VECTORS
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
A vector is a quantity that has both direction and magnitude, or size, and is represented by an arrow drawn between two points.
In this section, we will learn how to find the magnitude of a vector and the direction of a vector. We will also learn how to add vectors.
Finding the Magnitude of a Vector
The magnitude of a vector AB is the distance from the initial point A to the terminal point B, and is written |AB|.
If a vector is drawn in a coordinate plane, we can use the Distance Formula to find its magnitude.
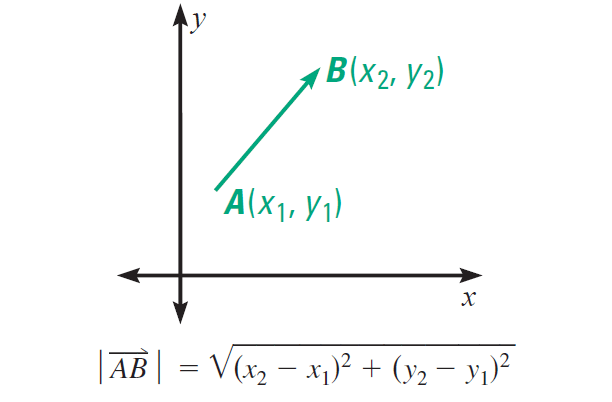
Finding the Magnitude of a Vector
Example 1 :
The initial and terminal points of the vector PQ are points P and Q. Draw PQ in a coordinate plane. Write the component form of the vector and find its magnitude.
(i) P(0, 0) and Q(-6, 3)
(ii) P(0, 2) and Q(5, 4)
(iii) P(3, 4) and Q(-2, -1)
Solution :
Part (i) :
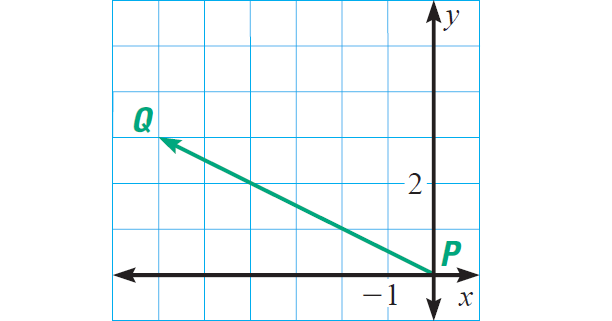
Component form = ⟨x2 - x1, y2 - y1⟩
Vector PQ = ⟨-6 - 0, 3 - 0⟩
Vector PQ = ⟨-6, 3⟩
We can use the distance formula to find the magnitude.
|PQ| = √[(-6 - 0)2 + (3 - 0)2]
|PQ| = √45
|PQ| ≈ 6.7
Part (ii) :
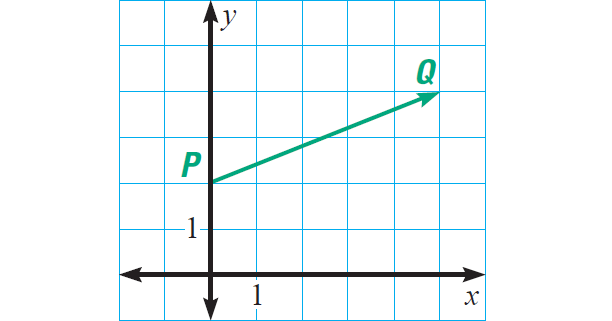
Component form = ⟨x2 - x1, y2 - y1⟩
Vector PQ = ⟨5 - 0, 4 - 2⟩
Vector PQ = ⟨5, 2⟩
We can use the distance formula to find the magnitude.
