AREA OF DIFFERENT TYPES OF TRIANGLES
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Finding area of a triangle is depending on the type of it.
To know the different types of triangles,
General Formula for Area of Triangle :
= (1/2) ⋅ base ⋅ height
Formula for Area of Scalene Triangle :
= √[s(s - a)(s - b)(s - c)]
where
S = (a + b + c)/2
Here a, b and c are side lengths of the triangle.
Formula for Area of Equilateral Triangle :
= (√3/4)a2
Example 1 :
Find the area of the equilateral triangle having the side length 10 cm.
Solution :
Formula for area of equilateral triangle is
= (√3/4)a2
Substitute 10 for a.
= (√3/4)(10)2
= (√3/4) x (10) x (10)
= (√3) x (5) x (5)
= 25 √3 cm2
Example 2 :
The altitude drawn to the base of an isosceles triangles is 8 cm and the perimeter is 32 cm. Find the area of the triangle.
Solution :
Let ABC be the isosceles triangle and AD be the altitude as shown below.
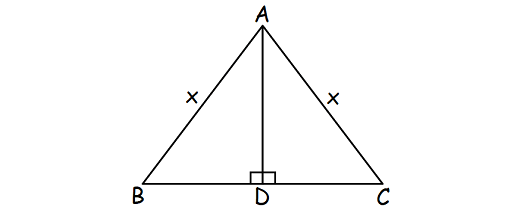
Because the triangle is isosceles, the length of two sides will be equal and the altitude bisects the base of the triangle.
Let AB = AC = x cm.
Perimeter of triangle ABC = 32 cm
AB + BC + CA = 32
x + BC + x = 32
BC = 32 - 2x -----(1)
DC = BC/2
DC = (32 - 2x)/2
DC = 16 - x
In right triangle ADC,
AC2 = AD2 + DC2
x2 = 82 + (16 - x)2
x2 = 64 + 162 + x2 - 32x
32x = 64 + 256
32x = 320
x = 10 cm
(1)-----> BC = 32 - 2(10)
BC = 32 - 20
BC = 12 cm
Area of triangle ABC = (1/2) x (bh)
= (1/2) x (12 x 8)
= 48 cm2
Example 3 :
Find the area of the scalene triangle whose side lengths are 12 cm, 18 cm and 20 cm.
Solution :
Because the lengths of the three sides are different, the triangle is scalene triangle.
S = (a + b + c)/2
Substitute a = 1, b = 18 and c = 20.
S = (12 + 18 + 20)/2
S = 50/2
S = 25
Formula for area of scalene triangle :
= √[s(s - a)(s - b)(s - c)]
Substitute.
= √[25 x (25 - 12) x (25 - 18) x (25 - 20)]
= √(25 x 13 x 7 x 5)
= 5√455 cm2
Example 4 :
The sides of a triangle are 12 cm, 16 cm and 20 cm. Find the altitude to the longest side.
Solution :
In order to find the altitude to the longest side of a triangle, first we have to find the area of the triangle.
S = (a + b + c)/2
Substitute a = 12, b = 16 and c = 20.
S = (12 + 16 + 20)/2
S = 48/2
S = 24
Formula for area of scalene triangle :
= √[s(s - a)(s - b)(s - c)]
Substitute.
= √[24 x (24 - 12) x (24 - 16) x (24 - 20)]
= √(24 x 12 x 8 x 4)
= 96 cm2
Because we want to find the altitude to the longest side, the longest side will be the base of the triangle as shown below.
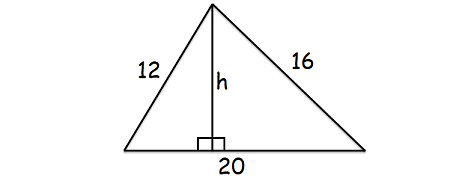
Here, the longest side is 20 cm.
Area of the above triangle = 96 cm2
(1/2) x 20 x h = 96
10h = 96
Divide each side by 10.
h = 9.6
So, the altitude to the longest side is 9.6 cm.
Example 5 :
Area of a triangle is 1176 cm2. If its base and corresponding altitude are in the ratio 3 : 4, then find the the altitude of the triangle.
