LOCUS
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Drawing a Locus Satisfying One Condition
A locus in a plane is the set of all points in a plane that satisfy a given condition or a set of given conditions. The word locus is derived from the Latin word for “location”. The plural of locus is Loci, pronounced “low-sigh”.
A locus is often described as the path of an object moving in a plane. For instance, the reason that many clock faces are circular is that the locus of the end of a clock’s minute hand is a circle.
Finding a Locus
To find the locus of points that satisfy a given condition, use the following steps.
1. Draw any figures that are given in the statement of the problem.
2. Locate several points that satisfy the given condition.
3. Condition drawing points until you can recognize the pattern.
4. Draw the locus and describe it in words.
Example 1 :
Draw point C on a piece of paper. Draw and describe the locus of all points on the paper that are e inches from c.
Solution :
Step 1 :
Draw point C. Locate several points e inches
from C.
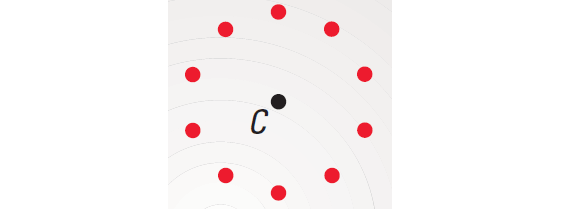
Step 2 :
Recognize a pattern: the points lie on a circle.
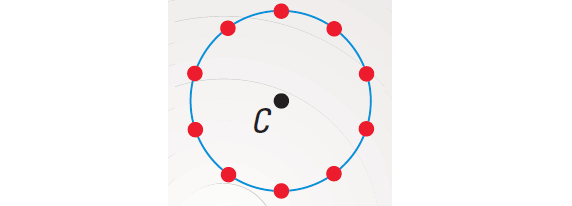
Step 3 :
Draw the circle using compass as shown below.
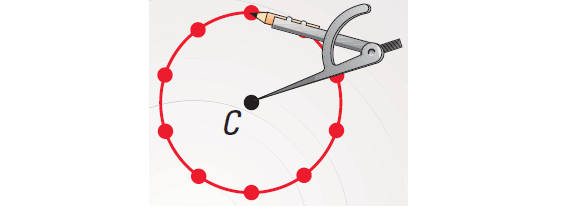
The locus of points on the paper that are e inches from C is a circle with center C and a radius of 3 inches.
Loci Satisfying Two or More Conditions
To find the locus of points that satisfy two or more conditions, first find the locus of points that satisfy each condition alone. Then find the intersection of these loci.
Example 2 :
Points A and B lie in a plane. What is the locus of points in the plane that are equidistant from points A and B and are a distance of AB from B ?
Solution :
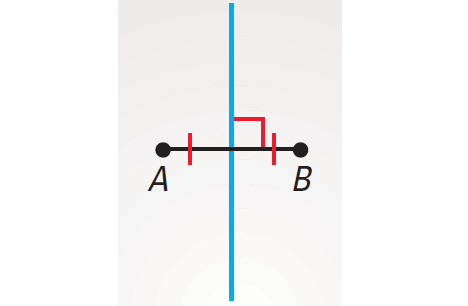
The locus of all points that are equidistant from A and B is the perpendicular bisector of AB as shown below.
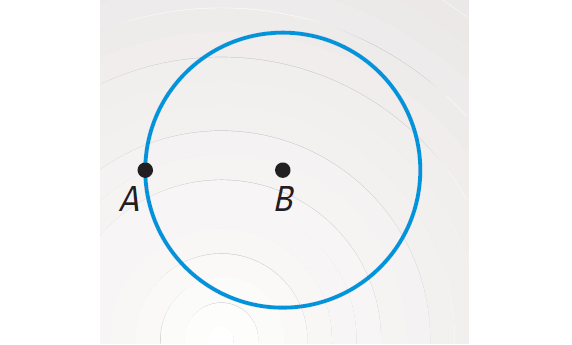
The locus of all points that are a distance of AB from B is the circle with center B and radius AB as shown below.
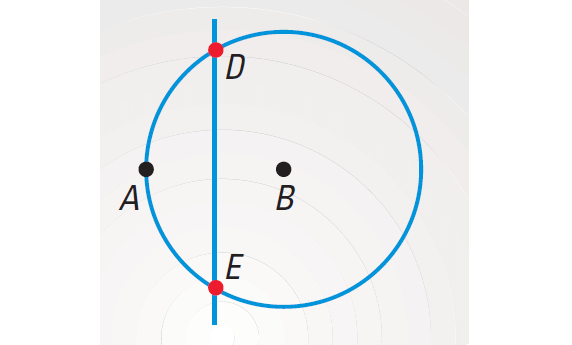
These loci intersect at D and E. So D and E are the locus of points that satisfy both conditions.
