USING ANGLE MEASURES IN TRIANGLES
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
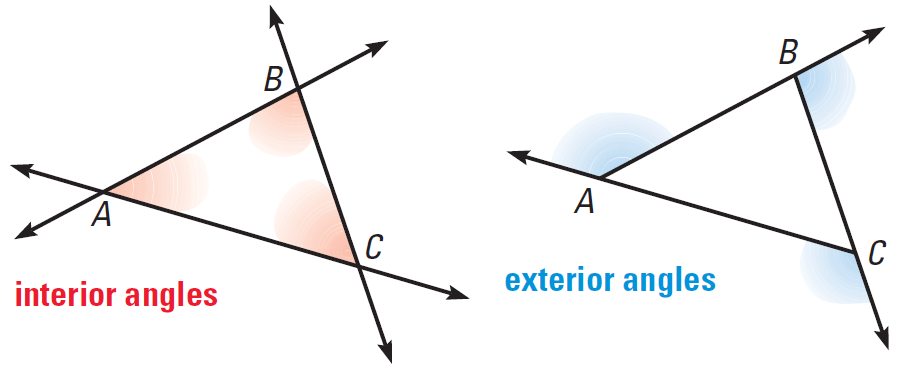
When the sides of a triangle are extended, other angles are formed. The three original angles are the interior angles. The angles that are adjacent to the interior angles are the exterior angles. Each vertex has a pair of congruent exterior angles. It is common to show only one exterior angle at each vertex.
Triangle Sum Theorem
The sum of the measures of the interior angles of a triangle is 180°.
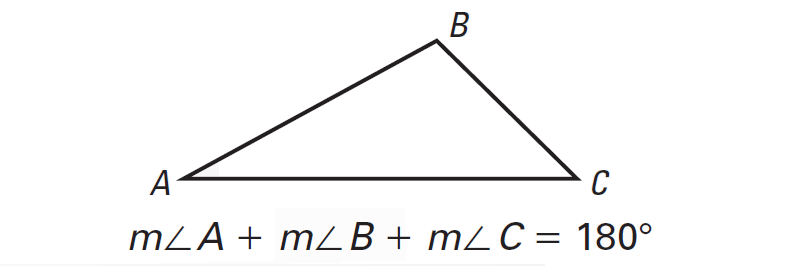
Exterior Angle Theorem
The measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the measures of the two nonadjacent interior angles.
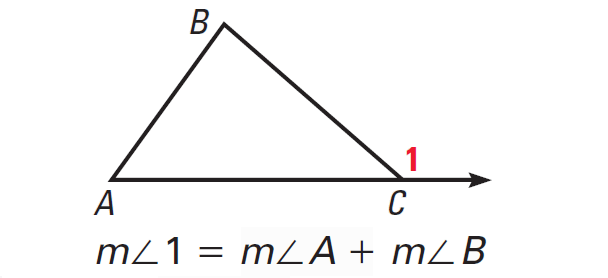
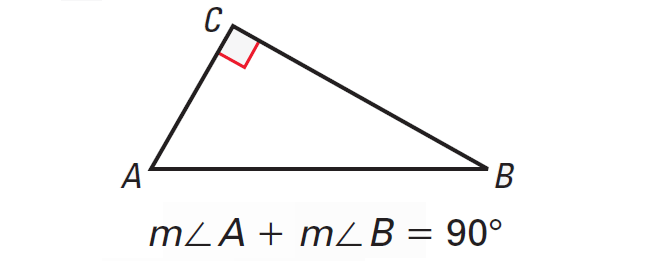
Corollary to the Triangle Sum Theorem
The acute angles of a right triangle are complementary.
Example 1 :
The measure of one acute angle of a right triangle is two times the measure of the other acute angle. Find the measure of each acute angle.
Solution :
Let A, B and C be the vertices of the triangle and right angle is at C.
Let ∠A = x°, then ∠B = 2x°. The diagram shown below illustrates this.
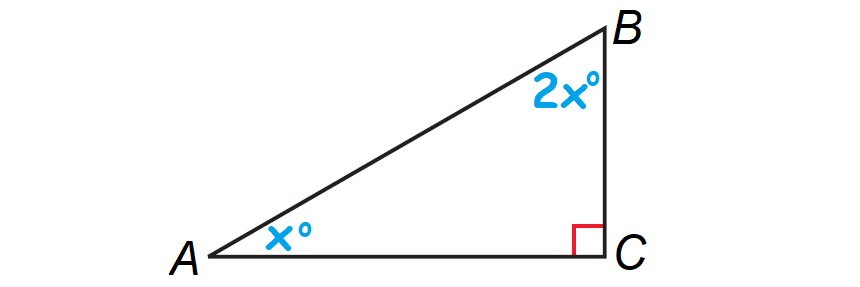
By Corollary to the Triangle Sum Theorem, the acute angles of a right triangle are complementary.
So, we have
x° + 2x° = 90°
Simplify.
