LINEAR RELATIONSHIPS AND BIVARIATE DATA
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
When data are collected in two variables simultaneously, say x and y, they are known as bivariate data.
The relationship represented by a bivariate data is linear, then its graph will be a line.
We can use the points on a graph of a linear relationship to write an equation for the relationship. The equation of a linear relationship is y = mx + b, where m is the rate of change, or slope, and b is the y-intercept (The value of y when x is 0).
Example 1 :
A handrail runs alongside a stairway. As the horizontal distance from the bottom of the stairway changes, the height of the handrail changes. Show that the relationship is linear, and then find the equation for the relationship.
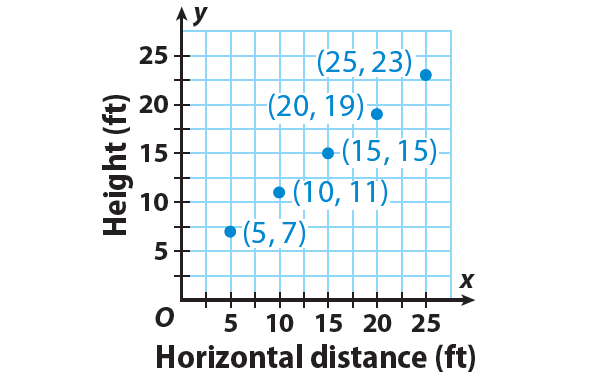
Solution :
Step 1 :
Connect the points in the graph given above.
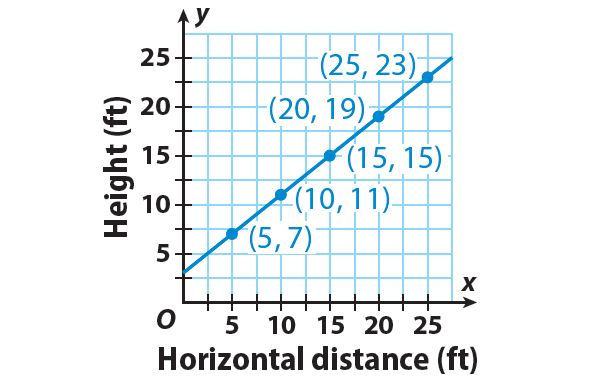
Since all of the points (5, 7), (10, 11), (15, 15), (20, 19), and (25, 23) lie on the same line, the relationship is linear.
Step 2 :
Choose any two points in the form (x, y), from the graph to find the slope :
For example, let us choose (5, 7) and (10, 11).
Use the slope formula.
m = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1)
Substitute :
(x1, y1) = (5, 7)
(x2, y2) = (10, 11)
Then,
m = (11 - 7) / (10 - 5)
m = 4 / 5
m = 0.8
Step 3 :
Choose a point and use the slope to find the value of 'b' (y-intercept b).
Substitute the point (5, 7) and m = 0.8 in the equation
y = mx + b
7 = (0.8)(5) + b
7 = 4 + b
3 = b
Step 4 :
To get the equation of the given linear relationship, substitute m = 0.8 and b = 3 in the equation y = mx + b.
y = 0.8x + 3
Example 2 :
The table shows the relationship between time and cost. Show that the relationship is linear, and then find the equation for the relationship.
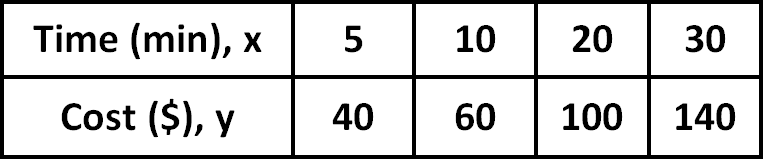
Solution :
Step 1 :
From the table, write the points in the form (x, y).
(5, 40), (10, 60), (20, 100) and (30, 140)
Step 2 :
Plot all the points in a graph paper and connect them.
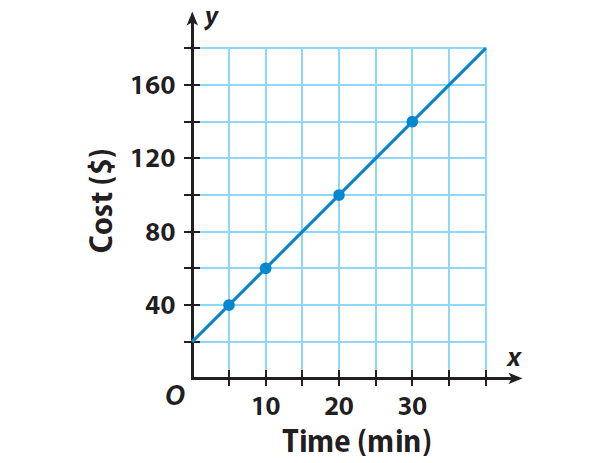
Since all of the points (5, 40), (10, 60), (20, 100) and (30, 140) lie on the same line, the relationship is linear.
Step 3 :
Choose any two points in the form (x, y), from the graph to find the slope :
For example, let us choose (5, 40) and (10, 60).
Use the slope formula.
m = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1)
Substitute :
(x1, y1) = (5, 40)
(x2, y2) = (10, 60)
Then,
m = (60 - 40) / (10 - 5)
m = 20 / 5
m = 4
Step 4 :
Choose a point and use the slope to find the value of 'b' (y-intercept b).
Substitute the point (5, 40) and m = 4 in the equation
y = mx + b
40 = (4)(5) + b
40 = 20 + b
20 = b
Step 5 :
To get the equation of the given linear relationship, substitute m = 4 and b = 20 in the equation y = mx + b.
y = 4x + 20
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 50)
Mar 06, 26 07:48 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 50) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 49)
Mar 06, 26 06:47 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 49) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 48)
Mar 06, 26 05:24 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 48)


