PROVING STATEMENTS ABOUT SEGMENTS AND ANGLES
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
A true statement that follows as a result of other statements is called a theorem. All theorems must be proved. We can prove a theorem using a two-column proof. A two-column proof has numbered statements and reasons that show the logical order of an argument.
Theorem : Properties of Segment Congruence
Reflexive
Symmetric
Transitive
For any segment AB, AB ≅ AB
If AB ≅ CD, then CD ≅ AB
If AB ≅ CD, and CD ≅ EF, then AB ≅ EF
Theorem : Properties of Angle Congruence
Reflexive
Symmetric
Transitive
For any angle A, ∠A ≅ ∠A
If ∠A ≅ ∠B, then ∠B ≅ ∠A
If ∠A ≅ ∠B, ∠B ≅ ∠C, then ∠A ≅ ∠C
A proof which is written in paragraph form is called as paragraph proof.
Here is a paragraph proof for the Symmetric Property of Segment Congruence.
Paragraph Proof :
We are given that PQ ≅ XY. By the definition of congruent segments, PQ = XY. By the symmetric property of equality, XY = PQ. Therefore, by the definition of congruent segments, it follows that XY ≅ PQ.
Here is a paragraph proof for the Symmetric Property of Angle Congruence.
Paragraph Proof :
We are given that ∠A ≅ ∠B. By the definition of congruent angles, A = B. By the symmetric property of equality, B = A. Therefore, by the definition of congruent angles, it follows that ∠B ≅ ∠A.
Example 1 :
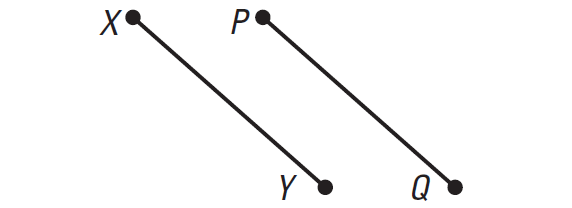
In the diagram given above, PQ ≅ XY. Prove XY ≅ PQ
Solution :
|
Statements PQ ≅ XY PQ = XY XY = PQ XY ≅ PQ |
Reasons Given Definition of congruence statements Symmetric property of equality Definition of congruence segments |
Example 2 :
Use the diagram and the given information to complete the missing steps and reasons in the proof.
Given : LK = 5, JK = 5, JK ≅ JL
Prove : LK ≅ JL
|
Statements A B LK = JK LK ≅ JK JK ≅ JL D |
Reasons Given Given Transitive property of equality C Given Transitive property of congruence |
Solution :
A. LK = 5
B. JK = 5
C. Definition of congruence segments
D. LK ≅ JL
Example 3 :
In the diagram given below, Q is the midpoint of PR.
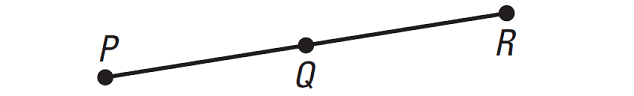
Show that PQ and QR are each equal to 1/2 ⋅ PR.
Solution :
Given : Q is the midpoint of PR
Prove : PQ = 1/2 ⋅ PR and QR = 1/2 ⋅ PR
|
Statements aaaa Q is the aaa aamidpoint of PR PQ = QR PQ + QR = PR PQ + PQ = PR 2 ⋅ PQ = PR PQ = 1/2 ⋅ PR QR = 1/2 ⋅ PR |
Reasons Given aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa aaaaaaaaaaaaa Definition of midpoint Segment Addition Postulate Substitution property of equality Distributive property Division property of equality Substitution property of equality |
Example 4 :
Prove the Transitive Property of Congruence for angles.
Solution :
To prove the Transitive Property of Congruence for angles, begin by drawing three congruent angles.
Label the vertices as A, B and C.
