INVERSES OF SIN COS AND TAN
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Inverses of sin, cosine and tangent functions takes the ratio of corresponding functions and gives the angle measure θ.
Trigonometric Ratio Table
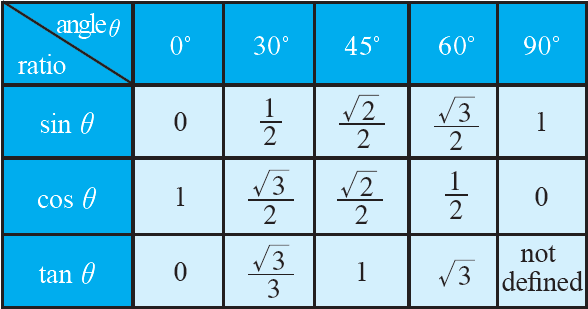
From the trigonometric ratio table above, we have
sin0° = cos90° = 0
sin90° = cos0° = 1
sin30° = cos60° = 1/2
sin60° = cos30° = √3/2
sin45° = cos45° = √2/2
sin0° = tan0° = 0
Examples 1-5 : If θ is an acute angle, find the value of θ in degrees.
Example 1 :
sin θ = 1/2
Solution :
sin θ = 1/2
θ = sin-1(1/2) ----(1)
From the table above, we have
sin 30° = 1/2
30° = sin-1(1/2) ----(2)
From (1) and (2),
θ = 30°
Example 2 :
tanθ = √3
Solution :
tanθ = √3
θ = tan-1(√3) ----(1)
From the table above, we have
tan60° = √3
60° = tan-1(√3) ----(2)
From (1) and (2),
θ = 60°
Example 3 :
cosθ = √2/2
Solution :
cosθ = √2/2
θ = cos-1(√2/2) ----(1)
From the table above, we have
45° = cos-1(√2/2) ----(2)
From (1) and (2),
θ = 45°
Example 4 :
sinθ = √2/2
Solution :
sinθ = √2/2
θ = sin-1(√2/2) ----(1)
From the table above, we have
sin45° = √2/2
45° = sin-1(√2/2) ----(2)
From (1) and (2),
θ = 45°
Example 5 :
cosθ = √3/2
Solution :
cosθ = √3/2
θ = cos-1(√3/2) ----(1)
From the table above, we have
cos30° = √3/2
30° = cos-1(√3/2) ----(2)
From (1) and (2),
θ = 30°
Examples 6-10 : If θ is an acute angle, find the value of θ in radians.
Example 6 :
sinθ = √3/2
Solution :
sinθ = √3/2
θ = sin-1(√3/2) ----(1)
From the table above, we have
sin60° = √3/2
60° = sin-1(√3/2) ----(2)
From (1) and (2),
θ = 60°
To convert degrees to radians, multiply by π/180°.
θ = 60° ⋅ (π/180°)
θ = π/3
Example 7 :
cosθ = 1/2
Solution :
cosθ = 1/2
θ = cos-1(1/2) ----(1)
From the table above, we have
cos60° = 1/2
60° = cos-1(1/2) ----(2)
From (1) and (2),
θ = 60°
To convert degrees to radians, multiply by π/180°.
θ = 60° ⋅ (π/180°)
θ = π/3
Example 8 :
tanθ = √3/3
Solution :
tanθ = √3/3
θ = tan-1(√3/3) ----(1)
From the table above, we have
tan30° = √3/3
30° = tan-1(√3/3) ----(2)
From (1) and (2),
θ = 30°
To convert degrees to radians, multiply by π/180°.
θ = 30° ⋅ (π/180°)
θ = π/6
Example 9 :
tanθ = 1
Solution :
tanθ = 1
θ = tan-1(1) ----(1)
From the table above, we have
45° = tan-1(1) ----(2)
From (1) and (2),
θ = 45°
To convert degrees to radians, multiply by π/180°.
θ = 45° ⋅ (π/180°)
θ = π/4
Example 10 :
tan θ = 1/0
Solution :
tan θ = 1/0
θ = tan-1(1/0) ----(1)
From the table above, we have
tan90° = not defined
tan90° = 1/0
90° = tan-1(1/0) ----(2)
From (1) and (2),
θ = 90°
To convert degrees to radians, multiply by π/180°.
θ = 90° ⋅ (π/180°)
θ = π/2
Using a calculator determine the solution for each equation, of two decimal places on the interval 0 ≤ x ≤ 2π
Example 11 :
3 sin x = sin x + 1
Solution :
3 sin x = sin x + 1
3 sin x - sin x = 1
2 sin x = 1
sin x = 1/2
x = sin-1(1/2)
Since the value is positive for sin, the value of lies in the first and second quadrant.
x = π/6
x = 0.52
Value of x in the second quadrant :
x = π - π/6
x = 5π/6
x = 2.61
So, the values of x are 0.52 and 2.61
Example 12 :
sin 2x = 1/√2
Solution :
sin 2x = 1/√2
2x = sin-1(1/√2)
2x = sin-1(0.707)
Finding value of x lies in the first quadrant :
Using calculator, we get
2x = 0.7676
x = 0.7676/2
x = 0.3838
Finding the value of x lies in the second quadrant :
2x = 3.14 - 0.7676
2x = 2.3724
x = 2.3724 / 2
x = 1.1862
Multiple angles lies in first and second quadrant are,
3.14 + 0.3838 and 3.14 + 1.1862
3.5238 and 4.3262
Example 13 :
sin 3x = -√3/2
Solution :
sin 3x = -√3/2
3x = sin-1(-√3/2)
Reference angle is π/3
3x = (π/3) - π
3x = -2π/3
3x = -2π/3 + 2π
3x = 4π/3
To get more values of x lies in 3rd quadrant :
3x = 4π/3 + 2nπ
x = 4π/9 + (2nπ/3)
When n = 0
x = 4π/9
x = 1.39
|
When n = 1 x = 4π/9 + 2π/3 x = 10π/9 x = 3.48 |
When n = 2 x = 4π/9 + 4π/3 x = 16π/9 x = 5.58 |
To get more values of x lies in 4th quadrant :
3x = 2π - (π/3) + 2nπ
3x = (5π/3) + 2nπ
x = 5π/9 + (2nπ/3)
When n = 0
x = 5π/9
x = 1.74
|
x = 5π/9 + (2nπ/3) When n = 1 x = 5π/9 + (2π/3) x = 11π/9 x = 3.83 |
x = 5π/9 + (2nπ/3) When n = 2 x = 5π/9 + (4π/3) x = 17π/9 x = 5.93 |
So, the values of x are
1.39, 1.74, 3.48, 3.83, 5.58, 5.93
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 35)
Mar 02, 26 08:07 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 35) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 34)
Mar 02, 26 06:36 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 34) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 33)
Mar 02, 26 06:10 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 33)