TYPES OF SOLUTIONS OF PAIR OF LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
In this section, we will learn the types of solution of a pair of linear equations are having. By comparing the coefficients of linear equations, we may find what type of solution they have.
To compare the coefficients of linear equations in two variables, the equations must be in the form.
a1x + b1y + c1 = 0
a2x + b2y + c2 = 0
The following three cases are possible for any given system of linear equations.
(i) a1/a2 ≠ b1/b2, we get a unique solution
(ii) a1/a2 = a1/a2 = c1/c2, there are infinitely many solutions.
(iii) a1/a2 = a1/a2 ≠ c1/c2, there is no solution
Example 1 :
Which of the following pairs of linear equations has unique solution, no solution, infinitely many solutions. In case there is unique solution, find it by using cross multiplication method.
(i) x – 3y – 3 = 0
3x – 9y – 2 = 0
Solution :
From the above information, let us take the values of a1, a2, b1, b2, c1 and c2
a1 = 1, b1 = -3, c1 = -3
a1 = 3, b1 = -9, c1 = -2
a1/a2 = 1/3
b1/b2 = -3/(-9) = 1/3
c1/c2 = -3/(-2) = 3/2
Here a1/a2 = b1/b2 ≠ c1/c2
From this we can decide the given lines are parallel.
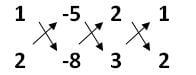
(ii) 2x + y = 5
3x + 2y = 8
Solution :
2x + y – 5 = 0
3x + 2y – 8 = 0
From the above information, let us take the values of a1, a2, b1, b2, c1 and c2
a1 = 2, b1 = 1, c1 = -5
a1 = 3, b1 = 2, c1 = -8
a1/a2 = 2/3
b1/b2 = 1/2
c1/c2 = (-5)/(-8) = 5/8
Here, a₁/a₂ ≠ b₁/b₂
Therefore two given lines are intersecting
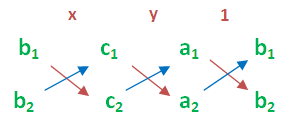
x/(-8 + 10) = y/(-15 + 16) = 1/(4 – 3)
x/2 = y/1 = 1/1
x/2 = 1 y/1 = 1
x = 2 y = 1
(iii) 3x – 5y = 20
6x – 10y = 40
Solution :
3 x – 5 y – 20 = 0 --------(1)
6 x – 10 y – 40 = 0 --------(2)
From the above information, let us take the values of a1, a2, b1, b2, c1 and c2
a1 = 3, b1 = -5, c1 = -20
a1 = 6, b1 = -10, c1 = -40
a1/a2 = 3/6 = 1/2
b1/b2 = -5/(-10) = 1/2
c1/c2 = (-20)/(-40) = 1/2
here, a1/a2 = b1/b2 = c1/c2
Therefore the two given lines are coincident.
(iv) x – 3y – 7 = 0
3x – 3y – 15 = 0
Solution :
From the above information, let us take the values of a1, a2, b1, b2, c1 and c2
a1 = 1, b1 = -3, c1 = -7
a1 = 3, b1 = -3, c1 = -15
a₁/a ₂ = 1/3
b₁/b ₂ = -3/(-3) = 1
c₁/c ₂ = (-7)/(-15) = 7/15
here, a1/a2 ≠ b1/ b2
So, the given two lines are intersecting.
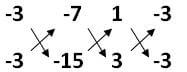
x/(45 - 21) = y/(-21 + 15) = 1/(-3+9)
x/24 = y/(-6) = 1/6
|
x/24 = 1/6 x = 24/6 x = 4 |
y/(-6) = 1/6 y = -6/6 y = -1 |
Example 2 :
The pair of linear equations 2𝑥 = 5y + 6 and 15y = 6𝑥 - 8 represents two lines which are
(a) Intersecting (b) Parallel (c) coincident
(d) either Intersecting or Parallel
Solution :
2𝑥 = 5y + 6 and 15y = 6𝑥 - 8
By comparing slope and y-intercept of these two lines, we can easily decide what type of lines these are.
|
5y = 2x - 6 y = (2/5)x - (6/5) y = mx + b Slope = 2/5 y-intercept = -6/5 |
15y = 6x - 8 y = (6/15)x - (8/15) y = (2/5)x - (8/15) Slope = 2/5 y-intercept = -8/15 |
Since both lines are having same slope and different y-intercepts, the lines must be parallel and they will not intersect each other. Then they will not have solution. So, option b parallel is correct.
Example 3 :
If the pair of linear equations 𝑥 - y = 1, 𝑥 + ky = 5 has a unique solution 𝑥 = 2, y = 1 then the value of k is
(a) -2 (b) -3 (c) 3 (d) 4
Solution :
𝑥 - y = 1 ------(1)
𝑥 + ky = 5 ------(2)
Here x = 2 and y = 1 is solution, by applying these values in (2), we get
2 + k(1) = 5
2 + k = 5
k = 5 - 2
k = 3
So, option c is correct.
Example 4 :
The pair of linear equations 3𝑥 + 5y = 3 and 6𝑥 + ky = 8 do not have a solution if k
(a) = 5 (b) = 10 (c) ≠10 (d) ≠ 5
Solution :
3𝑥 + 5y = 3 and 6𝑥 + ky = 8
Given that the lines do not have solution, then they must be parallel lines.
For parallel lines, slope will be equal and y-intercept will not be equal.
|
3𝑥 + 5y = 3 5y = -3x + 3 y = (-3/5)x + (3/5) Slope (m) = -3/5 y-intercept = 3/5 |
6𝑥 + ky = 8 ky = -6x + 8 y = (-6/k) x + (8/k) Slope (m) = -6/k y-intercept = 8/k |
Equating the slopes,
-3/5 = -6/k
k = 6(5/3)
k = 2(5)
k = 10
So, option b is correct.
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
SAT Math Problems on Exponents and Radicals
Feb 21, 26 08:28 PM
SAT Math Problems on Exponents and Radicals -
SAT Math Problems on Angles
Feb 21, 26 08:20 PM
SAT Math Problems on Angles -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 9)
Feb 21, 26 10:41 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 9)