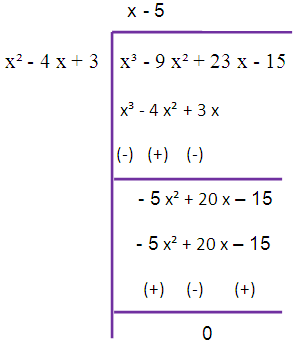
By dividing f(x) by g(x), we get 0 as remainder. So, the required GCD is x - 5.
Problem 2 :
3x3 + 18x2 + 33x + 18 and 3x2 + 13x + 10
Solution :
Let f(x) = 3x3 + 18x2 + 33x + 18 and g(x) = 3x2 + 13x + 10
Here, degree f(x) > degree g(x)
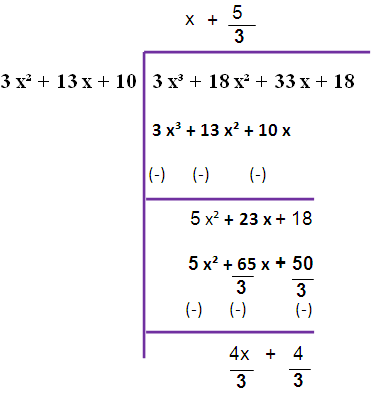
By dividing f(x) by g(x) we are not getting zero. So, we have to do this long division once again.
Now we are taking 4/3 as common from the remainder. So that we are getting (4/3)(x+1)
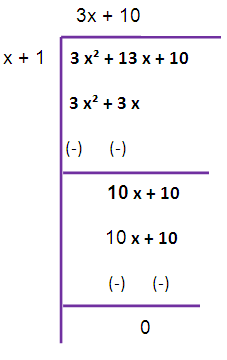
So, the greatest common divisor is x + 1.
Problem 3 :
2x3 + 2x2 + 2x + 2 and 6x3 + 12x2 + 6x + 12
Solution :
Let f(x) = 2x3 + 2x2 + 2x + 2 and g(x) = 6x3 + 12x2 + 6x + 12
f(x) = 2(x3 + x2 + x + 1)
g(x) = 6(x3 + 2x2 + x + 2)
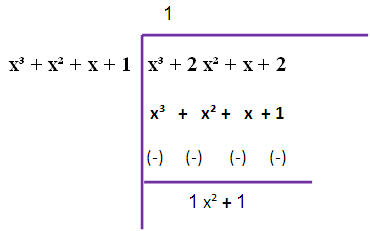
Since we are not getting zero, we have to do this long division once again
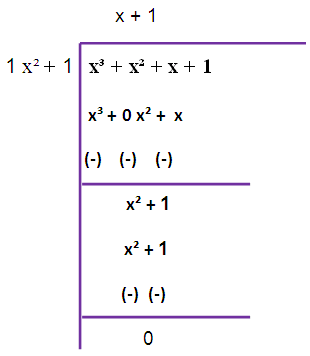
So, the required GCD is 2 (x2 + 1).
Problem 4 :
x3 - 3x2 + 4x - 12 and x4 + x3 + 4x2 + 4x
Solution :
Let f(x) = x3 - 3x2 + 4x - 12 and g(x) = x4 + x3 + 4x2 + 4x
f(x) = x3 - 3x2 + 4x - 12
g (x) = x(x3 + x2 + 4x + 4)
Here, degree f(x) = degree g(x)
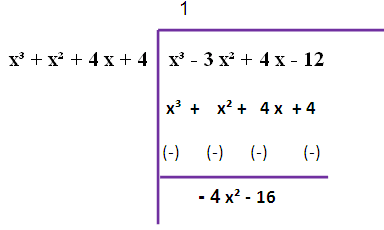
Since we are not getting zero, we have to do this long division once again
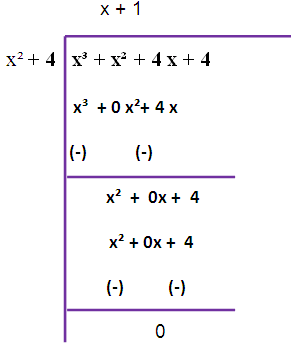
So, the required GCD is (x2 + 4).
