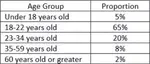
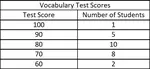
PROPERTIES OF NATURAL NUMBERS
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
In math, natural numbers are the numbers which are positive integers.
They are,
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, ............
There are some properties of natural numbers like closure property, commutative property and associative property.
Let us explore these properties on the four binary operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication and division) in mathematics.
Addition
(i) Closure Property :
The sum of any two natural numbers is always a natural number. This is called ‘Closure property of addition’ of natural numbers. Thus, N is closed under addition
If a and b are any two natural numbers, then (a + b) is also a natural number.
Example :
2 + 4 = 6 is a natural number
(ii) Commutative Property :
Addition of two natural numbers is commutative.
If a and b are any two natural numbers, then
a + b = b + a
Example :
2 + 4 = 6
4 + 2 = 6
Hence, 2 + 4 = 4 + 2.
(iii) Associative Property :
Addition of natural numbers is associative.
If a, b and c are any three natural numbers, then
a + (b + c) = (a + b) + c
Example :
2 + (4 + 1) = 2 + (5) = 7
(2 + 4) + 1 = (6) + 1 = 7
Hence, 2 + (4 + 1) = (2 + 4) + 1.
Subtraction
(i) Closure Property :
The difference between any two natural numbers need not be a natural number.
Hence N is not closed under subtraction.
Example :
2 - 5 = -3 is a not natural number.
(ii) Commutative Property :
Subtraction of two natural numbers is not commutative.
If a and b are any two natural numbers, then
(a - b) ≠ (b - a)
Example :
5 - 2 = 3
2 - 5 = -3
Hence, 5 - 2 ≠ 2 - 5.
Therefore, commutative property is not true for subtraction.
(iii) Associative Property :
Subtraction of natural numbers is not associative.
If a, b, c and d are any three natural numbers, then
a - (b - d) ≠ (a - b) - d
Example :
2 - (4 - 1) = 2 - 3 = -1
(2 - 4) - 1 = -2 - 1 = -3
Hence, 2 - (4 - 1) ≠ (2 - 4) - 1.
Therefore, associative property is not true for subtraction.
Multiplication
(i) Closure Property :
The product of two natural numbers is always a natural number. Hence N is closed under multiplication.
If a and b are any two natural numbers, then
a x b = ab is also a natural number
Example :
5 x 2 = 10 is a natural number
(ii) Commutative Property :
Multiplication of natural numbers is commutative.
If a and b are any two natural numbers, then
a x b = b x a
Example :
5 x 9 = 45
9 x 5 = 45
Hence, 5 x 9 = 9 x 5.
Therefore, commutative property is true for multiplication.
(iii) Associative Property :
Multiplication of natural numbers is associative.
If a, b and c are any three natural numbers,
then a x (b x c) = (a x b) x c
Example :
2 x (4 x 5) = 2 x 20 = 40
(2 x 4) x 5 = 8 x 5 = 40
Hence, 2 x (4 x 5) = (2 x 4) x 5.
Therefore, associative property is true for multiplication.
(iv) Multiplicative Identity :
The product of any natural number and 1 is the whole number itself. ‘One’ is the multiplicative identity for natural numbers.
If a is any natural number, then
a x 1 = 1 x a = a
Example :
5 x 1 = 1 x 5 = 5
Division
(i) Closure Property :
When we divide of a natural number by another natural number, the result does not need to be a natural number.
Hence, N is not closed under multiplication.
Example :
When we divide the natural number 3 by another natural number 2, we get 1.5 which is not a natural number.
(ii) Commutative Property :
Division of natural numbers is not commutative.
If a and b are two natural then
a ÷ b ≠ b ÷ a
Example :
2 ÷ 1 = 2
1 ÷ 2 = 1.5
Hence, 2 ÷ 1 ≠ 1 ÷ 2.
Therefore, Commutative property is not true for division.
(iii) Associative Property :
Division of natural numbers is not associative.
If a, b and c are any three natural numbers, then
a ÷ (b ÷ c) ≠ (a ÷ b) ÷ c
Example :
3 ÷ (4 ÷ 2) = 3 ÷ 2 = 1.5
(3 ÷ 4) ÷ 2 = 0.75 ÷ 2 = 0.375
Hence, 3 ÷ (4 ÷ 2) ≠ (3 ÷ 4) ÷ 2.
Therefore, Associative property is not true for division.
Distributive Property
(i) Distributive Property of Multiplication over Addition :
Multiplication of natural numbers is distributive over addition.
If a, b and c are any three natural numbers, then
a x (b + c) = ab + ac
Example :
2 x (3 + 4) = (2 x 3) + (2 x 4) = 6 + 8 = 14
2 x (3 + 4) = 2x (7) = 14
Hence, 2 x (3 + 4) = (2 x 3) + (2 x 4).
Therefore, Multiplication is distributive over addition.
(ii) Distributive Property of Multiplication over Subtraction :
Multiplication of natural numbers is distributive over subtraction.
If a, b and c are any three natural numbers, then
a x (b - c) = ab - ac
Example :
2 x (4 - 1) = (2 x 4) - (2 x 1) = 8 - 2 = 6
2 x (4 - 1) = 2 x (3) = 6
Hence, 2 x (4 - 1) = (2 x 4) - (2 x 1).
Therefore, multiplication is distributive over subtraction.
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 48)
Mar 06, 26 05:24 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 48) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 47)
Mar 05, 26 09:19 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 47) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 46)
Mar 05, 26 08:37 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 46)