PROPERTIES OF PARALLEL AND PERPENDICULAR LINES
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Properties of Parallel Lines
Property 1 :
Let m1 and m2 be the slopes of two lines.
If the two lines are parallel, then their slopes will be equal.
m1 = m2
Property 2 :
Let us consider the general form of equation of a straight line.
ax + by + c = 0
If the two lines are parallel, then their general forms of equations will differ only in the constant term and they will have the same coefficients of x and y.
ax + by + c1 = 0
ax + by + c2 = 0
Property 3 :
Let us consider the slope intercept form of equation of a straight line.
y = mx + b
If the two lines are parallel, then their slope-intercept form equations will will differ only in the "y"- intercept.
y = mx + b1
y = mx + b2
Property 4 :
Let l1 and l2 be two lines.
If the two lines are parallel, the angle between them and the positive side of x-axis will be equal.
The figure given below illustrates the above situation.
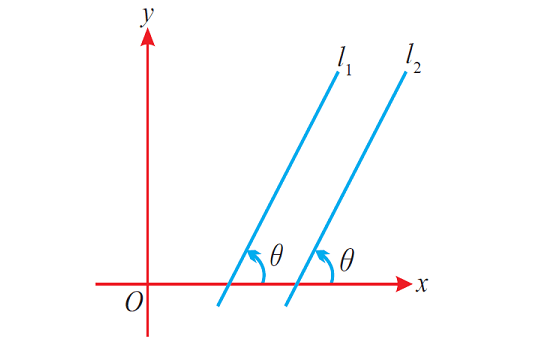
Property 5 :
If the two lines are parallel, the perpendicular distance between them will be same at everywhere.
The figure given below illustrates the above situation.
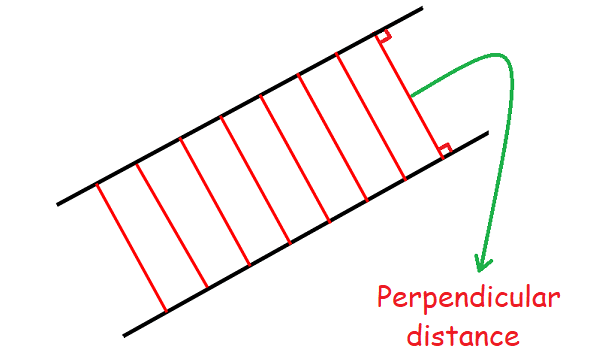
Property 6 :
Let l1 and l2 be two parallel lines and the line m intersects the lines l1 and l2.
The figure shown below illustrates the above situation.
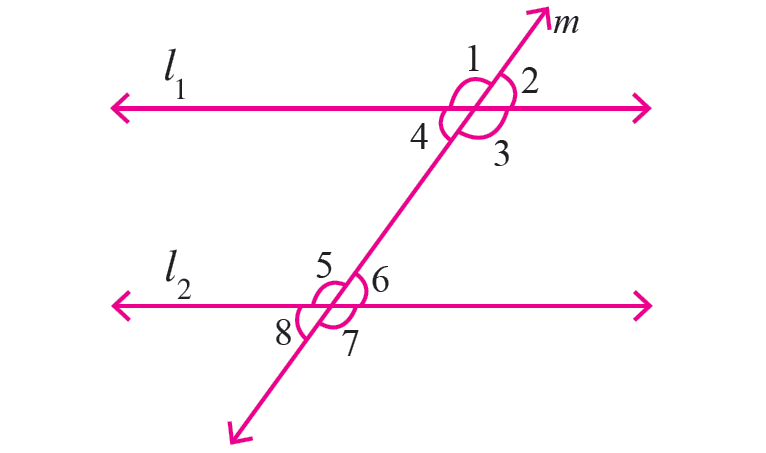
From the above figure, we can have the following important results.
|
Vertically opposite angles are equal. |
∠1 = ∠3 ∠2 = ∠4 ∠5 = ∠7 ∠6 = ∠8 |
|
Corresponding angles are equal. |
∠1 = ∠5 ∠2 = ∠6 ∠3 = ∠7 ∠4 = ∠8 |
|
Alternate interior angles are equal. |
∠3 = ∠5 ∠4 = ∠6 |
|
Consecutive interior angles are supplementary. |
∠3 + ∠6 = 180° ∠4 + ∠5 = 180° |
|
Same side exterior angles are supplementary. |
∠1 + ∠8 = 180° ∠2 + ∠7 = 180° |
Properties of Perpendicular Lines
Property 1 :
Let m1 and m2 be the slopes of two lines.
