SPECIAL RIGHT TRIANGLES
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Special right triangles are the triangles whose angle measures are
45° - 45° - 90°
or
30° - 60° - 90°
Video Lesson
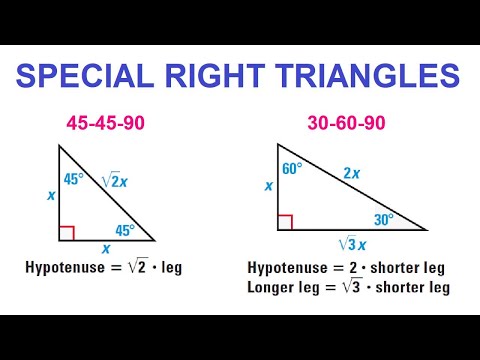
Theorems about Special Right Triangles
45° - 45° - 90° Triangle Theorem :
In a 45° - 45° - 90° triangle, the hypotenuse is √2 times as long as each leg.
It has been illustrated in the diagram shown below.
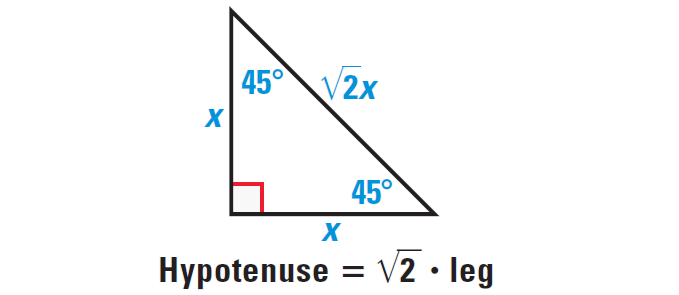
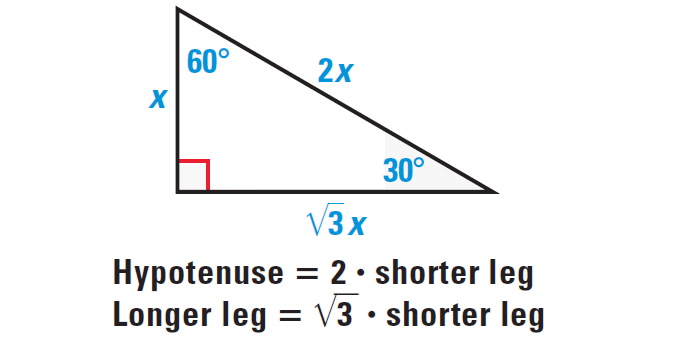
30° - 60° - 90° Triangle Theorem :
In a 30° - 60° - 90° triangle, the hypotenuse is twice as long as the shorter leg, and the longer leg is √3 times as long as the shorter leg.
It has been illustrated in the diagram shown below.
Finding the Hypotenuse in a 45° - 45° - 90° Triangle
Example 1 :
Find the length of the hypotenuse in the triangle shown below.
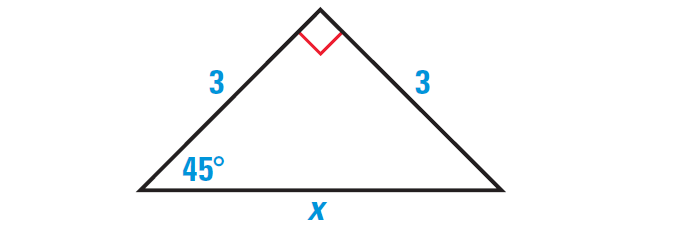
Solution :
By the Triangle Sum Theorem, the measure of the third angle is 45°.
The triangle is a 45°-45°-90° right triangle, so the length x of the hypotenuse is √2 times the length of a leg.
By 45°-45°-90° Triangle Theorem, we have
Hypotenuse = √2 ⋅ leg
In any right angled triangle, the side which is opposite the right angle is hypotenuse. In the triangle shown above, x represents hypotenuse. Because, the side x represents is opposite the right angle.
Substitute.
x = √2 ⋅ 3
Simplify.
x = 3√2
So, the length of the hypotenuse is 3√2.
Finding a Leg in a 45° - 45° - 90° Triangle
Example 2 :
Find the value of x in the triangle shown below.
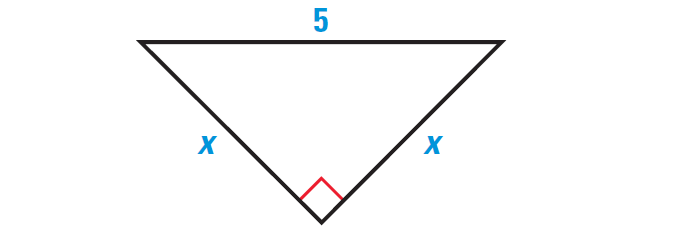
Solution :
Because the triangle is an isosceles right triangle, its base angles are congruent. The triangle is a 45°-45°-90°right triangle, so the length of the hypotenuse is √2 times the length of a leg.
By 45°-45°-90° Triangle Theorem, we have
Hypotenuse = √2 ⋅ leg
Substitute.
