TRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS OF 180 DEGREE PLUS THETA
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Trigonometric ratios of 180 degree plus theta is one of the branches of ASTC formula in trigonometry.
Trigonometric-ratios of 180 degree plus theta are given below.
sin (180° + θ) = - sin θ
cos (180° + θ) = - cos θ
tan (180° + θ) = tan θ
csc (180° + θ) = - csc θ
sec (180° + θ) = - sec θ
cot (180° + θ) = cot θ
Let us see, how the trigonometric ratios of 180 degree plus theta are determined.
To know that, first we have to understand ASTC formula.
The ASTC formula can be remembered easily using the following phrases.
"All Sliver Tea Cups"
or
"All Students Take Calculus"
ASTC formula has been explained clearly in the figure given below.
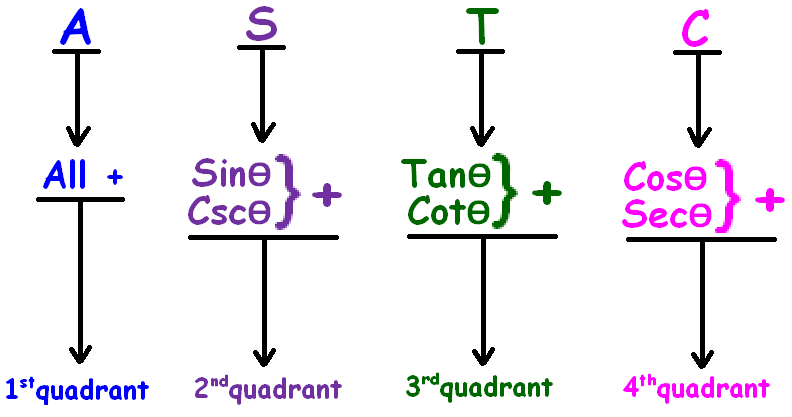
More clearly
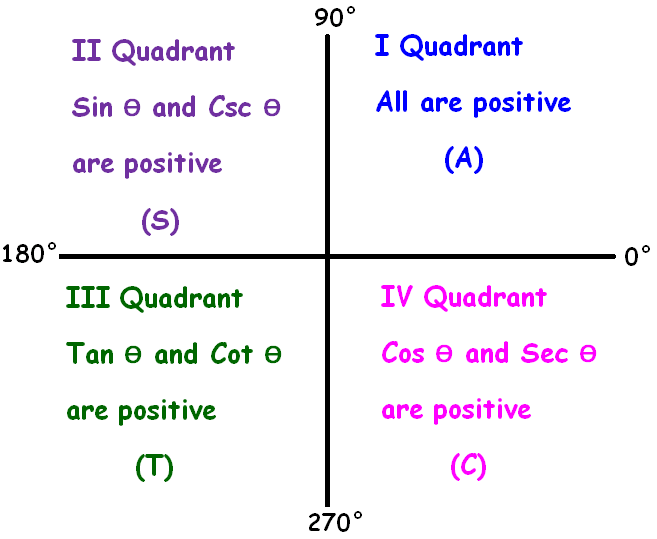
From the above picture, it is very clear that
(180° + θ) falls in the third quadrant
In the third quadrant (180° + θ), tan and cot are positive and other trigonometric ratios are negative.
Important Conversions
When we have the angles 90° and 270° in the trigonometric ratios in the form of
(90° + θ)
(90° - θ)
(270° + θ)
(270° - θ)
We have to do the following conversions,
sin θ <------> cos θ
tan θ <------> cot θ
csc θ <------> sec θ
For example,
sin (270° + θ) = - cos θ
cos (90° - θ) = sin θ
For the angles 0° or 360° and 180°, we should not make the above conversions.
Evaluation of Trigonometric Ratios 180 Degree Plus Theta
Problem 1 :
Evaluate :
sin (180° + θ)
Solution :
To evaluate sin (180° + θ), we have to consider the following important points.
(i) (180° + θ) will fall in the IIIrd quadrant.
(ii) When we have 180°, "sin" will not be changed as "cos"
(iii) In the IIIrd quadrant, the sign of "sin" is negative.
Considering the above points, we have
sin (180° + θ) = - sin θ
Problem 2 :
Evaluate :
cos (180° + θ)
Solution :
To evaluate cos (180° + θ), we have to consider the following important points.
