HOW TO PROVE THAT THE FUNCTION IS NOT DIFFERENTIABLE
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
The function is differentiable from the left and right. As in the case of the existence of limits of a function at x0, it follows that
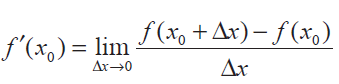
exists if and only if both
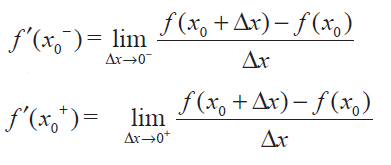
exist and f' (x0-) = f' (x0+)
Hence
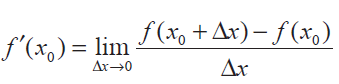
if and only if f' (x0-) = f' (x0+). If any one of the condition fails then f'(x) is not differentiable at x0.
From the above statements, we come to know that if f' (x0-) ≠ f' (x0+), then we may decide that the function is not differentiable at x0.
Question 1 :
Show that the following functions are not differentiable at the indicated value of x.
(i)
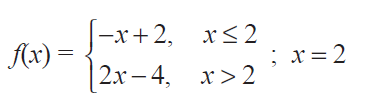
Solution :
f'(2-) = lim x->2- [(f(x) - f(2)) / (x - 2)]
= lim x->2- [(-x + 2) - (-2 + 2)] / (x - 2)
= lim x->2- -(x - 2) / (x - 2)
= lim x->2- (-1)
= -1 -----(1)
f'(2+) = lim x->2+ [(f(x) - f(2)) / (x - 2)]
= lim x->2+ [(2x - 4) - (4 - 4)] / (x - 2)
= lim x->2+ 2(x -2) / (x - 2)
= 2 -----(2)
f'(2-) ≠ f'(2+)
Hence the given function is not differentiable at the point x = 2.
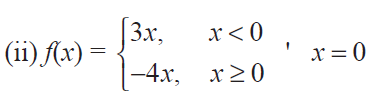
Solution :
f'(0-) = lim x->0- [(f(x) - f(0)) / (x - 0)]
= lim x->0- [(3x) - 0] / (x - 0)
= lim x->0- (3x/x)
= lim x->0- 3
= 3 -----(1)
f'(0+) = lim x->0+ [(f(x) - f(0)) / (x - 0)]
= lim x->0+ [(-4x) - 0] / (x - 0)
= lim x->0+ (-4x/x)
= lim x->0+ -4
= -4 -----(2)
f'(0-) ≠ f'(0+)
Hence the given function is not differentiable at the point x = 0.
Question 2 :
The graph of f is shown below. State with reasons that x values (the numbers), at which f is not differentiable.
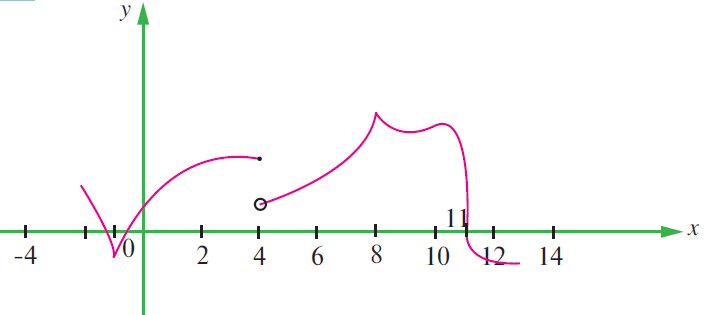
Solution :
If a function is continuous at a point, then it is not necessary that the function is differentiable at that point.
A function f is not differentiable at a point x0 belonging to the domain of f if one of the following situations holds:
(i) f has a vertical tangent at x0.
(ii) The graph of f comes to a point at x0 (either a sharp edge ∨ or a sharp peak ∧ )
(iii) f is discontinuous at x0.
