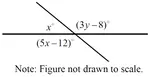
SOLVING QUADRATIC INEQUALITIES WORKSHEET FOR GRADE 11
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Problem 1 :
Solve :
2x2 + x - 15 ≤ 0
Problem 2 :
Solve :
-x2 + 3x - 2 ≥ 0

Detailed Answer Key
Problem 1 :
Solve :
2x2 + x - 15 ≤ 0
Solution :
First let us solve the given quadratic equation by factoring.
2x2 + x − 15 = 0
2x2 + 6x - 5x − 15 = 0
2x(x + 3) - 5(x + 3) = 0
(2x - 5) (x + 3) = 0
2x - 5 = 0 x + 3 = 0
2x = 5 x = -3
x = 5/2
The critical numbers are -3 and 5/2.
Now let us mark them in number line.
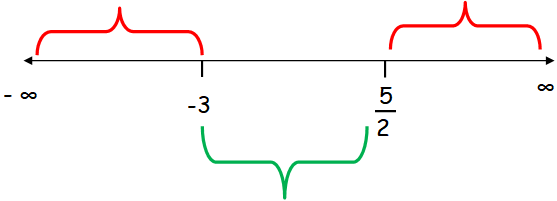
Applying any values within the interval, we get
|
Intervals |
Signs of factors (2x-5)(x+3) |
Sign of given inequality |
|
(-∞, -3] say x = - 4 |
(-) (-) |
+ |
|
[-3, 5/2] say x = 0 |
(-) (+) |
- |
|
[5/2, ∞) say x = 3 |
(+) (+) |
+ |
From the above table, we come to know that the interval [-3, 5/2] satisfies the given inequality.
So, the solution is [-3, 5/2].
Problem 2 :
Solve :
-x2 + 3x - 2 ≥ 0
Solution :
First let us solve the given quadratic equation by factoring.
The coefficient of x must be positive, so we have to multiply the inequality by negative.
x2 - 3x + 2 ≤ 0
Multiply the equation by negative.
x2 - 3x + 2 = 0
x2 - 1x - 2x + 2 = 0
x (x - 1) - 2(x - 1) = 0
(x - 2) (x - 1) = 0
x - 2 = 0 x - 1 = 0
x = 2 x = 1
Writing them as intervals, we get
(-∞, 1] [1, 2] [2, ∞)
Applying any values within the interval, we get
|
Intervals |
Signs of factors (x-2)(x-1) |
Sign of given inequality |
|
(-∞, 1] say x = 0 |
(-) (-) |
+ |
|
[1, 2] say x = 1.5 |
(-) (+) |
- |
|
[2, ∞) say x = 3 |
(+) (+) |
+ |
From the above table, we come to know that the interval [1, 2] satisfies the given inequality.
So, the solution is [1, 2].
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
SAT Math Problems on Exponents and Radicals
Feb 21, 26 08:28 PM
SAT Math Problems on Exponents and Radicals -
SAT Math Problems on Angles
Feb 21, 26 08:20 PM
SAT Math Problems on Angles -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 9)
Feb 21, 26 10:41 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 9)