5 = √2 ⋅ x
Divide each side by √2.
5/√2 = x
To rationalize denominator in 5/√2, multiply numerator and denominator by √2.
(√2/√2) ⋅ (5/√2) = x
5√2/2 = x
Side Lengths in a 30° - 60° - 90° Triangle
Example 3 :
Find the value of s and x in the triangle shown below.
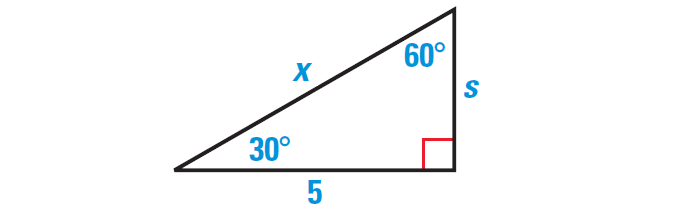
Solution :
Finding the value of s :
Because the triangle is a 30°-60°-90° triangle, the longer leg is √3 times the length s of the shorter length.
By 30°-60°-90° Triangle Theorem, we have
Longer leg = √3 ⋅ shorter leg
Substitute.
5 = √3 ⋅ s
Divide each side by √3.
5/√3 = s
To rationalize denominator in 5/√3, multiply numerator and denominator by √3.
(√3/√3) ⋅ (5/√3) = s
5√3/3 = s
Finding the value of x :
By 30°-60°-90° Triangle Theorem, the length x of the hypotenuse is twice the length s of the shorter leg.
So, we have
Hypotenuse = 2 ⋅ shorter leg
Substitute.
x = 2(5√3/3)
x = 10√3/3
Using Special Right Right Triangles in Real Life
Example 4 :
A tipping platform is a ramp used to unload trucks, as shown in the picture below. How high is the end of an 70 foot ramp when it is tipped by a 30° angle ? by a 45° angle ?
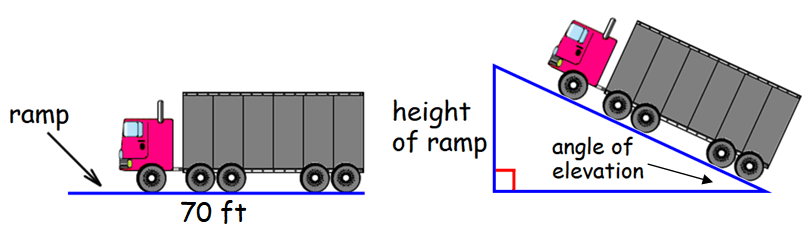
Solution :
Part I :
Let h be the height of the ramp.
When the angle of elevation is 30°, we get a 30°-60°-90° special right triangle.
The height h of the ramp is the length of the shorter leg of the 30°-60°-90° triangle. And also, the length of the hypotenuse is 70 feet.
By 30°-60°-90° Triangle Theorem, we have
Hypotenuse = 2 ⋅ Shorter length
70 = 2 ⋅ h
Divide each side by 2.
35 = h
Part II :
When the angle of elevation is 45°, we get a 45°-45°-90° special right triangle.
By 45°-45°-90° Triangle Theorem, we have
Hypotenuse = √2 ⋅ Leg
70 = √2 ⋅ h
Divide each side by √2.
70/√2 = h
Use calculator to approximate.
49.5 ≈ h
When the angle of elevation is 30°, the ramp height is 35 feet. When the angle of elevation is 45°, the ramp height is about 49 feet 6 inches.
Example 5 :
The road sign is shaped like an equilateral triangle. If the length of each side is 36 inches, estimate the area of the sign by finding the area of the equilateral triangle.
Solution :
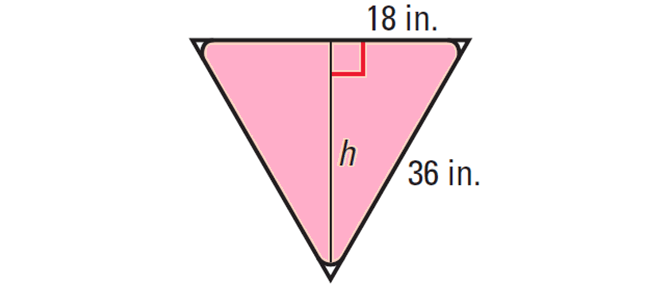
First find the height h of the triangle by dividing it into two 30°-60°-90° triangles. The length of the longer leg of one of these triangles is h. The length of the shorter leg is 18 inches.
By 30°-60°-90° Triangle Theorem, we have
h = √3 ⋅ 18
h = 18√3
Use h = 18√3 to find the area of the equilateral triangle.
Area = 1/2 ⋅ b ⋅ h
Substitute.
= 1/2 ⋅ 36 ⋅ 18√3
Use calculator to approximate.
≈ 561.18 square inches
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 50)
Mar 06, 26 07:48 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 50) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 49)
Mar 06, 26 06:47 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 49) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 48)
Mar 06, 26 05:24 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 48)


