USING DISTRIBUTIVE PROPERTY WITH RADICALS
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
When we use distributive property, the following operations may be useful.
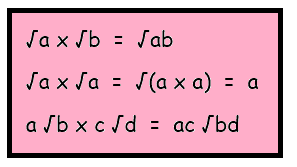
Expand and simplify
Example 1 :
√2 (√5+√2)
Solution :
Given, √2 (√5+√2)
By distribution, we get
√2 (√5+√2) = √2×√5 + √2×√2
= √10+2
So, the answer is √10+2.
Example 2 :
√3 (1-√3)
Solution :
Given, √3 (1-√3)
By distribution, we get
√3 (1-√3) = √3×1 - √3×√3
= √3-3
Example 3 :
√11 (2√11-1)
Solution :
Given, √11 (2√11-1)
By distribution, we get
√11 (2√11-1) = √11×2√11 - √11×1
= 2×11 - √11
= 22-√11
Example 4 :
2√3 (√3-√5)
Solution :
Given, 2√3 (√3-√5)
By distribution, we get
2√3 (√3-√5) = (2√3×√3)-(2√3×√5)
= (2x3) - 2√15
= 6-2√15
Example 5 :
(1+√2) (2+√2)
Solution :
Given, (1+√2) (2+√2)
By distribution, we get
(1+√2) (2+√2) = 2+√2+2√2+2
= 4+3√2
Example 6 :
(√3+2) (√3-1)
Solution :
Given, (√3+2) (√3-1)
By distribution, we get
(√3+2) (√3-1) = (√3×√3)-(√3×1)+(2×√3)-(2×1)
= 3-√3+2√3-2
= 1+√3
Example 7 :
(√5+2) (√5-3)
Solution :
Given, (√5+2) (√5-3)
By distribution, we get
(√5+2) (√5-3) = (√5×√5)-(√5×3)+(2×√5)-(2×3)
= 5-3√5+2√5-6
= -1-√5
Example 8 :
(2√2+√3) (2√2-√3)
Solution :
Given, (2√2+√3) (2√2-√3)
By algebraic identity, we get
(2√2+√3) (2√2-√3) = (2√2)2-(√3)2
= 4×2 - 3
= 5
Example 9 :
(2+√3) (2+√3)
Solution :
Given, (2+√3) (2+√3)
By distribution, we get
(2+√3) (2+√3) = 2×2+(2×√3)+(√3×2)+(√3×√3)
= 4+2√3+2√3+3
= 7+4√3
Example 10 :
(4-√2) (3+√2)
Solution :
Given, (4-√2) (3+√2)
By distribution, we get
(4-√2) (3+√2) = (4×3)+(4×√2)-(√2×3)-(√2×√2)
= 12+4√2-3√2-2
= 10+√2
Example 11 :
(√7-√3) (√7+√3)
Solution :
Given, (√7-√3) (√7+√3)
By using algebraic identity
(a+b)(a-b) = a2-b2
(√7-√3) (√7+√3) = (√7)2-( √3 )2
= 7-3
= 4
Example 12 :
(4-√2) (3-√2)
Solution :
Given, (4-√2) (3-√2)
By distribution, we get
(4-√2) (3-√2) = 4×3 - (4×√2) - (√2×3) + (√2×√2)
= 12-4√2-3√2+2
= 14-7√2
Example 13 :
The distance d (in miles) that you can see to the horizon with your eye level h feet above the water is given by
d = √3h/2
How far can you see when your eye level is 5 feet above the water?
Solution :
d = √(3h/2)
height = 5 feet
d = √(3(5)/2)
= √15/√2
To rationalize the denominator, we multiply both numerator and denominator by √2.
= (√15/√2) ⋅ (√2/√2)
= √15√2/√2√2
= √30/2
= 5.47/2
= 2.73 feet
So, we can see about 2.73 feet.
Example 14 :
The ratio of the length to the width of a golden rectangle is ( 1 + √5 ) : 2. The dimensions of the face of the Parthenon in Greece form a golden rectangle. What is the height h of the Parthenon?

Solution :
By comparing the given ratio width with length and width from the picture, we get
(1 + √5) : 2 = 31 : h
(1 + √5) / 2 = 31 / h
h(1 + √5) = 31(2)
h(1 + √5) = 62
h = 62/(1 + √5)
Rationalizing the denominator, we get
h = [62/(1 + √5)] [(1 - √5)/(1 - √5)]
= 62(1 - √5) / (1 + √5)(1 - √5)
= 62 (1 - √5)/(1-5)
= -62 (1 - √5)/4
= -15.5(1 - 2.23)
= -15.5(-1.23)
= 19.065 m
Example 15 :
The electric current I (in amperes) an appliance uses is given by the formula
I = √(P/R)
where P is the power (in watts and R is the resistance (in ohms). Find the current and appliance uses when the power is 147 watts and the resistance is 5 ohms.
Solution :
I = √(P/R)
When P = 147 and R = 5, then I = ?
I = √(147/5)
To rationalize the denominator, we have to multiply both numerator and denominator by √5
I = [√147/√5] [√5/√5]
= √(147x5) / 5
= √735 / 5
= 27.11/5
= 5.42 amperes
Example 16 :
Find the area of the rectangle given below.
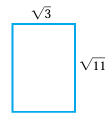
Solution :
Length of the rectangle = √11
Width = √3
Area of rectangle = length x width
= √11 x √3
= √(11 x 3)
= √33
Example 16 :
Find the area of the rectangle given below.
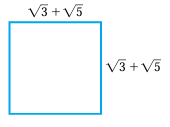
Solution :
Length of the rectangle = √3 + √5
Width = √3 + √5
Area of rectangle = length x width
= (√3 + √5) x (√3 + √5)
= √3√3 + √3(√5) + √5(√3) + √5 √5
= 3 + √(3 x 5) + √(3 x 5) + 5
= 8 + √15 + √15
= 8 + 2√15
Example 17 :
The period of the pendulum is the time required for it to make one complete swing back and forth. The formula of the period P of the pendulum is
P = 2π √(l/32)
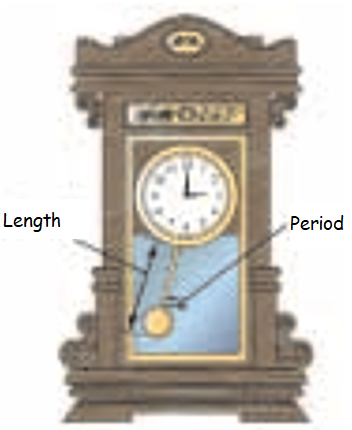
where l is the length of pendulum in feet. If a pendulum in a clock tower is 8 feet long find the period. Use 3.14 for π.
Solution :
P = 2π √(l/32)
l = 8 feet
P = 2π √(8/32)
P = 2π √(1/4)
P = 2x 3.14 x (1/2)
= 3.14 feet
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 50)
Mar 06, 26 07:48 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 50) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 49)
Mar 06, 26 06:47 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 49) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 48)
Mar 06, 26 05:24 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 48)


