FIND THE MISSING SIDE OF A TRIANGLE USING THE PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
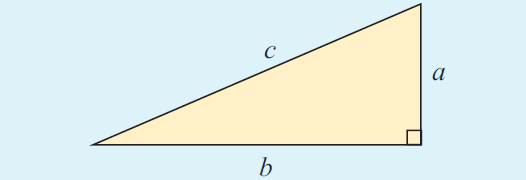
In any right angled triangle, the length of square of hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares on the other two sides
In a right angled triangle, with hypotenuse c and legs a and b,
c2 = a2 + b2
Find the value of unknowns.
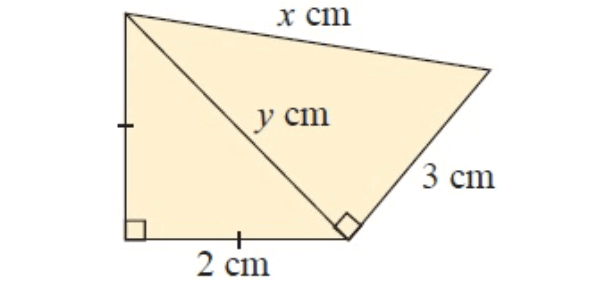
Example 1 :
Solution :
In figure ∆ABC
and ∆ACD
In ∆ABC,
AB = 2 cm, BC = 2 cm and AC = y cm
By using Pythagorean theorem,
AB2 + BC2 = AC2
22 + 22 = y2
4 + 4 = y2
y2 = 8
In ∆ACD,
AC = y cm, CD = 3 cm and AD = x cm
AC2 + CD2 = AD2
y2 + 32 = x2
8 + 9 = x2
x2 = 17
Now,
x = √17 and y = √8
x = 4.12 cm and y = 2.8 cm
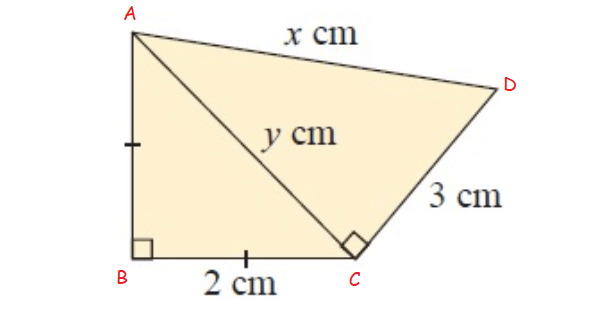
Example 2 :
Solution :
In figure ∆ABC and ∆DAC
In ∆ABC,
AB = 4 cm, BC = x cm and AC = y cm
By using Pythagorean theorem,
AB2 + BC2 = AC2
42 + x2 = y2
16 + x2 = y2
x2 = y2 – 16 -----(1)
In ∆DAC,
DA = 2 cm, AC = y cm and DC = 7 cm
DA2 + AC2 = DC2
22 + y2 = 72
4 + y2 = 49
y2 = 49 – 4
y2 = 45 -----(2)
By applying, y2 = 45 in (1)
We get,
x2 = y2 – 16
= 45 – 16
x2 = 29
x = √29 and y = √45
x = 5.38 and y = 6.70
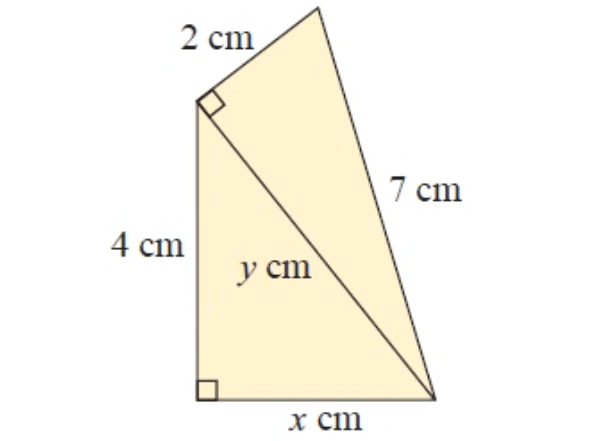
Example 3 :
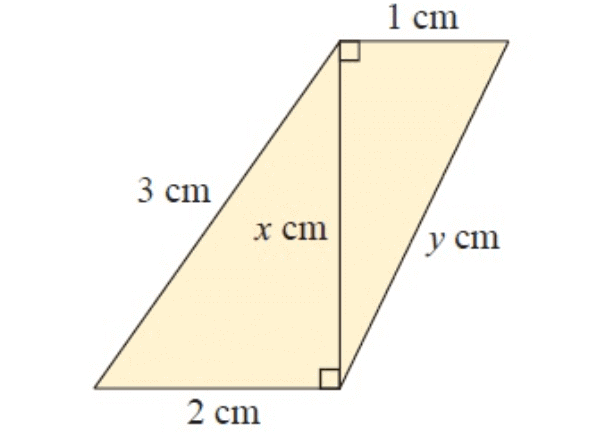
Solution :
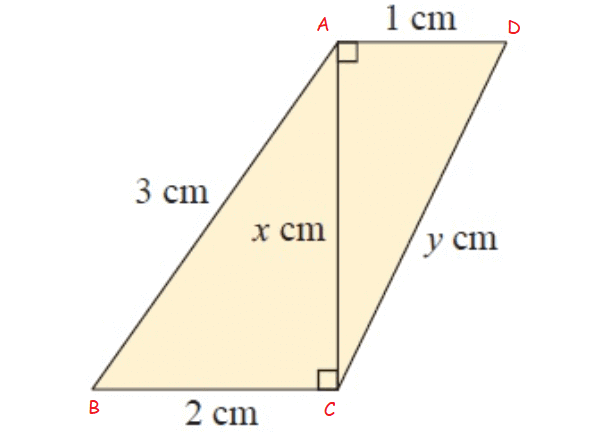
In figure ∆ACB and ∆DAC
In ∆ACB,
AC = x cm, BC = 2 cm and AB = 3 cm
By using Pythagorean theorem,
AC2 + BC2 = AB2
x2 + 22 = 32
x2 + 4 = 9
x2 = 5
In ∆DAC,
DA = 1 cm, AC = x cm and DC = y cm
DA2 + AC2 = DC2
12 + x2 = y2
1 + 5 = y2
y2 = 6
x = √5 and y = √6
x = 2.23 and y = 2.44
Example 4 :
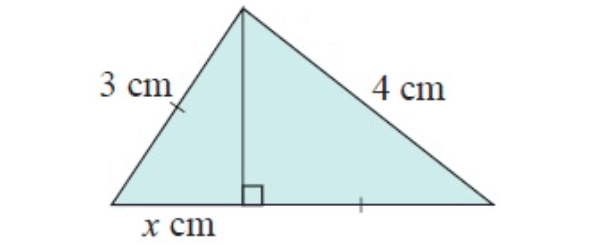
Solution :