|PQ| = √[(5 - 0)2 + (4 - 2)2]
|PQ| = √29
|PQ| ≈ 5.4
Part (iii) :
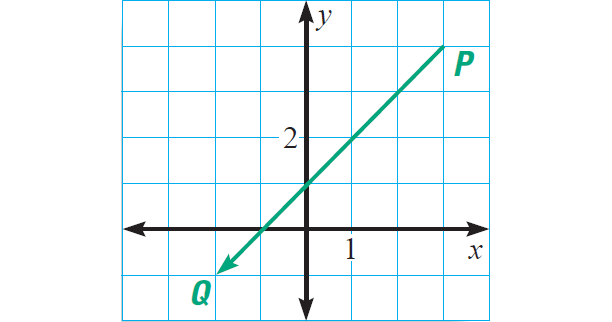
Component form = ⟨x2 - x1, y2 - y1⟩
Vector PQ = ⟨-2 - 3, -1 - 4⟩
Vector PQ = ⟨-5, -5⟩
We can use the distance formula to find the magnitude.
|PQ| = √[(-2 - 3)2 + (-1 - 4)2]
|PQ| = √50
|PQ| ≈ 7.1
Direction of a Vector
The direction of a vector is determined by the angle it makes with a horizontal line. In real-life applications, the direction angle is described relative to the directions north, east, south, and west.
In a coordinate plane, the x-axis represents an east-west line. The y-axis represents a north-south line.
Example 2 :
The vector AB describes the velocity of a moving ship. The scale on each axis is in miles per hour.
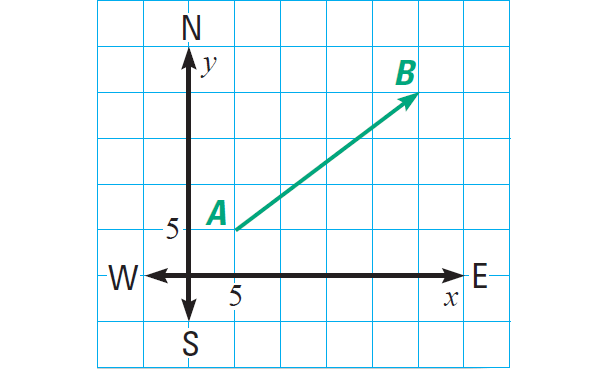
(i) Find the speed of the ship.
(ii) Find the direction it is travelling relative to east.
Solution :
Part (i) :
The magnitude of the vector AB represents the speed of the ship.
We can use the distance formula to find the magnitude of the vector AB.
|AB| = √[(25 - 5)2 + (20 - 5)2]
|AB| = √[202 + 152]
|AB| = √[400 + 225]
|AB| = √625
|AB| = 25
The speed of the ship is 25 miles per hour.
Part (ii) :
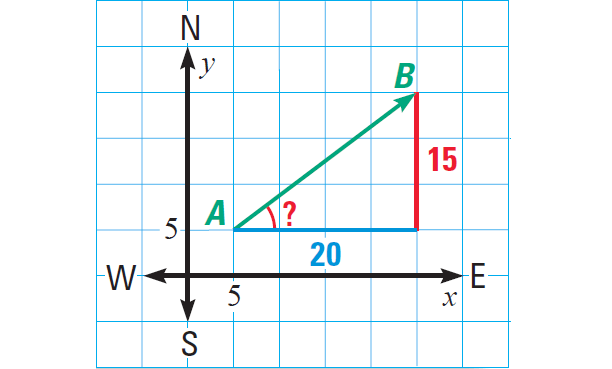
The tangent of the angle formed by the vector and a line drawn parallel to the x-axis is
15/20 or 0.75
We can use the calculator to find angle measure as shown below.

The ship is travelling in a direction about 37° north of east.
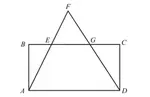
Equal and Parallel Vectors
Equal Vectors :
Two vectors are equal, if they have the same magnitude and direction. They do not have to have the same initial and terminal points.
Parallel Vectors :
Two vectors are parallel, if they have the same or opposite directions.