3x° = 90°
Divide both sides by 3.
x = 30
m∠A = 30°
m∠B = 2(30°) = 60°
The measures of two acute angles are 30° and 60°.
Example 2 :
Find the missing angles in the triangle shown below.
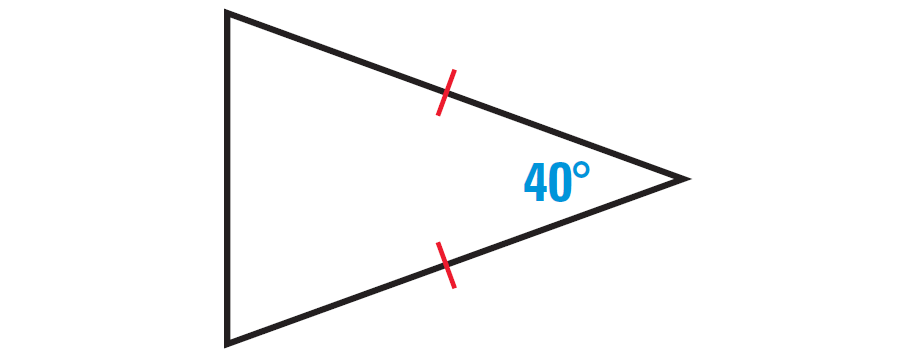
Solution :
In the triangle shown above, two sides are congruent. Angles opposite to congruent sides are always congruent.
So, if one missing angle is assumed to be x°, then the other missing angle also must be x°. Because the two angles are congruent.
The diagram shown below illustrates this.
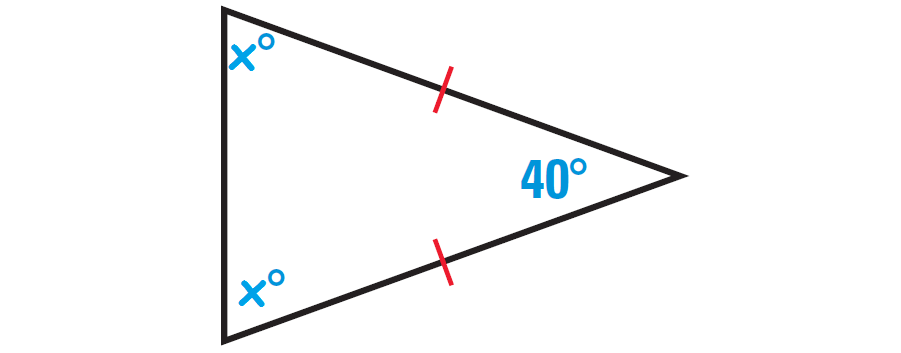
By Triangle Sum Theorem, the sum of the measures of the interior angles of a triangle is 180°.
So, we have
x° + x° + 40° = 180°
Simplify.
2x + 40 = 180
Subtract 40 from both sides.
2x = 140
Divide both sides by 2.
x = 70
The measure of each missing angle is 70°.
Example 3 :
Find the value of x in the diagram shown below.
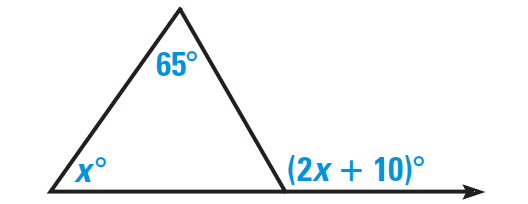
Solution :
By Exterior Angle Theorem, the measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the measures of the two nonadjacent interior angles.
So, we have
x° + 65° = (2x + 10)°
or
x + 65 = 2x + 10
Subtract x from both sides.
65 = x + 10
Subtract 10 from both sides.
55 = x
Example 4 :
Find the missing angles in the triangle shown below.
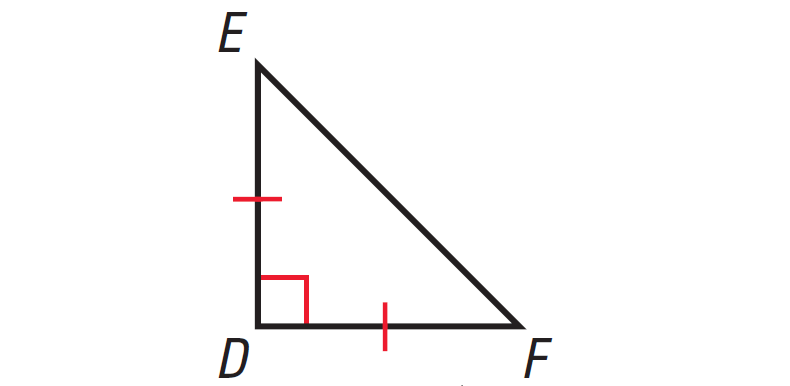
Solution :
In the triangle shown above, two sides are congruent. Angles opposite to congruent sides are always congruent.
So, if one missing angle is assumed to be x°, then the other missing angle also must be x°. Because the two angles are congruent.