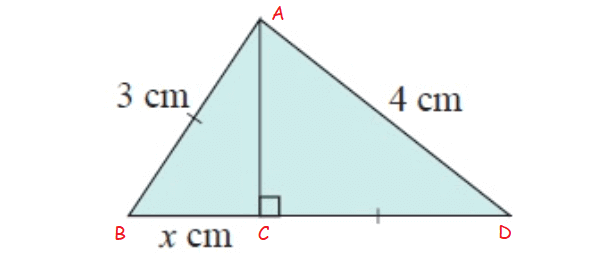
In figure ∆ACB
and ∆ACD
In ∆ACB,
AC = ?, BC = x cm and AB = 3 cm
By using Pythagorean theorem,
AC2+BC2 = AB2
AC2+x2 = 32
AC2 = 9–x2 -----(1)
In ∆ACD,
AC = ?, CD = 3 cm and AD = 4 cm
AC2+CD2 = AD2
AC2+32 = 42
AC2 = 7
-----(2)
By applying, AC2 = 7 in (1)
AC2 = 9–x2
7 = 9–x2
x2 = 9–7
x2 = 2
x = √2
x = 1.414
Example 5 :
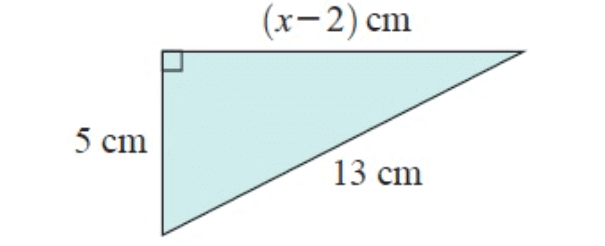
Solution :
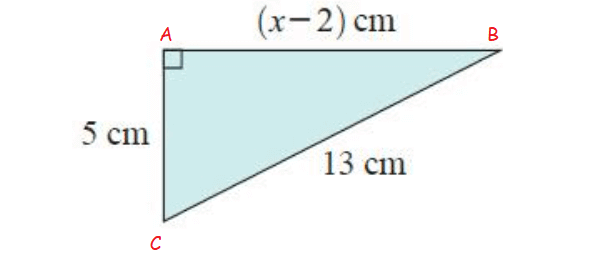
In figure ∆ABC
In ∆ABC,
AB = (x – 2) cm, BC = 5 cm and AC = 13 cm
By using Pythagorean theorem,
AB2 + BC2 = AC2
(x–2)2+52 = 132
x2–4x+4+25 = 169
x2–4x+29–169 = 0
x2–4x–140 = 0
By factorization, we get
(x + 10) (x – 14) = 0
x = - 10 and 14
Now, taking positive value 14.
So, the value of x is 14 cm.
Example 6 :
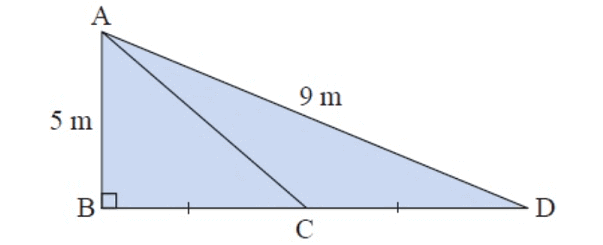
Solution :
In figure ∆ABC and ∆ABD
In ∆ABC,
AB = 5 m, let BC = x m and AC = ?
By using Pythagorean theorem,
AB2 + BC2 = AC2
52 + x2 = AC2
25 + x2 = AC2
AC2 = 25 + x2 -----(1)
In ∆ABD,
AB = 5 m, AD = 9 m
BD = BC + CD
= x + x
= (2x) m
AB2 + BD2 = AD2
52 + (2x)2 = 92
25 + 4x2 = 81
4x2 = 81 – 25
4x2 = 56
x2 = 56/4
x2 = 14 -----(2)
By applying, x2 = 14 in (1)
AC2 = 25 + x2
AC2 = 25 + 14
AC2 = 39
Now,
AC = √39
AC = 6.24
We taking this value Approximately,
So, the Length of AC is 6 m
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 50)
Mar 06, 26 07:48 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 50) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 49)
Mar 06, 26 06:47 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 49) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 48)
Mar 06, 26 05:24 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 48)


