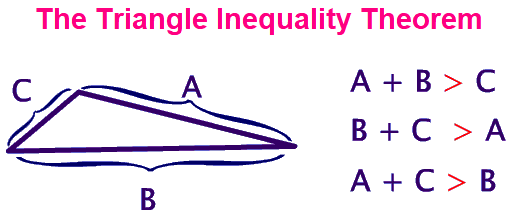
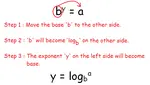TRIANGLE INEQUALITY THEOREM
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
We can use this theorem to check whether the given three measures can be the lengths of a triangle or not.
Theorem :
The sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle is greater than the third side.
Example :
A triangle with the side lengths 5 cm, 6 cm and 4 cm actually exists.
Because, sum of the lengths of any two sides is greater than the third side.
That is, 5 cm + 6 cm > 4 cm.
6 cm + 4 cm > 5 cm
5 cm + 4 cm > 6 cm
The diagram given below illustrates the theorem :
Solved Problems
Problem 1 :
State if the three numbers given below can be the measures of the sides of a triangle.
8, 12 and 9
Solution :
According to the theorem explained above, if the sum of the lengths of any two sides is greater than the third side, then the given sides will form a triangle.
Let us apply the theorem for the given numbers.
8 + 12 > 9
12 + 9 > 8
8 + 9 > 12
Because the given numbers meet the condition said in the theorem, the numbers 8, 12 and 9 can be the measures of the sides of a triangle.
Problem 2 :
State if the three numbers given below can be the measures of the sides of a triangle.
10, 7 and 13
Solution :
According to the theorem explained above, if the sum of the lengths of any two sides is greater than the third side, then the given sides will form a triangle.
Let us apply the theorem for the given numbers.
10 + 7 > 13
7 + 13 > 10
10 + 13 > 7
Because the given numbers meet the condition said in the theorem, the numbers 10, 7 and 13 can be the measures of the sides of a triangle.
Problem 3 :
State if the three numbers given below can be the measures of the sides of a triangle.
6, 12 and 3
Solution :
According to the theorem explained above, if the sum of the lengths of any two sides is greater than the third side, then the given sides will form a triangle.
Let us apply the theorem for the given numbers.
6 + 12 > 3
12 + 3 > 6
6 + 3 < 12 (Does not satisfy the theorem)
Because the given numbers do not meet the condition said in the theorem, the numbers 6, 12 and 3 can not be the measures of the sides of a triangle.
Problem 4 :
Two sides of a triangle have the measures 6 and 7. Find the range of possible measures for the third side.
Solution :
Let x be the length of the third side of the triangle.
According to the theorem explained above, if the sum of the lengths of any two sides is greater than the third side, then the given sides will form a triangle.
Sum of the lengths of the given two sides :
6 + 7 = 13
Because the sum of the lengths of the two sides 6 and 7 is 13, the maximum length of the third side must be less than 13.
That is
x < 13 -----(1)
Let us find the minimum value of x.
According to the theorem, we must have
x + 6 > 7
x + 7 > 6
To satisfy both the inequalities above, the value of x must be greater than 1.
That is
x > 1 (or) 1 < x -----(2)
From (1) and (2), the range of x is
1 < x < 13
Problem 5 :
Find the range of possible measures of x in the following given sides of a triangle :
10, 7, x
Solution :
According to the theorem explained above, if the sum of the lengths of any two sides is greater than the third side, then the given sides will form a triangle.
Sum of the lengths of the given two sides :
10 + 7 = 17
Because the sum of the lengths of the two sides 10 and 7 is 17, the value of x must be less than 17.
That is
x < 17 -----(2)
Let us find the minimum value of x.
According to the theorem, we must have
x + 10 > 7
x + 7 > 10
To satisfy both the inequalities above, the value of x must be greater than 3.
That is
x > 3 (or) 3 < x -----(2)
From (1) and (2), the range of x is
3 < x < 17
Shortcut :
For better understanding, problem 4 and 5 have been explained in detail.
But there is a shortcut to find the range of possible measures for the third side.
Problem 4 :
Lengths of the given two sides are 6 and 7.
Difference of the lengths = 7 - 6 = 1
Sum of the lengths = 7 + 6 = 13
Hence, the range of possible measures for the third side is
1 < x < 13
Problem 5 :
Lengths of the given two sides are 10 and 7.
Difference of the lengths = 10 - 7 = 3
Sum of the lengths = 10 + 7 = 17
Hence, the range of possible measures for the third side is
3 < x < 17
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
Solving Exponential Equations
Feb 23, 26 10:06 AM
Solving Exponential Equations - Concept - Examples -
SAT Math Problems on Exponents and Radicals
Feb 21, 26 08:28 PM
SAT Math Problems on Exponents and Radicals -
SAT Math Problems on Angles
Feb 21, 26 08:20 PM
SAT Math Problems on Angles