HOW TO FIND THE AREA OF A RHOMBUS WITH VERTICES
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Let d1 and d2 be the lengths of the diagonals of a rhombus.
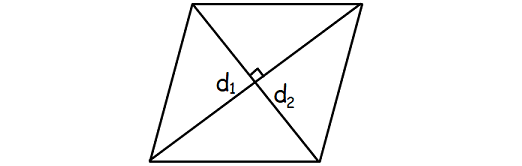
Formula for area of a rhombus :
If the four vertices of a rhombus are given, find the length of each diagonal using distance formula and find the area of the rhombus using the formula given above.
Distance between the two points (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) :
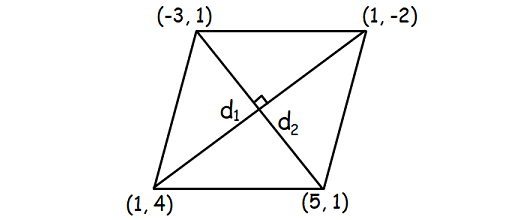
Example 1 :
Find the area of a rhombus with the following vertices taken in order.
(1, 4), (5, 1), (1, -2), (-3, 1)
Solution :
Length of of diagonal d1 :
d1 = √[(x2 - x1)2 + (y2 - y1)2]
Substitute (x1, y1) = (1, 4) and (x2, y2) = (1, -2).
d1 = √[(1 - 1)2 + (-2 - 4)2]
= √[0 + (-6)2]
= √36
= 6
Length of of diagonal d2 :
d2 = √[(x2 - x1)2 + (y2 - y1)2]
Substitute (x1, y1) = (5, 1) and (x2, y2) = (-3, 1).
d2 = √[(-3 - 5)2 + (1 - 1)2]
= √[(-8)2 + 0]
= √64
= 8
Area of rhombus :
= (1/2) x d1 x d2
Substitute d1 = 8 and d2 = 6.
= (1/2) x 8 x 6
= 24 square units
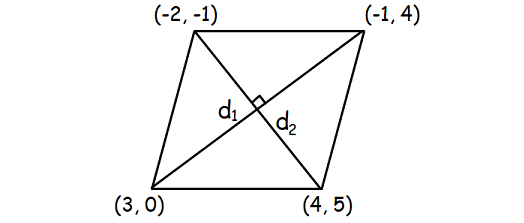
Example 2 :
Find the area of a rhombus with the following vertices taken in order.
(3, 0), (4, 5), (-1, 4), (-2, -1)
Solution :
Length of of diagonal d1 :
d1 = √[(x2 - x1)2 + (y2 - y1)2]
Substitute (x1, y1) = (3, 0) and (x2, y2) = (-1, 4).
d1 = √[(-1 - 3)2 + (4 - 0)2]
= √[(-4)2 + 42]
= √[16 + 16]
= √32
= √(2 x 16)
= 4√2
Length of of diagonal d2 :
d2 = √[(x2 - x1)2 + (y2 - y1)2]
Substitute (x1, y1) = (4, 5) and (x2, y2) = (-2, -1).
d2 = √[(-2 - 4)2 + (-1 - 5)2]
= √[(-6)2 + (-6)2]
= √[36 + 36]
= √72
= √(2 x 36)
= 6√2
Area of rhombus :
= (1/2) x d1 x d2
Substitute d1 = 4√2 and d2 = 6√2.
= (1/2) x 4√2 x 6√2
= 24 square units
Example 3 :
Kite CHSR has vertices at C(0, 3), H(-4, 0) S (0, -7) and R(4, 0). Find the area of kite CHSR.
