ROLLES THEOREM PRACTICE PROBLEMS WITH ANSWERS
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Verify Rolle's theorem for the following functions:
(1) f (x) = sin x 0 ≤ x ≤ π
(2) f (x) = x², 0 ≤ x ≤ 1
(3) f (x) = |x - 1|, 0 ≤ x ≤ 2
(4) f (x) = 4 x³ - 9 x, -3/2 ≤ x ≤ 3/2
(5) Using Rolle's theorem find the points on the curve'
y = x2 + 1,
- 2 ≤ x ≤ 2 where the tangent is parallel to x - axis.
(6) The table below gives selected values of a function 𝑓. The function is twice differentiable with f''(x) > 0
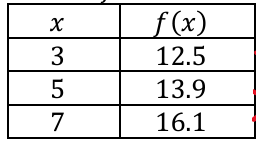
Which of the following could be the value of f'(5) ?
a) 0.5 b) 0.7 c) 0.9 d) 1.1
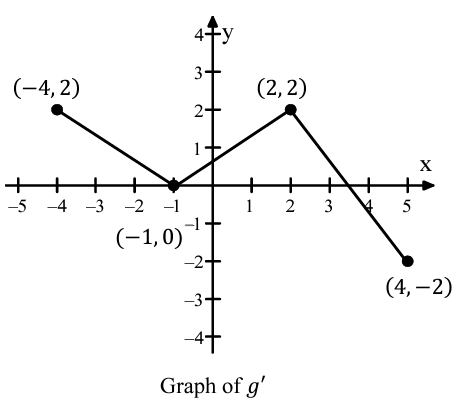
(7) Let 𝑔 be a continuous function. The graph of the piecewise-linear function g', the derivative of g is shown above for -4 ≤ x ≤ 4. Does the mean value theorem applied on the interval -4 ≤ x ≤ 4 guarantee the value of c, for -4 < x < 4, such that g''(c) is equal to this average rate of change ? why or why not ?

Problem 1 :
f(x) = sin x, 0 ≤ x ≤ π
Solution :
If f(x) be a real valued function that satisfies the following three conditions.
(1) f(x) is defined and continuous on [0, π]
(2) f(x) is differentiable on the open interval (0, π).
f(x) = sin x
f(0) = sin 0 ==> 0
f(π) = sin π ==> 0
f(0) = f(π)
from this we come to know that the given function satisfies all the conditions of Rolle's theorem. c ∈ (0,π) we can find the value of c by using the condition f '(c) = 0.
f(x) = sin x
f'(x) = cos x
f'(c) = cos c
f'(c) = 0
cos c = 0
c = (2n+1) (π/2)
c = π/2,3π/2,5π/2,.............
Here π/2 is the only value that is in the given interval. So, the value of c = π/2.
Problem 2 :
f(x) = x2, 0 ≤ x ≤ 1
Solution :
If f(x) be a real valued function that satisfies the following three conditions.
(1) f(x) is defined and continuous on [0, 1]
(2) f(x) is differentiable on the open interval (0, 1).
f(x) = x2
f(0) = 02 ==> 0
f(1) = 12 ==> 1
f(0) ≠ f(1)
The given function is not satisfying all the conditions of mean value theorem. So, we cannot find the value of c.
Problem 3 :
f(x) = |x-1|, 0 ≤ x ≤ 2
Solution :
If f(x) be a real valued function that satisfies the following three conditions.
1) f(x) is defined and continuous on [0, 2]
2) f(x) is not differentiable on (0, 2).
Since the given function is not satisfying all the conditions Rolle's theorem is not admissible.
Problem 4 :
f(x) = 4 x3-9x, -3/2 ≤ x ≤ 3/2
Solution :
If f(x) be a real valued function that satisfies the following three conditions.
(1) f(x) is defined and continuous on [-3/2, 3/2]
2) f(x) is not differentiable on (-3/2,3/2)
f(x) = 4x3-9 x
|
f(-3/2) = 4(-27/8)+27/2 = -27/2+27/2 = 0 |
f(3/2) = 4(27/8) - 27/2 = 27/2 - 27/2 = 0 |
f(-3/2) = f(3/2)
c ∈ (-3/2, 3/2) we can find the value of c by using the condition f'(c) = 0.
f(x) = 4x3-9x
f'(x) = 12x2- 9(1)
= 12x2-9
f'(c) = 12c2-9
f'(c) = 0
12c2-9 = 0
12c2 = 9
c2 = 9/12
c = ± √3/2
Problem 5 :
y = x² + 1 - 2 ≤ x ≤ 2
Solution :
If f(x) be a real valued function that satisfies the following three conditions.
1) f(x) is defined and continuous on [-2,2]
2) f(x) is not differentiable on the open interval (-2,2).
y = x2 + 1
|
f(-2) = (-2)2+1 = 4+1 = 5 |
f(2) = 22+1 = 4+1 = 5 |
from this we come to know that the given function satisfies all the conditions of Rolle's theorem.
c ∈ (-2,2). We can find the value of c by using the condition f'(c) = 0.
f(x) = x2 + 1
f'(x) = 2x
f'(c) = 2 c
f'(c) = 0
2c = 0
c = 0
f(0) = 02+1
= 1
Therefore the required point on the curve is (0, 1).
Problem 6 :
The table below gives selected values of a function 𝑓. The function is twice differentiable with f''(x) > 0
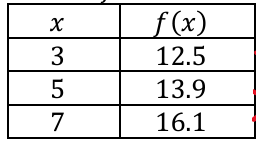
Which of the following could be the value of f'(5) ?
a) 0.5 b) 0.7 c) 0.9 d) 1.1
Solution :
= [f(5) - f(3)] / (5 - 3)
= (13.9 - 12.5)/2
= 1.4/2
= 0.7
= [f(7) - f(5)] / (7 - 5)
= (16.1 - 13.9)/2
= 2.2/2
= 1.1
The required values should be in between 0.7 and 1.1
So, the answer is 0.9 (option c).
Problem 7 :
Let 𝑔 be a continuous function. The graph of the piecewise-linear function g', the derivative of g is shown above for -4 ≤ x ≤ 4. Does the mean value theorem applied on the interval -4 ≤ x ≤ 4 guarantee the value of c, for -4 < x < 4, such that g''(c) is equal to this average rate of change ? why or why not ?

Solution :
Average rate of change = [g'(4) - g'(-4)] / (4 - (-4))
From the graph of g', we get two points (4, -2) and (-4, 2)
= (-2 - 2) / (4 + 4)
= -4/8
= -1/2
No, because 𝒈′𝒙 is not differentiable. It has several corners. The MVT only applies if the function is differentiable.
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
SAT Math Problems on Exponents and Radicals
Feb 21, 26 08:28 PM
SAT Math Problems on Exponents and Radicals -
SAT Math Problems on Angles
Feb 21, 26 08:20 PM
SAT Math Problems on Angles -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 9)
Feb 21, 26 10:41 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 9)