Solution :
From the given information,
base of the triangle = 3x
altitude = 4x
area of the triangle = 1176
(1/2) x (3x) x (4x) = 1176
6x2 = 1176
Divide each side by 6.
x2 = 196
x = 14
Altitude of the triangle = 4x = 4(14) = 56 cm
Example 6 :
The sides of a triangle are in the ratio (1/2) : (1/3) : (1/4). If the perimeter is 52 cm, then find the length of the smallest side.
Solution :
From the given information, the sides the triangle are
x/2, x/3 and x/4
Perimeter of the triangle = 52 cm.
(x/2) + (x/3) + (x/4) = 52
(6x + 4x + 3x)/12 = 52
13x/12 = 52
13x = 624
x = 48
Then,
x/2 = 24
x/3 = 16
x/4 = 12
So, the length of smallest side is 12 cm.
Example 7 :
The area of the triangle is 216 cm2 and the sides are in the ratio 3 : 4 : 5. Find the perimeter of the triangle.
Solution :
From the given information, the sides the triangle are
3x, 4x and 5x
S = (3x + 4x + 5x)/2
S = 6x
Area of the triangle = 216 cm2.
√[s(s - a)(s - b)(s - c)] = 216
√[6x(6x - 3x)(6x - 4x)(6x - 5x)] = 216
√[6x(3x)(2x(x] = 216
√(36x4) = 216
6x2 = 216
x2 = 36
x = 6
Then,
3x = 18
4x = 24
5x = 30
Perimeter of the triangle is
= 18 + 24 + 30
= 72 cm
Example 8 :
One side of a right angle triangle is twice the other, and the hypotenuse is 10 cm. Find the area of the triangle.
Solution :
Let x be the length of one of the legs of the triangle.
Then, the length of the other leg is 2x.
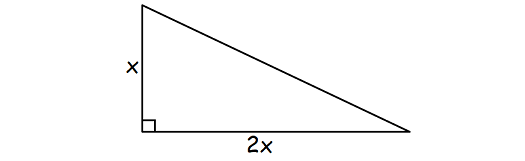
Using Pythagorean theorem,
x2 + (2x)2 = 102
x2 + 4x2 = 100
5x2 = 100
x2 = 20
√x2 = √20
x = √(4 x 5)
x = 2√5
Then,
2x = 2(2√5)
2x = 4√5
Area of triangle is
= (1/2)(x) (2x)
= (1/2)(2√5)(4√5)
= 20 cm2
Example 9 :
If the perimeter of the isosceles right triangle is (6 + 3√2) cm, then find the area of the triangle.
Solution :
Because the given triangle is isosceles right triangle, the length of two sides will be equal.
Let x be the length of one of the two equal sides and 'y' be the length of the hypotenuse.
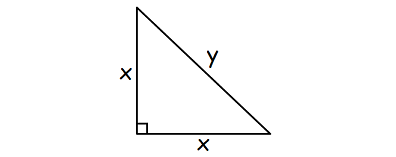
Using Pythagorean theorem,
y2 = x2 + x2
y2 = 2x2
√y2 = √(2x2)
y = √2x -----(1)
Perimeter of the triangle = 6 + 3√2.
x + x + y = 6 + 3√2
2x + y = 6 + 3√2
Substitute √2x for y.
2x + √2x = 6 + 3√2
x(2 + √2) = 3(2 + √2)
x = 3
Area of triangle is
= (1/2)(x) (x)
= (1/2)(3)(3)
= 4.5 cm2
Example 10 :
If the area of the equilateral triangle is 24√3 square cm, then find its perimeter.
Solution :
Area of equilateral triangle =24√3 cm2.
(√3/4) a2 = 24√3
a2/4 = 24
a2 = 96
√a2 = √96
a = √(16 x 6)
a = 4√6
Formula for perimeter of an equilateral triangle is
= 3a
Substitute a = 4√6.
= 3(4√6)
= 12√6 cm
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
SAT Math Practice Hard Questions
Feb 07, 26 08:28 AM
SAT Math Practice Hard Questions -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 1)
Feb 05, 26 09:37 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 1) -
AP Precalculus Problems and Solutions
Feb 05, 26 06:41 AM
AP Precalculus Problems and Solutions