Problem 5 :
x4 + 3x3 - x - 3 and x3 + x2 - 5x + 3
Solution :
Let f(x) = x4 + 3x3 - x - 3 and g(x) = x3 + x2 - 5x + 3
f(x) = x4 + 3x3 - x - 3
g (x) = x3 + x2 - 5x + 3
Here, degree f(x) > degree g(x)
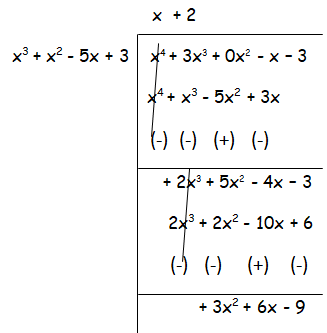
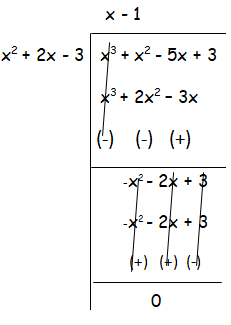
GCD of the polynomials is x2 + 2x - 3
Problem 6 :
Find the GCD of 4 + 9x - 9x2 and 9x2 - 24x + 16
Solution :
Writing each polynomial in standard form, we get
Let f(x) = - 9x2 + 9x + 4 and g(x) = 9x2 - 24x + 16
Degree of polynomial f(x) = degree of polynomial g(x)
Since both polynomials are quadratic, by finding factoring and listing the common factors we will get GCD.
Let f(x) = - 9x2 + 9x + 4
= -(9x2 - 9x - 4)
= -(9x2 - 12x + 3x - 4)
= -[3x(3x - 4) + 1(3x - 4)]
= -(3x + 1) (3x - 4) ------(1)
g(x) = 9x2 - 24x + 16
= 9x2 - 12x - 12x + 16
= 3x(3x - 4) - 4(3x - 4)
= (3x - 4)(3x - 4) ------(2)
From (1) and (2) common factors are
Greatest common factor = (3x - 4)
Problem 7 :
Find the GCD of 8(x4 + x3 + x2) and 20(x3 - 1)
Solution :
Writing each polynomial in standard form, we get
Let f(x) = 8(x4 + x3 + x2) and g(x) = 20(x3 - 1)
Since both polynomials are quadratic, by finding factoring and listing the common factors we will get GCD.
Let f(x) = 8(x4 + x3 + x2)
f(x) = 8x2(x2 + x + 1)
= 23x2(x2 + x + 1)-------(1)
g(x) = 20(x3 - 1)
g(x) = 22 ⋅ 5(x - 1)(x2 + x + 1) -------(2)
Common factors are 22 and (x2 + x + 1)
GCD = 4 (x2 + x + 1)
Problem 8 :
Find the GCD of (3 + 13x - 30x2) and (25x2 - 30x + 9)
a) 7x - 4 b) 5x - 3 c) 6x - 5 d) none
Solution :
Writing each polynomial in standard form, we get
Let f(x) = 3 + 13x - 30x2 and g(x) = 25x2 - 30x + 9
f(x) = -30 x2 + 13x + 3
= -30 x2 + 18x - 5x + 3
= -6x(5x - 3) - 1(5x - 3)
f(x) = (-6x - 1)(5x - 3) --------(1)
g(x) = 25x2 - 30x + 9
= 25x2 - 15x - 15x + 9
= 5x(5x - 3) - 3(5x - 3)
g(x) = (5x - 3)(5x - 3) --------(2)
The common factors are 5x - 3. So, the GCD is (5x - 3).
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 50)
Mar 06, 26 07:48 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 50) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 49)
Mar 06, 26 06:47 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 49) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 48)
Mar 06, 26 05:24 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 48)


