INTERPRETING LINEAR MODELS
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Linear model is basically the slope-intercept form equation of a line.
y = mx + b
In the above slope-intercept form equation of line,
m ----> slope
b ----> y-intercept
Interpreting Slope (m) :
The slope 'm' always designates a rate of change. That is, change in 'y' with respect to the change in 'x'.
For example, if the slope is 3/2, there is a change of 3 units in 'y' for every 2 units change in 'x'.
Since the slope is a positive value, we can explain this as, there is an increase of 3 units in 'y' for every 2 units of increase in 'x'.
If the slope is -3/2, there is a decrease of 3 units in 'y' for every 2 units of increase in 'x'.
Interpreting y-intercept (b) :
Usually y-intercept is the value of 'y' when x = 0.
In other words, y-intercept is the initial value value of 'y'.
In y = mx + b, the slope 'm' is multiplied by the variable 'x'. So, any change in 'x' will affect only the value of 'mx' and it does not affect the value of 'b'.
In the linear model, y = mx + b, the value on the right side which is not influenced by the variable 'x' is called y-intercept and that is the initial value of y.
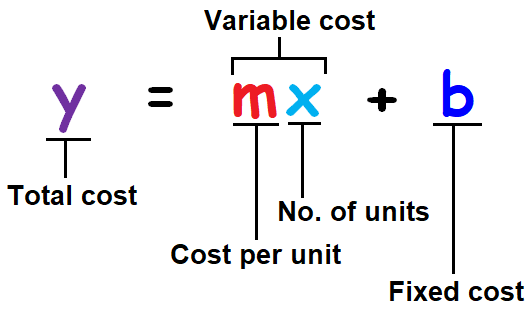
Linear Model as Linear Cost Function
We can interpret the linear model y = mx + b as linear cost function.
y = mx + b is the cost function where the cost curve of a particular product is a line.
This function is used to find the total cost of 'x' units of a products produced.
The picture shown below clearly explains what each letter in the linear cost function stands for.
Solving Problems Using Linear Model
Problem 1 :
For a lemonade stand, the total cost c, in dollars of selling n cups of lemonade is given by c = 100 + 1.5n. What is the best interpretation of the number 100 in this equation?
A) The cost of each cup of lemonade.
B) The number of cups of lemonade sold on the first day.
C) The initial cost of setting up the lemonade stand.
D) The maximum total cost of running the lemonade stand.
Solution :
In c = 100 + 1.5n, 'c' stands for the total cost of lemonade stand.
The number 100 in the equation is not influenced by the number of cups 'n'.
Moreover, when n = 0,
c = 100 + 1.5(0)
c = 100
So, 100 is the initial value of 'c' or the initial cost of setting up the lemonade stand.
The correct answer choice is (C).
Problem 2 :
The number of books in the warehouse can be found using the expression 4000 + 100bd, where 'b' is the number of boxes of books the warehouse receives each day over a period of 'd' days. What is the best interpretation of the number 100 in the expression?
A) The number of books in each box.
B) The number of books received each day.
C) The number of boxes received that contain boxes.
D) The number of days it takes to receive each box.
Solution :
In 4000 + 100bd,
b ----> number of boxes
d ----> number of days
bd = total number of boxes received in 'd' days
Since the given expression represents the total number of books in the warehouse, the number 100 must be the number of books in each box.
The correct answer choice is (A).
Problem 3 :
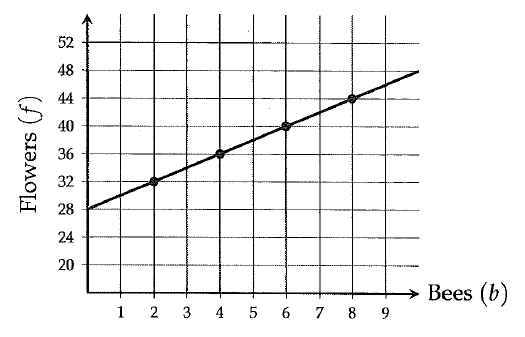
A botanist uses the graph above to show the number of flowers 'f' that blossom in a garden with 'b' bees.
(i) What is the meaning of f-intercept?
(ii) Write a linear function which describes the relationship between 'f' and 'b' and also interpret it.
Solution :
Part (i) :
f ---> number of flowers
b ----> number of bees
In the graph shown above, f-intercept is the value of 'f' when b = 0.
So, f-intercept is the number of flowers that blossom in the garden without any bees.
Part (ii) :
In the graph shown above, f-intercept is 28.
The line goes up 4 units for every 2 units to the right. So, the slope is
= 4/2
= 2
The linear function describes the relationship between 'f' and 'b' :
f = 28 + 2b
Interpreting f = 28 + b :
If b = o,
f = 28 + 2(0)
f = 28
When there is no bee in the garden, the number of flowers that blossom in the garden is 28.
If b = 1,
f = 28 + 2(1)
f = 30
If b = 2,
f = 28 + 2(2)
f = 32
Clearly, if there is an increase 1 bee, there is an increase of 2 flowers in the garden.
Problem 4 :
A food manufacturer fills containers of seasoning with various spices, pepper and salt. The amount of pepper 'p', in milligrams, used in the seasoning can be modeled by the equation
p = (10 + 3s)/4
where 's' is the amount of salt, in milligrams, in the seasoning. According to the model, how many milligrams of pepper are added for every 1 milligram increase in the amount of salt?
Solution :
Write the given equation in the form y = mx + b.
p = (10 + 3s)/4
p = 10/4 + 3s/4
p = 2.5 + (3/4)s
The slope is 3/4 (positive value).
There is an increase of 3 milligrams of pepper for every 4 milligram increase of salt.
4 milligrams of salt ---> 3 milligrams of pepper
1 milligram of salt ----> 3/4 or 0.75 milligrams of pepper
Therefore, 0.75 milligrams of pepper are added for every 1 milligram increase in the amount of salt.
Problem 5 :
Loretta works as a cook in northern Saskatchewan. She is paid $14 an hour plus $200 a week for working in a remote location. Let t represent the time in hours Loretta works each week and let d represent her weekly pay in dollars.
a) Write an equation that relates d and t.
b) What will Loretta’s weekly earnings be when she works 35 h?
c) For how many hours did Loretta work when her weekly pay was $718?
d) Can Loretta earn exactly $600 in one week? Explain.
Solution :
Part (a) :
d = 14t + 200
Part (b) :
Substitute t = 35 in the equation in part (a) and evaluate d..
d = 14(35) + 200
d = 490 + 200
d = 690
When Loretta works 35 h, her weekly earnings will be $690.
Part (c) :
Substitute d = 718 in the equation in part (a) and solve for t..
718 = 14t + 200
Subtract 200 from both sides.
518 = 14t
Divide both sides by 14.
37 = t
When Loretta's weekly pay was $718, she worked for 37 hours.
Part (d) :
Substitute d = 600 in the equation in part (a) and solve for t.
600 = 14t + 200
Subtract 200 from both sides.
400 = 14t
Divide both sides by 14.
28.57 ≈ t
Since the number of hours t is not an integer, Loretta can not earn exactly $600 in one week.
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Questions and Answers
Mar 11, 26 11:40 AM
Digital SAT Math Questions and Answers -
Digital SAT Math Practice Test with Answers
Mar 11, 26 11:35 AM
Digital SAT Math Practice Test with Answers -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 50)
Mar 06, 26 07:48 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 50)