Equal and Parallel Vectors
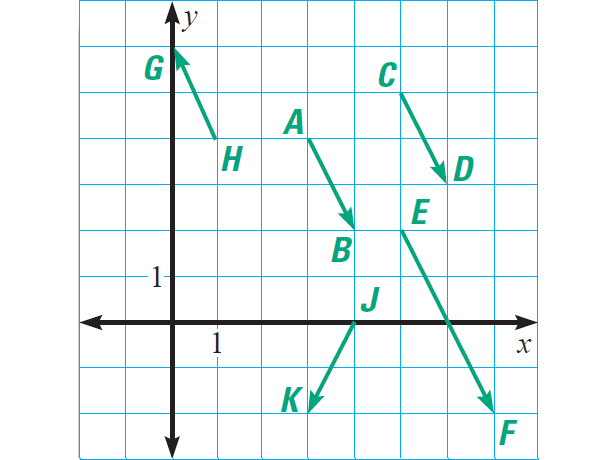
In the diagram shown above, the vectors AB, CD and EF have same direction.
But only the vectors AB and CD are equal in length.
So, the following vectors are equal vectors.
AB and CD
And the following vectors are parallel vectors.
AB, CD, EF and HG
Adding Vectors
Two vectors can be added to form a new vector. To add the vectors u and v geometrically, place the initial point of the vector v on the terminal point of the vector u, (or place the initial point of the vector u on the terminal point of the vector v).
The sum is the vector that joins the initial point of the first vector and the terminal point of the second vector .
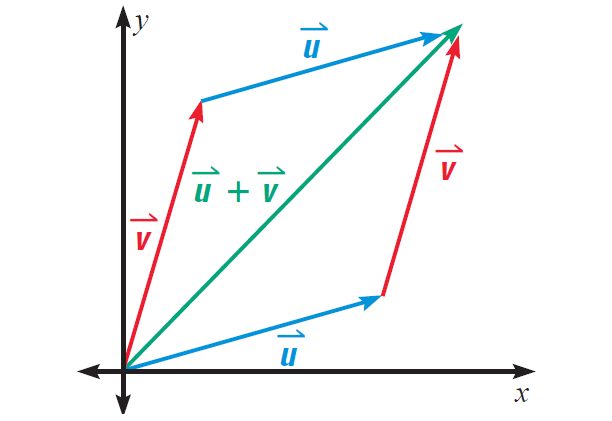
This method of adding vectors is often called the parallelogram rule because the sum vector is the diagonal of a parallelogram.
We can also add vectors algebraically.
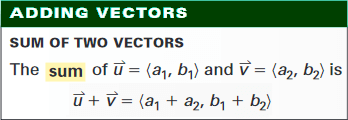
Finding the Sum of Two Vectors
Let the vector u = ⟨3, 5⟩ and the vector v = ⟨-6, -1⟩. To find the sum vector u + v, add the horizontal components and vertical components of the vectors u and v.
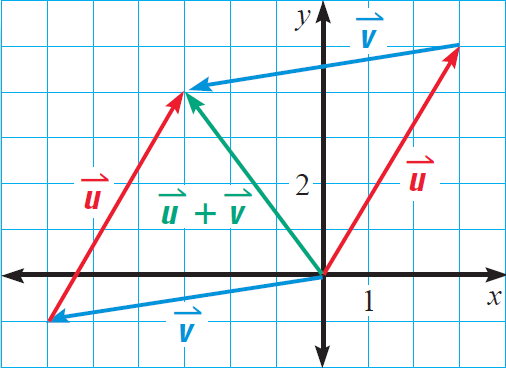
The sum vector is
u + v = ⟨3 + (-6), 5 + (-1)⟩
u + v = ⟨3 - 6, 5 - 1⟩
u + v = ⟨-3, 4⟩
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
SAT Math Problems on Exponents and Radicals
Feb 21, 26 08:28 PM
SAT Math Problems on Exponents and Radicals -
SAT Math Problems on Angles
Feb 21, 26 08:20 PM
SAT Math Problems on Angles -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 9)
Feb 21, 26 10:41 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 9)