(i) (180° + θ) will fall in the IIIrd quadrant.
(ii) When we have 180°, "cos" will not be changed as "sin"
(iii) In the IIIrd quadrant, the sign of "cos" is negative.
Considering the above points, we have
cos (180° + θ) = - cos θ
Problem 3 :
Evaluate :
tan (180° + θ)
Solution :
To evaluate tan (180° + θ), we have to consider the following important points.
(i) (180° + θ) will fall in the IIIrd quadrant.
(ii) When we have 180°, "tan" will not be changed as "cot"
(iii) In the IIIrd quadrant, the sign of "tan" is positive.
Considering the above points, we have
tan (180° + θ) = tan θ
Problem 4 :
Evaluate :
csc (180° + θ)
Solution :
To evaluate csc (180° + θ), we have to consider the following important points.
(i) (180° + θ) will fall in the IIIrd quadrant.
(ii) When we have 180°, "csc" will not be changed as "sec"
(iii) In the IIIrd quadrant, the sign of "csc" is negative.
Considering the above points, we have
csc (180° + θ) = - csc θ
Problem 5 :
Evaluate :
sec (180° + θ)
Solution :
To evaluate sec (180° + θ), we have to consider the following important points.
(i) (180° + θ) will fall in the IIIrd quadrant.
(ii) When we have 180°, "sec" will not be changed as "csc"
(iii) In the IIIrd quadrant, the sign of "sec" is negative.
Considering the above points, we have
sec (180° + θ) = - sec θ
Problem 6 :
Evaluate :
cot (180° + θ)
Solution :
To evaluate cot (180° + θ), we have to consider the following important points.
(i) (180° + θ) will fall in the IIIrd quadrant.
(ii) When we have 180°, "cot" will not be changed as "tan"
(iii) In the IIIrd quadrant, the sign of "cot" is positive.
Considering the above points, we have
cot (180° + θ) = cot θ
Summary (180 Degree Plus Theta)
sin (180° + θ) = - sin θ
cos (180° + θ) = - cos θ
tan (180° + θ) = tan θ
csc (180° + θ) = - csc θ
sec (180° + θ) = - sec θ
cot (180° + θ) = cot θ
Problem 7 :
Evaluate the function without using a calculator.
|
a) sec 135° b) tan 240° c) sin(−150°) d) csc(−420°) |
e) tan (− 3π/4) f) cot (−8π/3) g) cos 7π/4 h) sec 11π/6 |
Solution :
a) sec 135°
The angle lies in the second quadrant. sec θ will be negative.
Reference angle = 180 - θ
= 180 - 135
= 45
sec 135 = -sec 45
= 1/cos 45
= 1/ (1/√2)
= √2
b) tan 240°
Since the angle lies in the third quadrant, the reference angle will be
θ - 180
= 240 - 180
= 60
tan 240 = tan 60
= √3
c) sin(−150°)
sin (-150) = -sin 150
The angle lies in the second quadrant. Using reference angle
= 180 - θ
= 180 - 150
= 30
-sin 150 = -sin 30
= -1/2
d) csc(−420°) = csc 420
= -csc 60
= -1/sin 60
= -1/(√3/2)
= -2/√3
e) tan (− 3π/4) = - tan (3π/4)
= -tan (π - π/4)
Since the angle lies in the second quadrant, tan θ will be negative.
= tan π/4
= 1
f) cot (−8π/3) = - cot (2π + 2π/3)
= -cot (2π/3)
The angle lies in the second quadrant, the reference angle will be
= π - θ
= π - 2π/3
= π/3
-cot (2π/3) = cot (π/3)
= 1/tan (π/3)
= 1/√3
g) cos 7π/4
Since the angle lies in the third quadrant, the reference angle will be
= 2π - θ
= 2π - (7π/4)
= π/4
cos 7π/4 = cos π/4
= 1/√2
h) sec 11π/6
Since the angle lies in the third quadrant, the reference angle will be
= 2π - θ
= 2π - (11π/6)
= π/6
sec 11π/6 = sec π/6
= 1/cos π/6
= 1/(√3/2)
= 2/√3
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 29)
Mar 01, 26 07:26 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 29) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 28)
Mar 01, 26 06:25 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 28) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part -27)
Feb 28, 26 07:46 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part -27)