HOW TO FIND EQUATION OF NORMAL TO THE CURVE
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
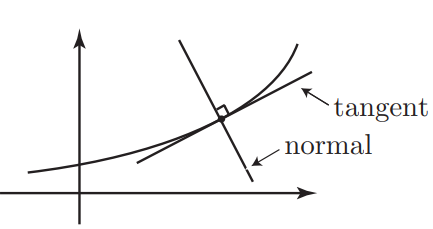
In mathematics the word ‘normal’ has a very specific meaning. It means ‘perpendicular’ or ‘at right angles’.
The normal is then at right angles to the curve so it is also at right
angles (perpendicular) to the tangent.
For each of the function given below determine the equation of normal at each of the points indicated.
(i) f(x) = x2+3x+1 at x = 0
(ii) f(x) = tanx at x = π/4
Question 1 :
f(x) = x2 + 3x + 1 at x = 0
Solution :
y = f(x) = x2+3x+1
When x = 0, then y = 1
So, we find equation of normal to the curve drawn at the point (0, 1).
When we differentiate the given function, we will get the slope of tangent.
dy/dx = f'(x) = 2x + 3 (Slope of tangent)
-1/m = -1/(2x+3) (Slope of normal)
Slope of normal at x = 0.
-1/m = -1/3
Equation of normal :
(y-y1) = (-1/m)(x-x1)
Slope of normal = -1/3 and the point (0, 1).
y-1 = (-1/3)(x-0)
3y-3 = -1(x)
3y-3 = -x
x+3y-3 = 0
Question 2 :
f(x) = tanx at x = π/4
Solution :
y = f(x) = tanx
When x = π/4, then y = 1
So, we find equation of normal to the curve drawn at the point (π/4, 1).
When we differentiate the given function, we will get the slope of tangent.
dy/dx = f'(x) = sec2x (Slope of tangent)
-1/m = -1/sec2x (Slope of normal)
Slope of normal at x = π/4
-1/m = -1/(√2)2
-1/m = -1/2
Equation of normal :
(y-y1) = (-1/m)(x-x1)
Slope of normal = -1/2 and the point (π/4, 1).
y-1 = (-1/2)(x-π/4)
2y-2 = -1(x-π/4)
2y-2 = -x+π/4
x+2y-2-π/4 = 0
Question 3 :
Find the equation of each normal of the function
f(x) = (x3/3)+ x2 + x − (1/3)
which is parallel to the line
y = (− x/4) + (1/3)
Solution :
f'(x) = x2+2x+1
Slope of normal :
-1/f'(x) = -1/(x2+2x+1) ---(1)
Normal line is parallel to the given line y = (− x/4) + (1/3)
Slope of the above line = -1/4 ---(2)
(1) = (2)
-1/(x2+2x+1) = -1/4
x2+2x+1 = 4
x2+2x-3 = 0
(x+3)(x-1) = 0
x = -3 and x = 1
y = f(x) = (x3/3)+x2+x−(1/3)
When x = -3
y = -9+9-3-(1/3)
y = -3-(1/3)
y = -10/3
When x = 1
y = (1/3)+1+1-(1/3)
y = 2
The required points (-3, -10/3) and (1, 2).
Equation of normal has slope -1/4 and passing through the point (-3, -10/3).
y+(10/3) = (-1/4)(x+3)
4(3y+10) = -3(x+3)
12y+40 = -3x-9
3x+12y+49 = 0
Equation of normal has slope -1/4 and passing through the point (1, 2).
y-2 = (-1/4)(x-1)
4(y-2) = -1(x-1)
4y-8 = -x+1
x+4y-9 = 0
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
SAT Math Problems and Solutions
Feb 14, 26 06:05 AM
SAT Math Problems and Solutions -
SAT Math Practice Questions with Answers
Feb 14, 26 05:47 AM
SAT Math Practice Questions with Answers -
SAT Math Practice Test with Answers
Feb 14, 26 02:30 AM
SAT Math Practice Test with Answers