PRACTICAL PROBLEMS INVOLVING MAXIMUM AND MINIMUM VALUES
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Problem 1 :
A rectangle has its base on the x axis and its two upper corners on the parabola y = 12-x2. What is the largest possible area of the rectangle ?
Solution :
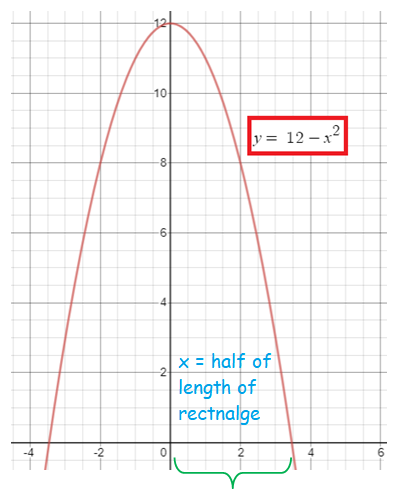
Let x and y be the length and width of the rectangle.
Area of the rectangle = length x width
Area of rectangle = xy
y = 12-x2
Let us derive equation of area of rectangle in one variable.
A(x) = 2x (12-x2)
A(x) = 24x-2x3
A'(x) = 24(1) - 6x2
A'(x) = 24 - 6x2
A'(x) = 0
24 - 6x2 = 0
24 = 6x2
x2 = 4
x = 2
A''(x) = - 6x
When x = 2
A''(2) = - 6(2) ==> -12 < 0
So, at x = 2, it is maximum.
y = 12-x2
When x = 2
y = 12-22 ==> 8
The area will be maximum when its dimensions are x = 2 and y = 8
Maximum Area = A(x) = 2x(12-x2)
= 2(2) (12-22)
= 4 (12-4)
= 4 (8)
= 32 square units
So, maximum area is 32 square units.
Problem 2 :
An open rectangular box is to be made from 9 x 12 inch piece of tin by cutting squares of side x inches from the corners and folding up the sides. What should be x be to maximize the volume of the box ?
Solution :
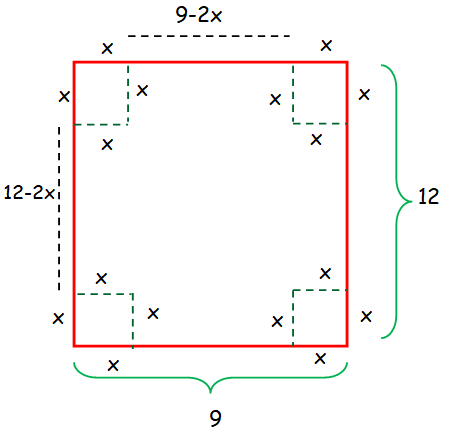
When we fold the rectangular box by cutting the squares at corners, we get the shape cuboid.
Length of cuboid = 9-2x
Width of cuboid = 12-2x and
height of cuboid = x
Volume of cuboid = length ⋅ width ⋅ height
V(x) = (9-2x)(12-2x)x
V(x) = (9-2x)(12-2x)x
V(x) = (9x-2x2)(12-2x)
V(x) = 108x-42x2+4x3
V'(x) = 108-84x+12x2
V'(x) = 0
12x2-84x+108 = 0
x2-7x+9 = 0
Solving this quadratic equation using formula,
(-b±√b2-4ac)/2a
= (7±√49-36)/2
= (7±√13)/2
= (7±3.6)/2
= (7+3.6)/2 or (7-3.6)/2
= 10.6/2 or 3.4/2
x = 5.3 or 1.7
V'(x) = 108-84x+12x2
To find at which point it is maximum, we find the second derivative.
V''(x) = -84+24x
V''(5.3) = -84+24(5.3)
= -84+127.2
= 43.2 > 0 minimum
V''(x) = -84+24x
V''(1.7) = -84+24(1.7)
= -84+40.8
= -43.2 < 0 maximum
So, the value of x should be 1.7 to maximize the volume.
Problem 3 :
A 384 square meter plot of land is to be enclosed by a fence and divided into two equal parts by another fence parallel to one pair of sides. what dimensions of these outer rectangle will minimize the amount of fence used ?
Solution :
Let x and y be the length and width of the rectangle.
Area of rectangular field = 384
xy = 384
y = 384/x
Perimeter of outer dimension = x+y+x+y+y
P = 2x+3y
Deriving the function in terms of one variable, we get
p(x) = 2x+3(384/x)
Minimizing the amount of fence = Perimeter of field along with the parallel side that we find inside the plot
p'(x) = 2-3(384/x2)
p'(x) = 0
2-3(384/x2) = 0
1152/x2 = 2
x2 = 576
x = 24
p''(x) = 6(384/x3)
p''(x) = 6(384/(24)3) > 0 minimum
When x = 24, the perimeter is minimum.
y = 384/24
y = 16
So, the required dimension is 16 cm x 24 cm.
Problem 4 :
What is the radius of a cylindrical soda can with volume of 512 cubic inches that will use the minimum material ?
Solution :
Volume of the cylindrical can = 512 cubic inches
πr2h = 512
To find the material used to make the cylindrical soda can, we should find the total surface area of cylinder.
