INTERCEPTING A DIAMETER WORKSHEET
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
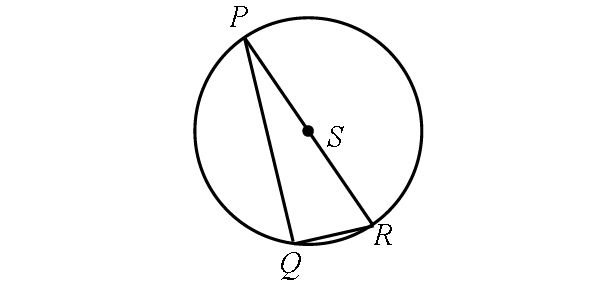
Problem 1 :
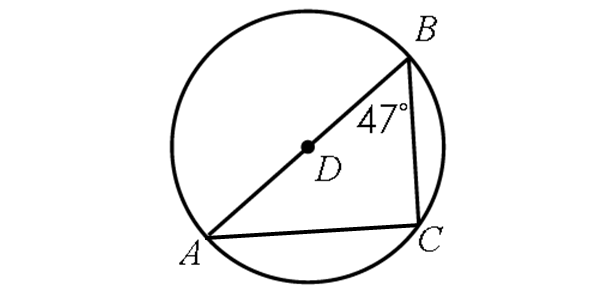
In the diagram shown below, find m∠BAC.
Problem 2 :
In the diagram shown below, m∠QPR = 30°, find m∠PRQ.
Problem 3 :
Solve for x.
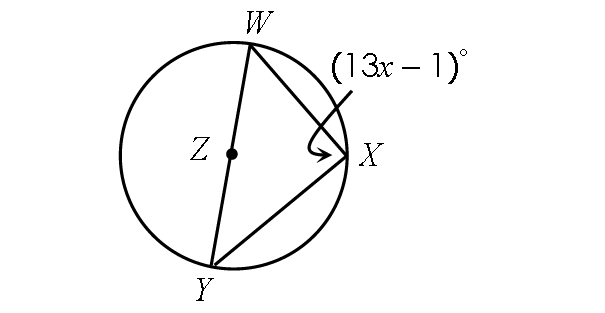
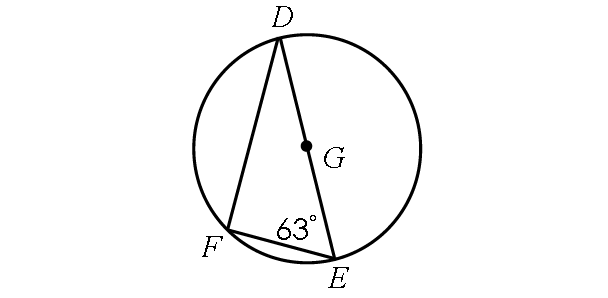
Problem 4 :
Find m∠arc EF.
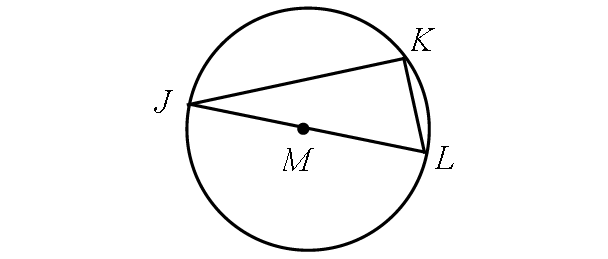
Problem 5 :
If m∠KJL = (3x + 2)° and m∠KLJ = (7x - 32)°, find m∠arc KL.
Problem 6 :
Solve for x.

Detailed Answer Key
Problem 1 :
In the diagram shown below, find m∠BAC.

Solution :
In the diagram shown above, the inscribed angle m∠BCA intercepts the diameter AB.
Then,
m∠BCA = 90°
In Δ ABC,
m∠A + m∠B + m∠C = 180°
Substitute m∠B = 47° and m∠C = 90°.
m∠A + 47° + 90° = 180°
m∠A + 137° = 180°
Subtract 137° from each side.
m∠A = 43°
So,
m∠BAC = 43°
Problem 2 :
In the diagram shown below, m∠QPR = 30°, find m∠PRQ.