The diagram shown below illustrates this.
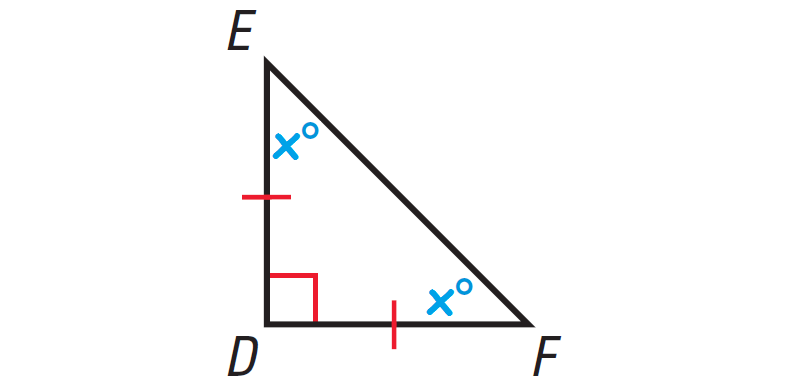
In the triangle shown above, one of the angles is right angle. So, it is right triangle.
By Corollary to the Triangle Sum Theorem, the acute angles of a right triangle are complementary.
So, we have
x° + x° = 90°
Simplify.
2x = 90
Divide both sides by 2.
x = 45
The measure of each missing angle is 45°.
Example 4 :
Find the value of x.
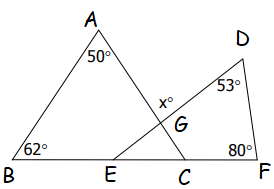
Solution :
In triangle ABC,
<ACB = 180 - (<A + <B)
= 180 - (50 + 62)
= 180 - 112
<ACB = 68
In triangle DEF,
<DEF = 180 - (<D + <F)
= 180 - (53 + 80)
= 180 - 133
<DEF = 47
In triangle EGC, the sum of interior angles of triangle is 180 degree.
<EGC = 180 - (<ACB + <DEF)
= 180 - (68 + 47)
= 180 - 115
<EGC = 65
x = 65(vertically opposite angle)
Example 5 :
Find the value of x.
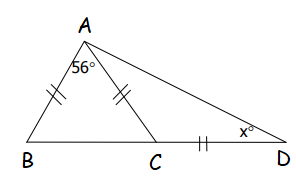
Solution :
<ABC = <ACB (because equal sides will make equal angle measures)
In triangle ABC,
<A + <B + <C = 180
56 + <B + <C = 180
2<B = 180 - 56
2<B = 124
<B = 124/2
<B = 62
In triangle ABD,
<ABD + <BDA + <DAB = 180
62 + x + 56 + x = 180
118 + 2x = 180
2x = 180 - 118
2x = 62
x = 62/2
x = 31
Example 6 :
Find the missing angle measures.
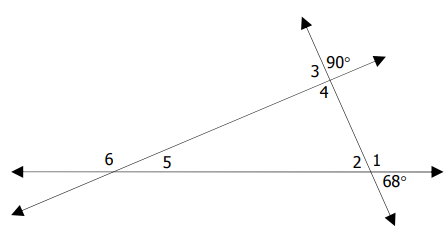
Solution :
<1 = 180 - 68
= 112
<2 = 68(vertically opposite angles)
<3 = 90
<4 = 90
<5 = 180 - (<4 + <2)
= 180 - (90 + 68)
= 180 - 158
<5 = 22
<6 = 180 - <5
= 180 - 22
<6 = 158
Example 7 :
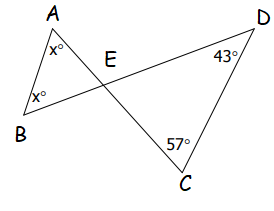
Solution :
In triangle DEC,
<DEC = 180 - (<EDC + <DCE)
= 180 - (43 + 57)
= 180 - 100
= 80
<BEA = 80 (Vertical angles)
2x = 180 - 80
2x = 100
x = 100/2
x = 50
Example 8 :
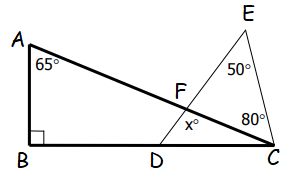
Solution :
In triangle ABC,
<B = 90
<A + <B + <C = 180
65 + 90 + <C = 180
155 + <C = 180
<C = 180 - 155
<C = 25
In triangle EDC,
<EDC = 180 - (50 + 80 + 25)
= 180 - 155
= 25
In triangle FDC,
x = 180 - (25 + 25)
x = 180 - 50
x = 130
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
US Common Core K-12 Curricum Algebra Solving Simple Equations
Jan 07, 26 01:53 PM
US Common Core K-12 Curricum Algebra Solving Simple Equations -
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 4)
Jan 05, 26 06:56 PM
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 4) -
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 3)
Jan 05, 26 06:34 PM
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 3)