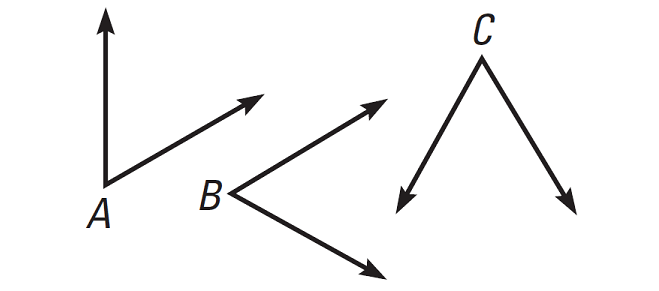
Given :
∠A ≅ ∠B
∠B ≅ ∠C
Prove :
∠A ≅ ∠C
Statements
∠A ≅ ∠B, ∠B ≅ ∠C
m∠A = m∠B
m∠B = m∠C
m∠A = m∠C
∠A ≅ ∠C
Reasons
Given
Definition of congruent angles
Definition of congruent angles
Transitive property of equality
Definition of congruent angles
Example 5 :
In the diagram shown below,
m∠3 = 40°, ∠1 ≅ ∠2, ∠2 ≅ ∠3
Prove m∠1 = 40°
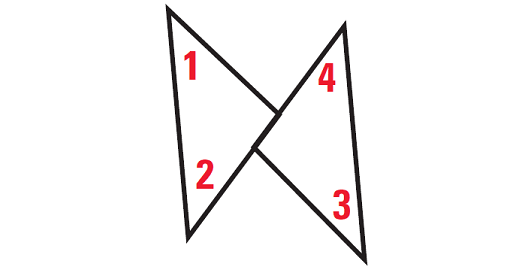
Solution :
Statements
m∠3 = 40°
∠1 ≅ ∠2
∠2 ≅ ∠3
∠1 ≅ ∠3
m∠1 = m∠3
m∠1 = 40°
Reasons
Given
Transitive Property of Congruence
Definition of congruent angles
Substitution property of equality
Example 6 :
In the diagram shown below,
∠1 and ∠2 are right angles
Prove ∠1 ≅ ∠2
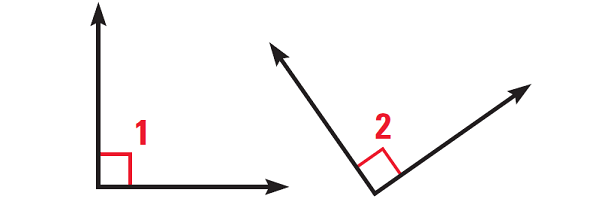
Solution :
Statements
aaaa ∠1 and ∠2 are aa aaaaa right angles
m∠1 = 90°, m∠2 = 90°
m∠1 = m∠2
∠1 ≅ ∠2
Reasons
Given aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa aaaaaaaaa
Definition of right angle
Transitive property of equality
Definition of congruent angles
Example 7 :
In the diagram shown below,
∠1 and ∠2 are supplements,
∠3 and ∠4 are supplements,
∠1 ≅ ∠4
Prove ∠2 ≅ ∠3
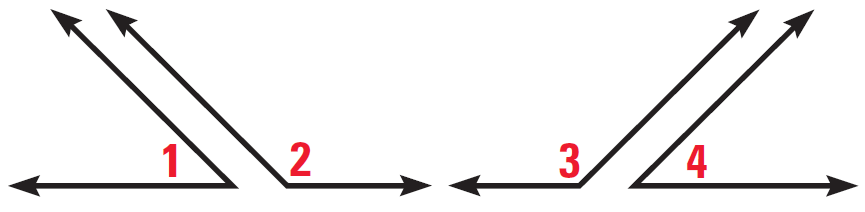
Solution :
Statements
∠1 and ∠2 are supplements
∠3 and ∠4 are supplements
∠1 ≅ ∠4
m∠1 + m∠2 = 180° m∠3 + m∠4 = 180°
m∠1 = m∠4
a ∠1 + ∠2 = ∠3 + ∠1 aaaaaa
m∠2 = m∠3
∠2 ≅ ∠3
Reasons
aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa
Given aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa aaaaaa
Definition of Supplementary angles aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa
Definition of congruent angles
Substitution property of equality aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa
Subtraction property of equality
Definition of congruent angles
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 23)
Feb 27, 26 04:01 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 23) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 22)
Feb 26, 26 08:43 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 22) -
10 Tricky SAT Math Questions with Answers
Feb 25, 26 08:07 AM
10 Tricky SAT Math Questions with Answers