CHECK IF THE LINEAR IS A FACTOR OF THE GIVEN POLYNOMIAL
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Factor theorem is commonly used for factoring a polynomial and finding the roots of the polynomial. It is a special case of a polynomial remainder theorem.
As discussed in the introduction, a polynomial f(x) has a factor (x-a), if and only if, f(a) = 0.
Problem 1 :
Determine whether (x+1) is a factor of the following polynomials.
(i) 6x4+7x3-5x-4
(ii) 2x4+9x3+2x2+10x+15
(iii) 3x3+8x2-6x-5
(iv) x3-14x2+3x+12
(i) Solution :
6x4+7x3-5x-4
By factor theorem, if p(-1) = 0, then (x+1) is a factor of
p(x) = 6x4+7x3-5x-4
p(-1) = 6(-1)4+7(-1)3-5(-1)-4
= 6-7+5-4
p(-1) = 0
(x+1) is a factor of the given polynomial.
(ii) Solution :
2x4+9x3+2x2+10x+15
By factor theorem, if p(-1) = 0, then (x+1) is a factor of
p(x) = 2x4+9x3+2x2+10x+15
p(-1) = 2(-1)4+9(-1)3+2(-1)2+10(-1)+15
= 2-9+2-10+15
= 0
So, (x+1) is a factor of the given polynomial.
(iii) Solution :
3x3+8x2-6x-5
By factor theorem, if p(-1) = 0, then (x+1) is a factor of
p(x) = 3x3+8x2-6x-5
p(-1) = 3(-1)3+8(-1)2-6(-1)-5
= -3+8+6-5
p(-1) ≠ 0
(x+1) ix not the factor of 3x3+8x2-6x-5.
(iv) Solution :
x3-14x2+3x+12
By factor theorem, if p(-1) = 0, then (x+1) is a factor of
p(x) = x3-14x2+3x+12
p(-1) = (-1)3-14(-1)2+3(-1)+12
p(-1) = -1-14-3+12
p(-1) ≠ 0
(x+1) is not the factor of x3-14x2+3x+12.
Problem 2 :
Determine whether (x+4) is a factor of
x3 + 3x2 - 5x + 36
Solution :
By factor theorem, if p(-4) = 0, then (x+4) is a factor of
p(x) = x3 + 3x2 - 5x + 36
p(-4) = (-4)3+3(-4)2-5(-4)+36
= -64+48+20+36
p(-4) ≠ 0
(x+4) is not the factor of x3+3x2-5x+36.
Problem 3 :
Using factor theorem show that (x-1) is a factor of
4x3-6x2+9x-7
Solution :
By factor theorem, if p(1) = 0, then (x-1) is a factor of
p(x) = 4x3-6x2+9x-7
p(1) = 4(1)3-6(1)2+9(1)-7
= 4-6+9-7
p(1) = 0
(x-1) is the factor of 4x3-6x2+9x-7.
Problem 4 :
Determine whether (2x+1) is a factor of
4x3+4x2-x-1
Solution :
By factor theorem, if p(-1/2) = 0, then (2x+1) is a
Factor of p(x) = 4x3+4x2-x-1
p(-1/2) = 4(-1/2)3+4(-1/2)2-(-1/2)-1
= -1/2+1+1/2-1
p(-1/2) = 0
(2x+1) is the factor of 4x3+4x2-x-1.
Problem 5 :
Determine the value of p if (x+3) is a factor of
x3-3x2-px+24
Solution :
By factor theorem, if p(-3) = 0, then (x+3) is a
factor of p(x) = x3-3x2-px+24
p(-3) = (-3)3-3(-3)2- p(-3)+24
This implies that -27-27+3p+24 = 0
-30 + 3p = 0
3p = 30
p = 10
So, the value of p is 10.
Problem 6 :
g(x) = ax2 + 24
For the function g defined above, a is constant and g(4) = 8. What is the value of g(-4) ?
a) 8 b) 0 c) -1 d) -8
Solution :
g(x) = ax2 + 24
g(4) = 8
When x = 4, we get
g(4) = a(4)2 + 24
8 = 16a + 24
8 - 24 = 16a
16a = -16
a = -16/16
a = -1
Applying the value of a, we get
g(x) = -1x2 + 24
To find the value of g(-4), we apply -4 in the place of x.
g(-4) = -1(-4)2 + 24
= -1(16) + 24
= -16 + 24
= 8
So, the answer is 8, option a is correct.
Problem 7 :
If x2 + x - 12 divides p(x) = x3 + ax2 + bx - 84 exactly find a and b.
Solution :
By solving the equation x2 + x - 12 = 0, we get
x2 + x - 12 = 0
(x + 4) (x - 3) = 0
x + 4 and x - 3 are factors. Equating each factor to 0, we get
x = -4 and x = 3
Here -4 and 3 are solutions.
Since -4 and 3 are solutions, p(-4) and p(3) the remainder will be 0.
p(x) = x3 + ax2 + bx - 84
p(-4) = (-4)3 + a(-4)2 + b(-4) - 84
0 = -64 + 16a - 4b - 84
0 = -148 + 16a - 4b
148 = 16a - 4b
Dividing by 4, we get
4a - b = 37 ------(1)
p(3) = (3)3 + a(3)2 + b(3) - 84
0 = 27 + 9a + 3b - 84
0 = -57 + 9a + 3b
57 = 9a + 3b
Dividing by 3, we get
19 = 3a + b
3a + b = 19 -------(2)
(1) + (2)
4a - b + 3a + b = 37 + 19
7a = 56
a = 8
Applying the value of a in (1), we get
4(8) - b = 37
32 - b = 37
b = 32 - 37
b = -5
Problem 8 :
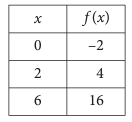
Some values of the linear function f are shown in the table above, what is the value of f(3) ?
a) 6 b) 7 c) 8 d) 9
Solution :
The table shows the linear function, every linear function will be in the form of
y = mx + b
(0, -2) and (2, 4)
Slope (m) = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1)
= (4 + 2) / (2 - 0)
= 6 / 2
m = 3
y = 3x + b
Applying one of the points from the table (0, -2), we get
-2 = 3(0) + b
b = -2
f(x) = y = 3x - 2
To find f(3), we get
f(3) = 3(3) - 2
= 9 - 2
= 7
So, option b is correct.
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 39)
Dec 28, 25 08:30 PM
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 39) -
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 41)
Dec 28, 25 06:05 PM
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 41) -
GMAT Quantitative Reasoning Questions and Answers
Dec 27, 25 09:33 PM
GMAT Quantitative Reasoning Questions and Answers