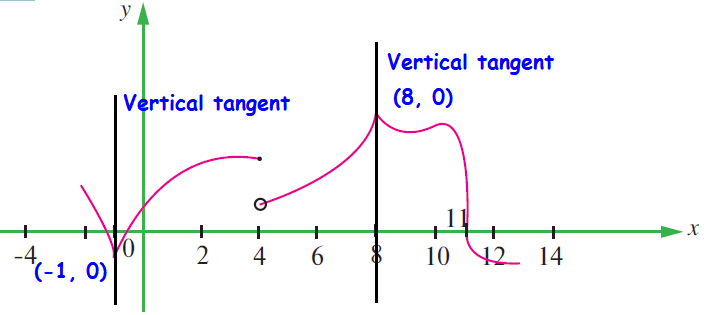
At x = 1 and x = 8, we get vertical tangent (or) sharp edge and sharp peak. So it is not differentiable at x = 1 and 8.
At x = 4, we hjave a hole. Hence it is not continuous at x = 4.
At x = 11, we have perpendicular tangent. So it is not differentiable at x = 11.
Question 3 :
If f(x) = |x + 100| + x2, test whether f'(-100) exists.
Solution :
f'(-100-) = lim x->-100- [(f(x) - f(-100)) / (x - (-100))]
= lim x->-100- [(-(x + 100)) + x2) - 1002] / (x + 100)
= lim x->-100- [(-(x + 100)) + (x2 - 1002)] / (x + 100)
= lim x->-100- [(-(x + 100)) + (x + 100) (x -100)] / (x + 100)
= lim x->-100- (x + 100)) [-1 + (x -100)] / (x + 100)
= [-1 + (-100 -100)]
= -201 --------(1)
f'(-100+) = lim x->-100+ [(f(x) - f(-100)) / (x - (-100))]
= lim x->-100- [(x + 100)) + x2) - 1002] / (x + 100)
= lim x->-100- [(x + 100)) + (x2 - 1002)] / (x + 100)
= lim x->-100- [(x + 100)) + (x + 100) (x -100)] / (x + 100)
= lim x->-100- (x + 100)) [1 + (x -100)] / (x + 100)
= lim x->-100- (x - 99)
= -199 --------(2)
Hence f'(-100) does not exists.
Question 4 :
Examine the differentiability of functions in R by drawing the diagrams.
(i) | sin x |
Solution :
Graph of y = sin x
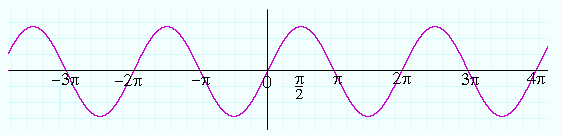
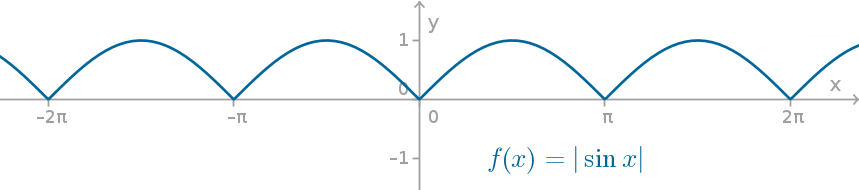
There is vertical tangent for nπ. Hence it is not differentiable at x = nπ, n ∈ z
(ii) | cos x|
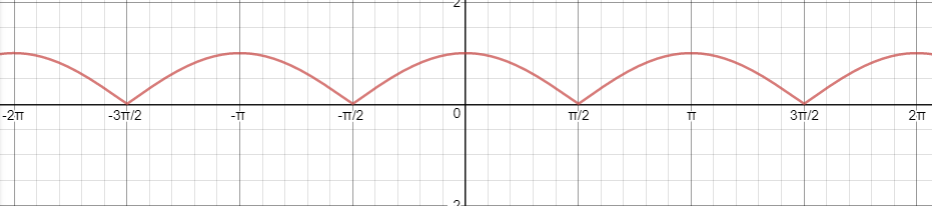
Solution :
There is vertical tangent for (2n + 1)(π/2). Hence it is not differentiable at x = (2n + 1)(π/2), n ∈ z
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 50)
Mar 06, 26 07:48 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 50) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 49)
Mar 06, 26 06:47 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 49) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 48)
Mar 06, 26 05:24 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 48)