Total surface area = 2πr(h+r) ---(1)
πr2h = 512
h = 512/πr2
By applying the value of h in (1), we get
T(x) = 2πr(h+r)
T(x) = 2πr((512/πr2)+r)
T(x) = 2πr((512+πr3)/πr2)
T(x) = 2((512+πr3)/r)
T(x) = 1024/r+2πr2
T'(x) = -1024/r2+4πr
T'(x) = 0
4πr = 1024/r2
r3 = 512/π
r = 4.33
T''(x) = 2048/r3+4π
T''(4.33) = 2048/(4.33)3+4π > 0 minimum
So, when r = 4.33 it will take minimum material to be used.
Problem 5 :
A swimmer is at a point 500 m from the closest point on the straight shoreline. She needs to reach a cottage located 1800 m down shore from the closest point. If she swims at 4m/s, she walks at 6 m/s, how far from the cottage should she come ashore so as to arrive at the cottage in the shortest line ?
Solution :
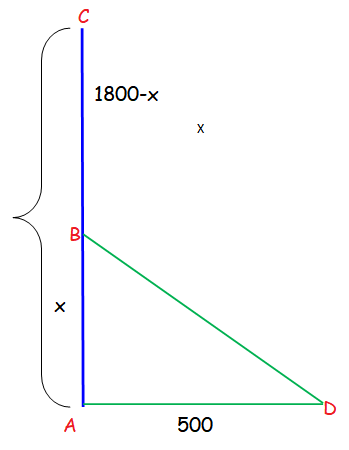
AD is the distance between swimmer and the shore line.
AB = From the point D he has to reach B, so the distance between BD
BD2 = AC2 + AD2
BD2 = x2 + 5002
BD = √x2+5002
BD is the distance covered by swimming and BC is the distance covered by walk.
Time = Distance / Speed
Time taken in swimming(T1) = √(x2+5002)/4
Time taken in walking(T2) = (1800-x)/6
T1 + T2 = √(x2+5002)/4 + (1800-x)/6
T(x) = √(x2+5002)/4 + (1800-x)/6
T'(x) = 2x/8√(x2+5002) - 1/6
T'(x) = x/4√(x2+5002) - 1/6
T'(x) = 0
x/4√(x2+5002) = 1/6
6x = 4√(x2+5002)
(3x/2)2 = (x2+5002)
(9x2-4x2)/4 = x2+5002
x2 = (500⋅500⋅4)/5
x = 200√5
T''(x) = [4√(x2+5002) - (x2/√(x2+5002))]/16(x2+5002)
T''(200√5) > 0
Problem 6 :
Find the closest point on the curve
x2+y2 = 1
to the point (2, 1).
Solution :
Let (x, y) be the required point.
y2 = 1-x2 ----(1)
Distance between the point (x, y) and (2, 1).
d = √(x-2)2+(y-1)2
f(x) = d2 = (x-2)2+(y-1)2
f(x) = (x-2)2+(√(1-x2)-1)2
f(x) = x2-4x+4+(1-x2)-2√(1-x2)+1
f(x) = -4x+6-2√(1-x2)
f'(x) = -4 -(2/2√(1-x2))(-2x)
f'(x) = -4 + (2x/√(1-x2))
f'(x) = 0
(2x/√(1-x2)) = 4
2x = 4√(1-x2)
4x2 = 16(1-x2)
4x2 = 16-16x2
20x2 = 16
x2 = 16/20
x = ±4/2√5
x = ±2/√5
|
x = 2/√5 y2 = 1-(2/√5)2 y2 = 1-(4/5) y2 = 1/5 y = 1/√5 |
x = -2/√5 y2 = 1-(-2/√5)2 y2 = 1-(4/5) y2 = 1/5 y = 1/√5 |
So, the closest point on the curve are (2/√5, 1/√5) and (-2/√5, 1/√5)
Problem 7 :
A window consists of a open rectangle topped by a semicircle and is to have a perimeter of 288 inches. Find the radius of the semicircle that will be maximize the area of the window ?
Solution :
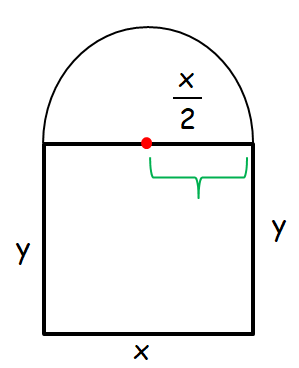
Perimeter = 288
x + y + y + perimeter of semicircle = 288
x+2y+π(x/2) = 288
2y = 288-x-(πx/2)
y = 144-(x/2)-(πx/4)
Area = x(y) + (1/2)πr2
Area = x(144-(x/2)-(πx/4)) + (1/2)π(x/2)2
Area = 144x-(x2/2)-(πx2/4) + (πx2/8)
Area = 144x-x2[(1/2)+(π/4)- (π/8)]
A'(x) = 144-2x[(1/2)+(π/4)- (π/8)]
2x[(1/2)+(π/4)- (π/8) = 144
2x[(4+2π-π)/8] = 144
x[(4+π)/4] = 144
x = 144(4)/7.14
x = 80.67
radius = x/2 ==> 80.67/2
radius = 40.3
So, the radius is 40.3.
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
Simplifying Square Roots Worksheet
Feb 10, 26 07:29 AM
Simplifying Square Roots Worksheet -
Simplifying Square Roots
Feb 10, 26 07:26 AM
Simplifying Square Roots - Concept - Solved Questions -
GMAT Quantitative Reasoning Questions and Answers
Feb 10, 26 06:09 AM
GMAT Quantitative Reasoning Questions and Answers
