NAME THE QUADRANT CONTAINING EACH POINT
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Let X′OX and YOY′ be two lines at right angles to each other as in the figure given below.
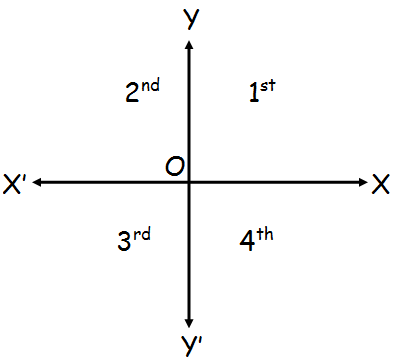
we call X′OX and YOY′ as x-axis and y-axis respectively.
XOY - First
YOX - Second
X′OY′ - Third
Y′OX - Fourth
|
Quadrants I II III IV |
Points will be in the form (x, y) (-x, y) (-x, -y) (x, -y) |
Example 1 :
Name the quadrants containing the points.
(a) (2, 4)
Solution :
The given point is in the form of (x, y), both x and y coordinates are positive.
So, it is the first quadrant.
(b) (0, 3)
Solution :
In the given point
x-coordinate = 0
y-coordinate = positive
The point lies on the y-axis and between first and second quadrant.
(c) (-2, 3)
Solution :
In the given point
x-coordinate = negative,
y - coordinate = positive
So, the point lies on the second quadrant.
(d) (-1, -4)
Solution :
In the given point
x-coordinate = negative,
y - coordinate = negative
So, the point lies on the third quadrant.
(e) (1/2, 3/2)
Solution :
In the given point
x-coordinate = positive
y - coordinate = positive
So, the point lies on the first quadrant.
(f) (-2, 0)
Solution :
In the given point
x-coordinate = negative
y - coordinate = zero
So, the point is on the x axis, and it will lie between second and third quadrant.
Example 2 :
Estimate the coordinates of the points.
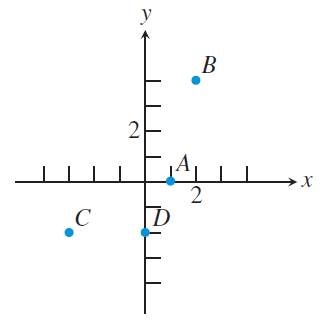
Solution :
A :
The point A lies on the x-axis, then its y-coordinate is 0. So, the point is A(1, 0).
B (2, 4), C (-3, -2)
The point D lies on y-axis, then its x-coordinate is 0. So, the point is D (0, -2).
Example 3 :
Estimate the coordinates of the points.
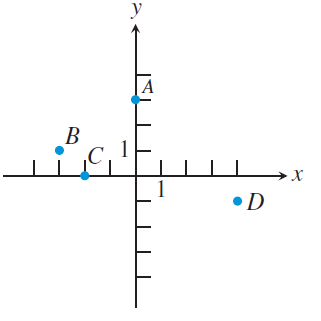
Solution :
A (0, 3), B (-3, 1), C (-2, 0) and D(4, -1).
Example 4 :
Point (–3, 5) lies in the
(A) first quadrant (B) second quadrant
(C) third quadrant (D) fourth quadrant
Solution :
The point (-3, 5) is in the form of (-, +), the point lies in the second quadrant.
Example 5 :
Signs of the abscissa and ordinate of a point in the second quadrant are respectively
(A) +, + (B) -, + (C) +, - (D) -, -
Solution :
The point which lies on the second quadrant will be in the form (-, +).
Example 6 :
Point (0, –7) lies
(A) on the x –axis (B) on the y-axis
(C) in the second quadrat (D) in the fourth quadrant
Solution :
The point lies in the form (+, -), will be in the fourth quadrant.
Considering the value of x, it is 0. So, it lies on the y-axis. Option B is correct.
Example 7 :
Point (– 10, 0) lies
(A) on the negative direction of the x-axis
(B) on the negative direction of the y-axis
(C) in the third quadrant
(D) in the fourth quadrant
Solution :
The value of y is 0, then the point will lie in the x-axis. The point (-10, 0) will lie on the negative directions of the x-axis.
Example 8 :
Abscissa of all the points on the x-axis is
(A) 0 (B) 2 (C) 1 (D) any number
Solution :
Abscissa is the word refers to x-coordinate, the point lies on the x-axis may be any number.
Example 9 :
Ordinate of all points on the x-axis is
(A) 0 (B) 1 (C) – 1 (D) any number
Solution :
The word ordinate refers value of y. The value of y of all the points lies on the x-axis is 0.
Example 10 :
Find the coordinates of the point
(i) which lies on x and y axes both.
(ii) whose ordinate is – 4 and which lies on y-axis.
(iii) whose abscissa is 5 and which lies on x-axis.
Solution :
(i) The point which lies on the x-axis will be in the form (a, 0). Here a may be positive or negative number.
The point which lies on the x-axis will be in the form (0, b). Here b may be positive or negative number.
(ii) Here y = -4, when it lies on the y-axis, its x-value will become 0. So, the required point is (0, -4).
(iii) Here x = 5, since it lies on the x-axis, its y-value will become 0. So, the required point is (5, 0).
Example 11 :
(i) A point lies on the x-axis at a distance of 7 units from the y-axis. What are its coordinates?
(ii) What will be the coordinates if it lies on y-axis at a distance of 7 units from x-axis?
Solution :
(i) From this, we understand that the horizontal distance from origin is 7 units. We may go in any direction may be left or right. Then x = -7 or x = 7.
(ii) From this, we understand that the vertical distance from x-axis is 7 units. We may do in any direction, may be up or down. Then y = 7 or y = -7.
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 44)
Jan 12, 26 06:35 AM
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 44) -
US Common Core K-12 Curricum Algebra Solving Simple Equations
Jan 07, 26 01:53 PM
US Common Core K-12 Curricum Algebra Solving Simple Equations -
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 4)
Jan 05, 26 06:56 PM
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 4)