PROVE THAT PROBLEMS USING COMPOUND ANGLES FORMULA
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Problem 1 :
Prove that (i) cos(30° + x) = (√3 cos x − sin x)/2
(ii) cos(π + θ) = −cos θ
(iii) sin(π + θ) = −sin θ.
Solution :
(i) cos(30° + x) :
cos (A + B) = cos A cos B - sin A sin B
cos(30° + x) = cos 30 cos x - sin 30 sin x
= (√3/2) cos x - (1/2) sin x
= (√3 cos x - sin x)/2
(ii) cos(π + θ) :
(π + θ) lies in the 3rd quadrant
In third quadrant, we will have negative sign for all trigonometric ratios other than tan θ and cot θ. Here we have cos θ.
So, cos(π + θ) = -cos θ
(iii) sin(π + θ) = −sin θ :
(π + θ) lies in the 3rd quadrant
In third quadrant, we will have negative sign for all trigonometric ratios other than tan θ and cot θ. Here we have sin θ.
So, sin(π + θ) = -sin θ
Problem 2 :
Find a quadratic equation whose roots are sin 15° and cos 15°.
Solution :
Since the roots of the required quadratic equation are sin 15° and cos 15°.
let α = sin 15° and β = cos 15°
α = sin 15° = sin (45 - 30)
sin (A - B) = sin A cos B - cos A sin B
= sin 45 cos 30 - cos 45 sin 30
= (1/√2) (√3/2) - (1/√2) (1/2)
= (√3/2√2) - (1/2√2)
α = sin 15° = (√3 - 1)/2√2 ---(1)
α = cos 15° = cos (45 - 30)
cos (A - B) = cos A cos B + sin A sin B
= cos 45 cos 30 + sin 45 sin 30
= (1/√2) (√3/2) + (1/√2) (1/2)
= (√3/2√2) + (1/2√2)
β = cos 15° = (√3 + 1)/2√2 ---(2)
|
α + β 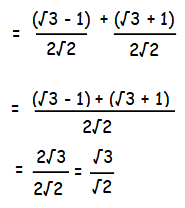 |
αβ 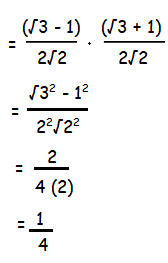 |
General form of quadratic equation
x2 + (α + β)x + α β = 0
x2 + (√3/√2)x + (1/4) = 0
4x2+ 2√3x + 1 = 0
Problem 3 :
Use the compound-angle identities to simplify each of these expressions to one term:
a) cos 23° cos 22° - sin 23° sin 22°
Solution :
cos 23° cos 22° - sin 23° sin 22°
cos A cos B - sin A sin B = cos (A + B)
Using the above formula, we get
= cos (A + B)
= cos (23 + 22)
= cos 45
= √2/2
b) 1 - 2sin 45° cos 45°
Solution :
= 1 - 2sin 45° cos 45°
This problem can be done in two ways:
i) Using algebraic identity
ii) applying the values directly.
Method 1 :
= 1 - 2sin 45° cos 45°
= sin245 + cos2 45 - 2sin 45° cos 45°
a2 + b2 - 2ab = (a - b)2
= (sin 45 - cos 45)2
= (√2/2 - √2/2)2
= 0
Method 2 :
= 1 - 2sin 45° cos 45°
= 1 - 2√2/2 (√2/2)
= 1 - 2/2
= 1 - 1
= 0
Problem 4 :
sin (d + 45) - cos (d + 45) = √2 sin d
Solution :
L.H.S
= sin (d + 45) - cos (d + 45)
= (sin d cos 45 + cos d sin 45) - (cos d cos 45 - sin d sin 45)
= sin d cos 45 + cos d sin 45 - cos d cos 45 + sin d sin 45
= sin d (√2/2) + cos d (√2/2) - cos d (√2/2) + sin d (√2/2)
= (√2sin d/2) + (√2cos d/2) - (√2cos d/2) + (√2 sin d/2)
= (√2sin d + √2cos d - √2cos d + √2 sin d) / 2
= (2√2sin d) / 2
= √2sin d
R.H.S
Hence it is proved
Problem 5 :
[sin (45 + b + 30) cos (60 + b)]/sin 2b = (1/2) cosec b
Solution :
[sin (b + 30) cos (60 + b)]/sin 2b = (1/2) cosec b
sin (b + 30) = sin b cos 30 + cos b sin 30
= sin b (√3/2) + cos b (1/2)
= (√3 sin b + cos b)/2
cos (60 + b) = cos 60 cos b - sin 60 sin b
= (1/2) cos b - (√3/2) sin b
= (cos b - √3 sin b)/2
[sin (b + 30) cos (60 + b)]
= [(√3 sin b + cos b)/2] [(cos b -