PROBLEMS INVOLVING MAXIMUM AND MINIMUM VALUES IN DERIVATIVES
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Optimization is a process of finding an extreme value (either maximum or minimum) under certain conditions.
A procedure for solving for an extremum or optimization problems.
Step 1 :
Draw an appropriate figure and label the quantities relevant to the problem.
Step 2 :
Find a expression for the quantity to be maximized or minimized.
Step 3 :
Using the given conditions of the problem, the quantity to be extremized .
Step 4 :
Determine the interval of possible values for this variable from the conditions given in the problem.
Step 5 :
Using the techniques of extremum (absolute extremum, first derivative test or second derivative test) obtain the maximum or minimum.
Problem 1 :
Find the dimensions of the largest rectangle that can be inscribed in a semi circle of radius r cm.
Solution :
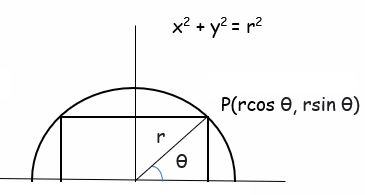
Let θ be the angle made by OP with the positive direction of x axis.
Area of rectangle A(θ) = (2 r cos θ) (r sinθ)
= r2 sin 2θ
A'(θ) = 2r2 cos 2θ
A'(θ) = 0
2r2 cos 2θ = 0
2θ = cos-1(0)
2θ = π/2
θ = π/4
A''(θ) = -4r2 sin 2θ
A''(π/4) = -4r2 sin 2(π/4)
A''(π/4) = -4 r2 < 0 (Maximum)
Length of the rectangle = 2r cos θ = 2rcos(π/4)
= 2 r (1/√2)
= 2 r (1/√2)
= √2r
Width of the rectangle = r sin θ
= r sin (π/4)
= r (1/√2)
= r/√2
Problem 2 :
A manufacturer wants to design an open box having a square base and a surface area of 108 sq.cm. Determine the dimensions of the box for the maximum volume.
Solution :
Let x be the side length of square base box.
Volume of the box = length x width x height
Let h be the height
Surface area of box = x2 + 4xh
x2 + 4xh = 108
4xh = 108-x2
h = (108-x2)/4x ---(1)
Volume of the box = Base area x height
V(x) = x2 (h) ---(2)
V(x) = x2(108-x2)/4x
V(x) = (108x-x3)/4
V'(x) = (108 - 3x2)/4
V'(x) = 0
(108 - 3x2)/4 = 0
3x2 = 108
x2 = 36
x = 6
V''(x) = -6x/4
V''(x) = -3x/2
V''(6) = -3(6)/2
V''(6) = -9 < 0 (Maximum)
Applying x = 6 in (1), we get
h = (108-x2)/4x
h = (108-36)/24
h = 3 cm
So, side length of the base is 4 cm and height is 3 cm.
Problem 3 :
The volume of a cylinder is given by the formula
V = π r2h
Find the greatest and least values of V if r + h = 6.
Solution :
Given :
V = π r2h and r + h = 6
h = 6 - r
V(r) = π r2(6-r)
V(r) = π(6r2-r3)
V'(r) = π(12r-3r2)
V'(r) = 0
3rπ(4-r) = 0
r = 0 and r = 4
|
V''(r) = π(12-6r) V''(0) = π(12-6(0)) V''(0) = 12π > 0 Minimum |
V''(r) = π(12-6r) V''(4) = π(12-6(4)) V''(0) = -12π < 0 Maximum |
r+h = 6
Case 1 : When r = 0, h = 6
Case 2 : When r = 4, h = 2
V = π r2h
By applying case 1, V = 0
By applying case 2, V = π (4)2(2) ==> 32π
So, the greatest value of V is 32π and least value of V is 0.
Problem 4 :
A hollow cone with base radius a cm and height b cm is placed on a table. Show that the volume of the largest cylinder that can be hidden underneath is 4/9 times volume of the cone.
Solution :
Volume of cone = (1/3)π r2h----(1)
Here r = a and h = b
= (1/3)π r2h
= (1/3)π a2b
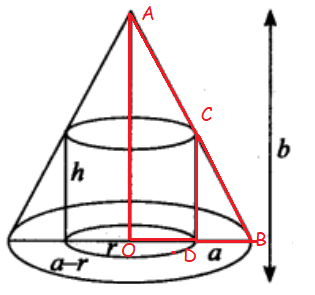
OAB and CDB are similar.
OA/DC = OB/DB
b/h = a/(a-r)
h = (b/a)(a-r)
V(r) = (1/3)π r2[(b/a)(a-r)]
V(r) = (b/3a)π r2(a-r)
V(r) = (bπ/3a) (ar2-r3)
V'(r) = (bπ/3a) (2ar-3r2)
V'(r) = (bπ/3a) (2ar-3r2) = 0
r(2a-3r) = 0
r = 0, r = 2a/3
V''(r) = (bπ/3a) (2a-6r)
V''(0) = (bπ/3a) (2a) > 0 Minimum
V''(r) = (bπ/3a) (2a-6(2a/3))
V''(2a/3) = (bπ/3a) (2a-6(2a/3)) < 0 Maximum
Volume of cylinder = πr2h
r = 2a/3 and h = (b/a)(a-(2a/3))
h = (b/a) (a/3)
h = b/3
= π(2a/3)2(b/3)
Volume of cylinder = (4/9)(1/3)πa2b
Volume of cylinder = (4/9)Volume of cone
Problem 5 :
An open box is to be made by cutting congruent squares of side length x from the corners of a 20 by 25 inch sheet of tin and bending up the sides. How large should the squares be to make the box hold as much as possible ? What is the resulting maximum volume ?
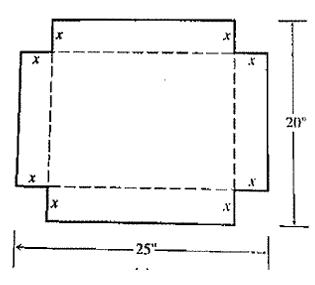
Solution :
Length = 25 - x - x
= 25 - 2x
Width = 20 - x - x
= 20 - 2x
height = x
Volume of the box = length · width · height
= (25 - 2x)(20 - 2x) x
= x(500 - 50x - 40x + 4x2)
= x(500 - 90x + 4x2)
V(x) = 500x - 90x2 + 4x3
V'(x) = 500 - 180x + 12x2
500 - 180x + 12x2 = 0
125 - 45x + 3x2 = 0
3x2 - 45x + 125 = 0
a = 3, b = -45 and c = 125
(-b ± √b2 - 4ac)/2a
= [45 ± √452 - 4(3)(125)]/2(3)
= [45 ± √2025 - 1500)]/6
= [45 ± √525)]/6
= 11.31, 3.68
V'(x) = 500 - 180x + 12x2
V''(x) = - 180 + 24x
When x = 3.68
V''(3.68) = - 180 + 24(3.68)
= -180 + 88.32
= - < 0 maximum
When x = 3.68, the box will have maximum volume.
V(x) = 500x - 90x2 + 4x3
V(3.68) = 500(3.68) - 90(3.68)2 + 4(3.68)3
= 1840 - 90(13.54) + 4(49.83)
= 1840 - 1218.6 + 199.44
= 820.84 cm3
So, the required volume is 820.84 cm3
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
SAT Math Problems on Exponents and Radicals
Feb 21, 26 08:28 PM
SAT Math Problems on Exponents and Radicals -
SAT Math Problems on Angles
Feb 21, 26 08:20 PM
SAT Math Problems on Angles -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 9)
Feb 21, 26 10:41 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 9)