USING PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM TO FIND DISTANCE BETWEEN TWO POINTS
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
The Pythagorean Theorem
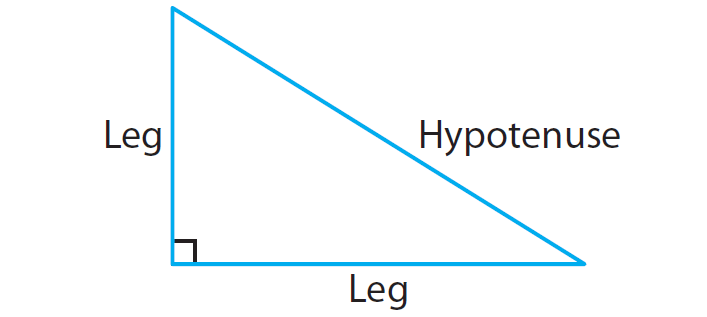
In a right triangle, the sum of the squares of the lengths of the legs is equal to the square of the length of the hypotenuse.
If a and b are legs and c is the hypotenuse, then
a2 + b2 = c2
Using Pythagorean Theorem to Find Distance Between Two Points
Example 1 :
Find the distance between the points (1, 3) and (-1, -1) using Pythagorean theorem. Check your answer for reasonableness.
Solution :
Step 1 :
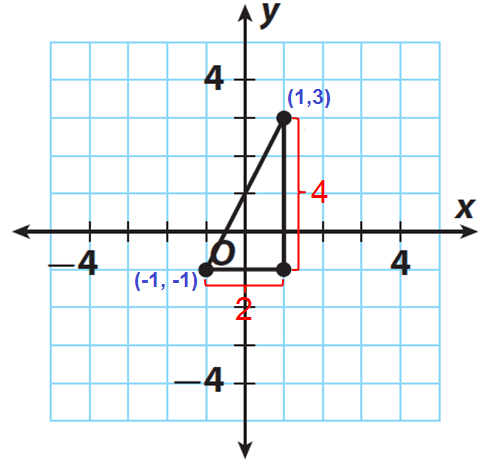
Locate the points (1, 3) and (-1, -1) on a coordinate plane.
Step 2 :
Draw horizontal segment of length 2 units from (-1, -1) and vertical segment of length of 4 units from (1, 3) as shown in the figure.
Step 3 :
Find the length of each leg.
The length of the vertical leg is 4 units.
The length of the horizontal leg is 2 units.
Step 4 :
Let a = 4 and b = 2 and c represent the length of the hypotenuse.
Because a and b are legs and c is hypotenuse, by Pythagorean Theorem, we have
a2 + b2 = c2
Step 5 :
Plug a = 4 and b = 2 in (a2 + b2 = c2) to solve for c.
42 + 22 = c2
Simplify.
16 + 4 = c2
20 = c2
Take the square root of both sides.
√20 = √c2
√20 = c
Step 6 :
Find the value of √20 using calculator and round to the nearest tenth
4.5 ≈ c
Step 7 :
Check for reasonableness by finding perfect squares close to 20.
√20 is between √16 and √25, so 4 < √20 < 5.
Since 4.5 is between 4 and 5, the answer is reasonable.
Hence, the distance between the points (1, 3) and (-1, -1) is about 4.5 units.
Example 2 :
Find the distance between the points (-3, 2) and (2, -2) using Pythagorean theorem. Check your answer for reasonableness.
Solution :
Step 1 :
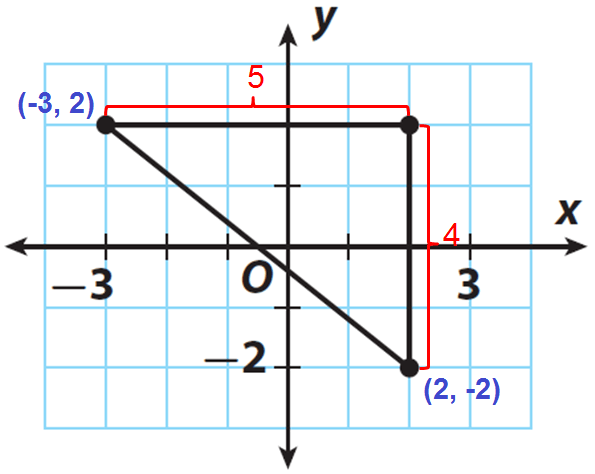
Locate the points (-3, 2) and (2, -2) on a coordinate plane.
Step 2 :
Draw horizontal segment of length 5 units from (-3, -2) and vertical segment of length of 4 units from (2, -2) as shown in the figure.
Step 3 :
Find the length of each leg.
The length of the vertical leg is 4 units.
The length of the horizontal leg is 5 units.
Step 4 :
Let a = 4 and b = 5 and c represent the length of the hypotenuse.
Because a and b are legs and c is hypotenuse, by Pythagorean Theorem, we have
a2 + b2 = c2
Step 5 :
Substitute a = 4 and b = 5 in (a2 + b2 = c2) to solve for c.
42 + 52 = c2
Simplify.
16 + 25 = c2
41 = c2
Take the square root of both sides.
√41 = √c2
√41 = c
Step 6 :
Find the value of √41 using calculator and round to the nearest tenth
6.4 ≈ c
Step 7 :
Check for reasonableness by finding perfect squares close to 41.
√41 is between √36 and √49, so 6 < √41 < 7.
Since 6.4 is between 6 and 7, the answer is reasonable.
Hence, the distance between the points (-3, 2) and (2, -2) is about 4.5 units.
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 50)
Mar 06, 26 07:48 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 50) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 49)
Mar 06, 26 06:47 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 49) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 48)
Mar 06, 26 05:24 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 48)