Solution :
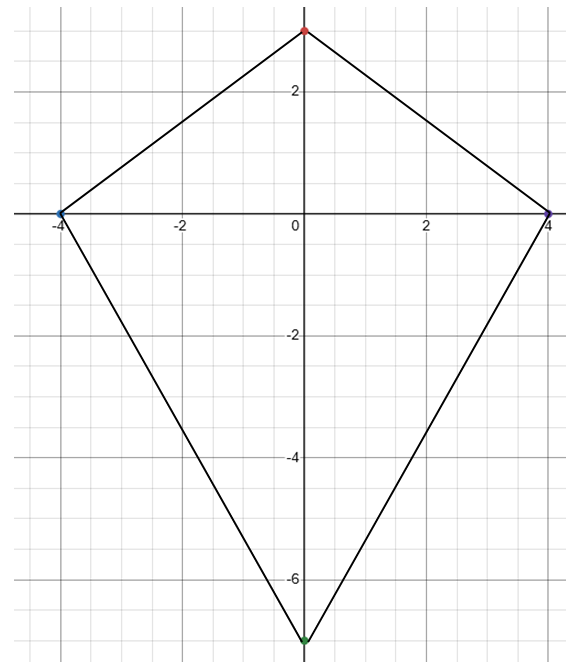
Distance between (-4, 0) and (4, 0) :
d1 = √[(x2 - x1)2 + (y2 - y1)2]
= √[(4 + 4)2 + (0 - 0)2]
= √82 + 0
= 8
Distance between (0, 3) and (0, -7) :
d2 = √[(x2 - x1)2 + (y2 - y1)2]
= √[(0 - 0)2 + (-7 - 3)2]
= √02 + (-10)2
= 10
Area of kite = (1/2) x 8 x 10
= 4 x 10
= 40 square units.
Example 4 :
The area of rhombus is 84 sq.cm and the length of one diagonal is 24 cm. The length of the other diagonal is
Solution :
Area of rhombus = 84 sq.cm
Length of one diagonal (d1) = 24 cm
Length of other diagonal (d2) = ?
(1/2) x 24 x d2 = 84
12 x d2 = 84
d2 = 84 / 12
= 7 cm
So, the length of the other diagonal is 7 cm.
Example 5 :
The diagonal of a quadrilateral are perpendicular bisectors of each other. If the length of one diagonal is 3 cm and the area of the quadrilateral is 180 cm2, find the length of the other diagonal.
Solution :
Every quadrilateral will have four sides. In rhombus, the diagonals will bisect each other.
Area of rhombus = 180 cm2
d1 = 3 cm
(1/2) x d1 x d2 = 180
(1/2) x 3 x d2 = 180
1.5 x d2 = 180
d2 = 180 / 1.5
d2 = 120
So, the length of the other diagonal is 120 cm.
Example 6 :
The length of one of the diagonals of a kite is 4 cm longer than twice the length of the other diagonal. The area of the kite is 15 cm2. Find the length of each diagonal.
Solution :
Let x be the length of the other diagonal.
Length of one diagonal = 2x + 4
Area of kite = 15
(1/2) x (2x + 4) = 15
2x2 + 4x = 30
2x2 + 4x - 30 = 0
Dividing by 2, we get
x2 + 2x - 15 = 0
(x + 5)(x - 3) = 0
x = -5 and x = 3
Length of one diagonal = 3 cm
Length of other diagonal = 2(3) + 4
= 10 cm
Example 7 :
The length of one of the diagonals of a rhombus is 5 cm less than the length of the other diagonal. The area of the rhombus is 33 cm2. Find the length of each diagonal.
Solution :
Let x be the length other diagonal.
Length of one diagonal = x - 5
Area of rhombus = 33
(1/2) x (x - 5) = 33
x2 - 5x = 66
x2 - 5x - 66 = 0
(x - 11) (x + 6) = 0
x = 11 and x = -6
x - 5 ==> 11 - 5 ==> 6 cm
So, length of each diagonals are 11 cm and 6 cm respectively.
Example 8 :
Show that the points A(2, –1), B(3, 4), C(–2, 3) and D(–3, –2) forms a rhombus but not a square. Find the area of the rhombus also.
Solution :
By proving the diagonals are bisecting each other at right angle, we can prove that the shape is rhombus not a square.
|
Slope of diagonal AC : m = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1) = (3 + 1) / (-2 - 2) = 4 / (-4) = -1 |
Slope of diagonal BD : m = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1) = (-2 - 4) / (-3 - 3) = -6 / (-6) = 1 |
Slope AC x Slope of BD = -1
-1(1) = -1
-1 = -1
Since the diagonals are perpendicular it must be a square.
Length of diagonal AC = √[(x2 - x1)2 + (y2 - y1)2]
= √[(-2-2)2 + (3+1)2]
= √[(-4)2 + 42]
= √(16+16)
= √32
Length of diagonal BD = √[(-3-3)2 + (-2-4)2]
= √[(-6)2 + (-6)2]
= √(36+36)
= √72
Area of rhombus = (1/2) √32 √72
= (1/2) x 4√2 (6√2)
= 12(2)
= 24 square units.
So, the required area is 24 square units.
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 25)
Feb 28, 26 07:16 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 25) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 21)
Feb 28, 26 06:49 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 21) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 24)
Feb 28, 26 03:00 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 24)