Solution :
In the diagram shown above, the inscribed angle m∠PQR intercepts the diameter PR.
Then,
m∠PQR = 90°
In Δ PQR,
m∠P + m∠Q + m∠R = 180°
Substitute m∠P = 30° and m∠Q = 90°.
30° + 90° + m∠R = 180°
120° + m∠R = 180°
Subtract 120° from each side.
m∠R = 60°
So,
m∠PRQ = 60°
Problem 3 :
Solve for x.
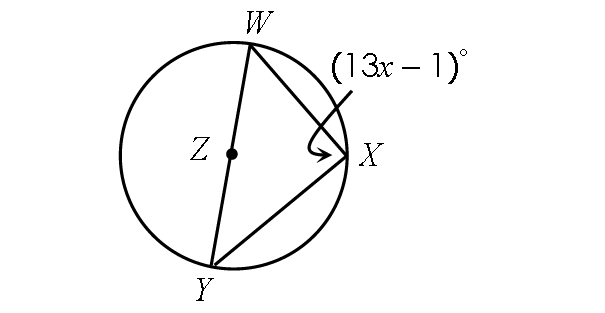
Solution :
In the diagram shown above, the inscribed angle m∠WXY intercepts the diameter WY.
Then,
m∠WXY = 90°
(13x - 1)° = 90°
13x - 1 = 90
Add 1 to each side.
13x = 91
Divide each side 13.
x = 7
Problem 4 :
Find m∠arc EF.

Solution :
In the diagram shown above, the inscribed angle m∠DFE intercepts the diameter DE.
Then,
m∠DFE = 90°
In Δ DEF,
m∠D + m∠E + m∠F = 180°
Substitute.
m∠D + 63° + 90° = 180°
m∠D + 153° = 180°
Subtract 153° from each side.
m∠D = 27°
m∠EDF = 27°
By Inscribed Angle Theorem,
m∠arc EF = 2 ⋅ m∠EDF
m∠arc EF = 2 ⋅ 27°
m∠arc EF = 54°
Problem 5 :
If m∠KJL = (3x + 2)° and m∠KLJ = (7x - 32)°, find m∠arc KL.

Solution :
In the diagram shown above, the inscribed angle m∠JKL intercepts the diameter JL.
Then,
m∠JKL = 90°
In Δ PQR,
m∠J + m∠K + m∠L = 180°
Substitute.
(3x + 2)° + 90° + (7x - 32)° = 180°
3x + 2 + 90 + 7x - 32 = 180
10x + 60 = 180
Subtract 60 from each side.
10x = 120
Divide each side by 10.
x = 12
Finding m∠KJL :
m∠KJL = (3x + 2)°
Substitute x = 12
m∠KJL = [3(12) + 2]°
m∠KJL = [36 + 2]°
m∠KJL = 38°
By Inscribed Angle Theorem,
m∠arc KL = 2 ⋅ m∠KJL
m∠arc KL = 2 ⋅ 38°
m∠arc KL = 76°
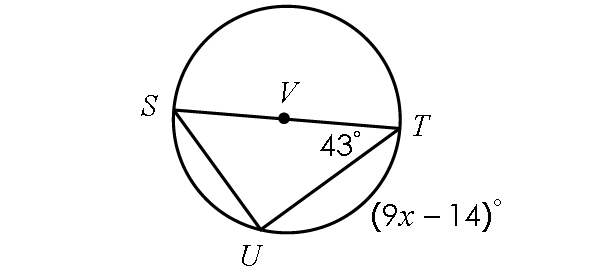
Problem 6 :
Solve for x.

Solution :
In the diagram shown above, the inscribed angle m∠SUT intercepts the diameter ST.
Then,
m∠SUT = 90°
In Δ SUT,
m∠S + m∠U + m∠T = 180°
Substitute.
m∠S + 90° + 43° = 180°
m∠S + 133° = 180°
Subtract 133° from each side.
m∠S = 47°
m∠UST = 47°
By Inscribed Angle Theorem,
m∠arc UT = 2 ⋅ m∠UST
Substitute.
(9x - 14)° = 2 ⋅ 47°
(9x - 14)° = 94°
9x - 14 = 94
Add 14 to each side.
9x = 108
Divide each side by 9.
x = 12
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions
Feb 18, 26 03:01 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions -
Conquering the Hardest SAT Math Questions
Feb 18, 26 02:24 AM
Conquering the Hardest SAT Math Questions -
Problem Solving Strategies for SAT Math
Feb 17, 26 08:09 PM
Problem Solving Strategies for SAT Math