OPPOSITE ANGLES IN A CYCLIC QUADRILATERAL WORKSHEET
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
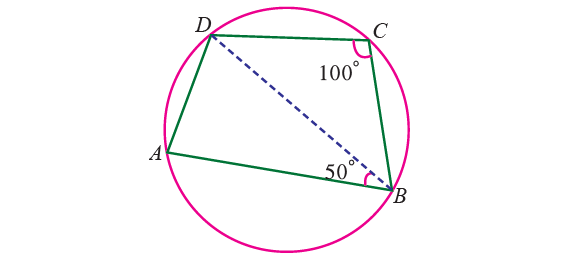
1. In the diagram shown below. ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral in which ∠BCD = 100° and ∠ABD = 50°. Find ∠ADB.
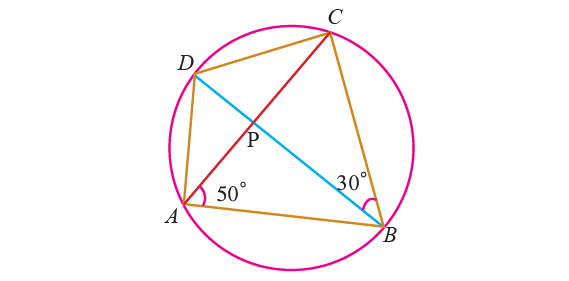
2. In the diagram shown below, ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral whose diagonals intersect at P such that ∠CBD = 30° and ∠BAC = 50°. Find ∠CAD and ∠BCD.
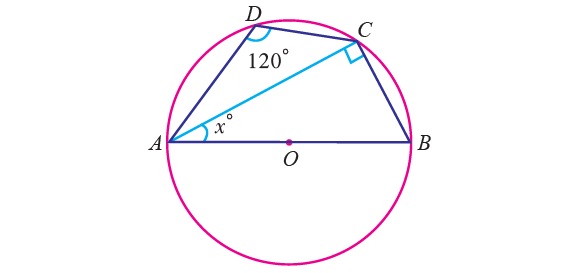
3. In the diagram shown below, O is the center of the circle and ∠ADC = 120°. Find the value of x.
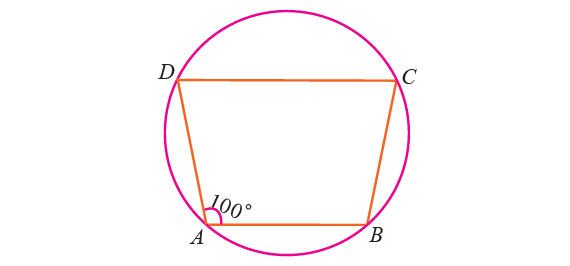
4. In the figure given below, ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral in which AB || DC. If ∠BAD = 100° find ∠BCD, ∠ADC and ∠ABC.
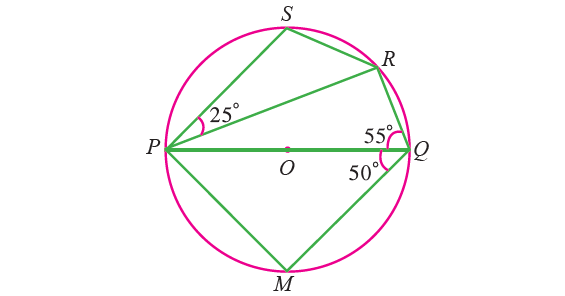
5. In the diagram shown below, PQ is a diameter of a circle with center O. If ∠PQR = 55°, ∠SPR = 25° and ∠PQM = 50°. Find ∠QPR, ∠QPM and ∠PRS.
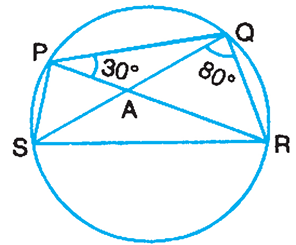
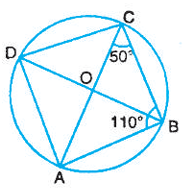
6. In the figure PQRS is a cyclic quadrilateral whose diagonals intersect at A. If ∠SQR = 80o and ∠QPR = 30o, find ∠SRQ.
7. In the figure, ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral whose diagonals intersect at O. If ∠ACB = 50o and ∠ABC = 110o, find ∠BDC.
8. Given <ADC = 80. The measure of <CBE is =
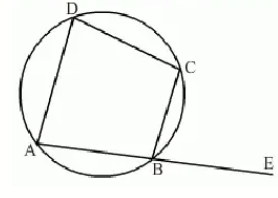
a) 100 b) 180 c) 160 d) 80
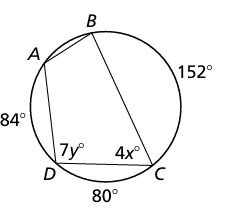
9. Find the values of x and y.