If, the two lines are perpendicular, then the product of their slopes is equal to -1.
m1 x m2 = -1
Property 2 :
Let us consider the general form of equation of a straight line ax + by + c = 0.
If the two lines are perpendicular, then their general form of equations will differ as shown below.
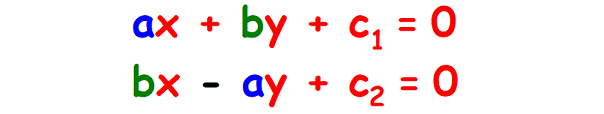
Property 3 :
Let us consider the slope intercept form of equation of a straight line y = mx + b.
If the two lines are perpendicular, then their slope-intercept form equations will differ as shown below.
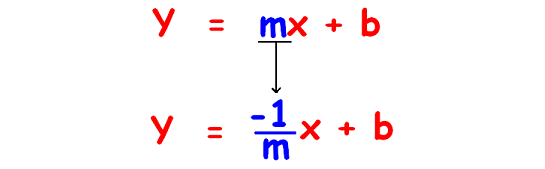
Property 4 :
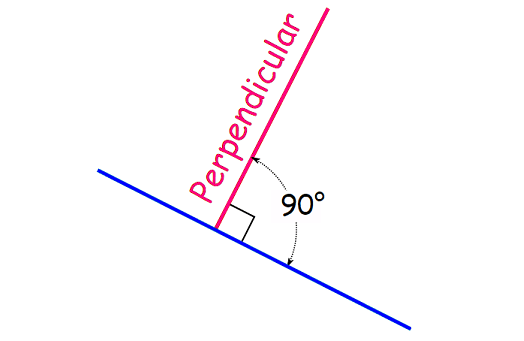
If the two lines are perpendicular, the angle between them will be 90°.
The figure shown below illustrates the above property.
Solving Problems Using Properties of Parallel and Perpendicular Lines
Problem 1 :
The slopes of the two lines are 7 and (3k + 2). If the two lines are parallel, find the value of k.
Solution :
If two lines are parallel, then their slopes are equal.
3k + 2 = 7
Subtract 2 from both sides.
3k = 5
Divide both sides by 5.
k = 5/3
Problem 2 :
If the following equations of two lines are parallel, then find the value of k.
3x + 2y - 8 = 0
(5k + 3)x + 2y + 1 = 0
Solution :
If the two lines are parallel, then their general forms of equations will differ only in the constant term and they will have the same coefficients of x and y.
To find the value of k, equate the coefficients of x.
5k + 3 = 3
Subtract 3 from both sides.
5k = 0
Divide both sides by 5.
k = 0
Problem 3 :
The slopes of the two lines are 7 and (3k + 2). If the two lines are perpendicular, find the value of k.
Solution :
If the given two lines are perpendicular, then the product of the slopes is equal to -1.
7(3k + 2) = -1
Use distributive property.
21k + 14 = -1
Subtract 14 from each side.
21k = -15
Divide each side by 21.
k = -15/21
k = -5/7
Problem 4 :
The equations of the two perpendicular lines are
3x + 2y - 8 = 0
(5k + 3) - 3y + 1 = 0
Find the value of k.
Solution :
If the two lines are perpendicular, then the coefficient y term in the first line is equal to the coefficient of x term in the second line.
5k + 3 = 2
Subtract 3 from both sides.
5k = -1
Divide both sides by 5.
k = -1/5
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 50)
Mar 06, 26 07:48 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 50) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 49)
Mar 06, 26 06:47 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 49) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 48)
Mar 06, 26 05:24 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 48)