Example 3 :
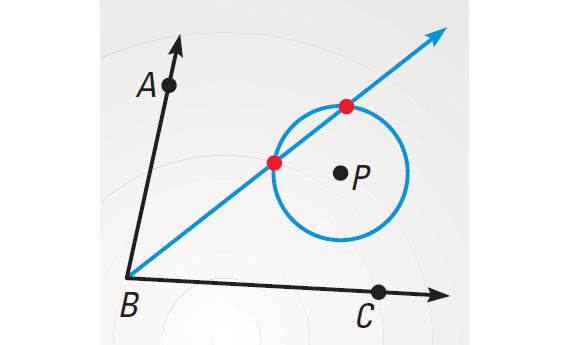
Point P is in the interior of ∠ABC. What is the locus of points in the interior of ∠ABC that are equidistant from both sides of ∠ABC and 2 inches form P ? How does the location of P within ∠ABC affect the locus ?
Solution :
The locus of points equidistant from both sides of ∠ABC is the angle bisector. The locus of points 2 inches form P is a circle. The intersection of the angle bisector and the circle depends on the location of P. The locus can be 2 points, 1 point, or 0 points.
The locus is two points :
The locus is one point :
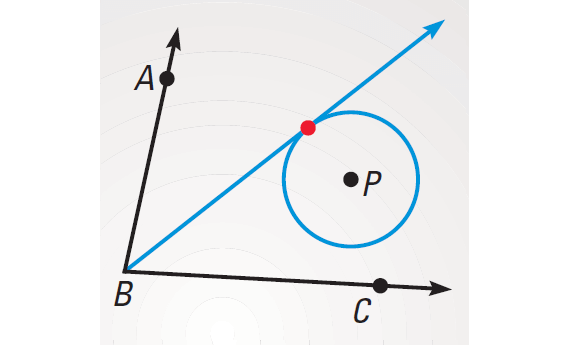
The locus is zero points :
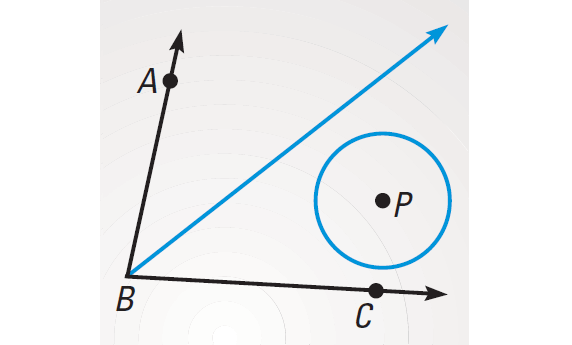
Finding a Locus Satisfying Three Conditions
Example 4 :
We have the following readings of an earthquake from three seismographs.
(i) At A(-5, 5), the epicenter is 4 miles away.
(ii) At B(-4, -3.5), the epicenter is 5 miles away.
(iii) At C(1, 1.5), the epicenter is 7 miles away.
Where is the epicenter ?
Solution :
Each seismograph gives us a locus that is a circle.
So, we have
Circle A has center (-5, 5) and radius 4
Circle B has center (-4, -3.5) and radius 5
Circle C has center (1, 1.5) and radius 7
Draw the three circles in a coordinate plane. The point of intersection of the three circles is the epicenter.
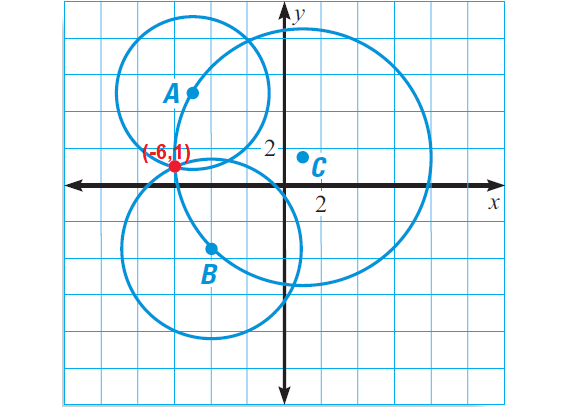
In the diagram above, three circles intersect at (-6, 1).
The epicenter is at about (-6, 1).
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 41)
Mar 04, 26 04:23 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 41) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 40)
Mar 03, 26 06:53 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 40) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 39)
Mar 03, 26 04:59 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 39)