1. Answer :
By Theorem,
∠BAD + ∠BCD = 180°
Substitute ∠BCD = 100°.
∠BAD + 100° = 180°
Subtract 100° from each side.
∠BAD = 80°
In triangle ABD,
∠ABD + ∠BAD + ∠ADB = 180°
50° + 80° + ∠ADB = 180°
130° + ∠ADB = 180°
Subtract 130° from each side.
∠ADB = 50°
2. Answer :
∠CAD :
The angles at the circumference subtended by the same arc are equal. ∠CAD and ∠CBD at the circumference subtended by the same arc CD.
∠CAD = ∠CBD
∠CAD = 30°
∠BCD :
By Theorem,
∠BAD + ∠BCD = 180°
In the above diagram, ∠BAD = ∠BAC + ∠CAD.
(∠BAC + ∠CAD) + ∠BCD = 180°
∠BAC + ∠CAD + ∠BCD = 180°
Substitute ∠BAC = 50° and ∠CAD = 30°.
50° + 30° + ∠BCD = 180°
80° + ∠BCD = 180°
Subtract 80° from each side.
∠BCD = 100°
3. Answer :
By Theorem,
∠ABC + ∠ADC = 180°
Substitute ∠ADC = 120°.
∠ABC + 120° = 180°
Subtract 120° from each side.
∠ABC = 60°
∠ACD = 90° (angle in a semi circle is a right angle)
In triangle ABC,
∠BAC + ∠ACB + ∠ABC = 180°
x° + 90° + 60° = 180°
x + 90 + 60 = 180
x + 150 = 180
Subtract 150 from each side.
x = 30
4. Answer :
∠BCD :
By Theorem,
∠BAC + ∠BCD = 180°
Substitute ∠BAD = 100°.
100° + ∠BCD = 180°
Subtract 100° from each side.
∠BCD = 80°
∠ADC :
Since AB || DC, AD is transversal.
When two parallel lines intersected by a transversal, same side interior angles are supplementary.
∠BAD + ∠ADC = 180°
Substitute ∠BAD = 100°.
100° + ∠ADC = 180°
Subtract 100° from each side.
∠ADC = 80°
∠ABC :
By Theorem,
∠ABC + ∠ADC = 180°
Substitute ∠ADC = 80°.
∠ABC + 80° = 180°
Subtract 80° from each side.
∠ABC = 100°
5. Answer :
∠QPR :
∠PRQ = 90° (angle in a semi circle is a right angle)
In triangle PRQ,
∠PRQ + ∠QPR + ∠PQR = 180°
90° + ∠QPR + 55° = 180°
∠QPR + 145° = 180°
Subtract 145° from each side.
∠QPR = 35°
∠QPM :
In triangle QPM,
∠QPM + ∠MQP + ∠QMP = 180°
∠QPM + 50° + 90° = 180°
∠QPM + 140° = 180°
Subtract 140° from each side.
∠QPM = 40°
∠PRS :
By Theorem,
∠PQR + ∠PSR = 180°
55° + ∠PSR = 180°
Subtract 55° from each side.
∠PSR = 125°
In triangle PSR,
∠PSR + ∠SPR + ∠PRS = 180°
125° + 25° + ∠PRS = 180°
150° + ∠PRS = 180°
Subtract 150° from each side.
∠PRS = 30°
6. Answer :
If ∠SQR = 80o and ∠QPR = 30o, find ∠SRQ.

Angles in the same segment they are equal.
<SPR = <SQR = 80
<QPR = <QSR = 30
In triangle SQR,
<QSR + <SRQ + <RQS = 180
30 + <SRQ + 80 = 180
110 + <SRQ = 180
<SRQ = 180 - 110
<SRQ = 70
7. Answer :
If ∠ACB = 50o and ∠ABC = 110o, find ∠BDC.

In triangle ABC,
<BAC + <ABC + <BCA = 180
<BAC + 110 + 50 = 180
<BAC + 160 = 180
<BAC = 180 - 160
<BAC = 20
<BAC = <BDC = 20 (angle in the same segment)
8. Answer :
Given <ADC = 80. The measure of <CBE is =

Sum of opposite angles is equal to 180 degree
<ADC + <CBE = 180
80 + <CBE = 180
<CBE = 180 - 80
<CBE = 100
So, option a is correct.
9. Answer :

Angles subtended at the center of the arc is twice the angle at the circumference of the circle.
Arc of AB + Arc of BC + Arc of CD + Arc of DA = 360
Arc of AB + 152 + 80 + 84 = 360
Arc of AB + 316 = 360
Arc of AB = 360 - 316
Arc of AB = 44
2<ADC = Arc of AB + Arc BC
= 44 + 152
2(7y) = 196
14y = 196
y = 196/14
y = 14
2<DCB = 84 + 44
2<DCB = 128
2(4x) = 128
8x = 128
x = 128/8
x = 16
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 47)
Mar 05, 26 09:19 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 47) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 46)
Mar 05, 26 08:37 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 46) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 45)
Mar 05, 26 08:02 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 45)