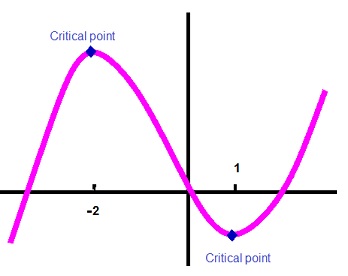
HOW TO FIND CRITICAL NUMBERS USING DERIVATIVE
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Definition of Critical Number :
A Critical-number of a function f is a number c in the domain of f such that either f'(c) = 0 or f'(c) does not exist.
Definition of stationary points :
Stationary points are critical numbers c in the domain of f, for which f'(c) = 0.
Procedure to find critical number :
- Find the first derivative
- set f'(c) = 0.
- Solve for c.
- The value of c are critical numbers.
Procedure to find Stationary points :
- Apply those values of c in the original function
y = f (x).
- (x, y) are the stationary points.
Example 1 :
Find the critical numbers and stationary points of the given function
y = 4x-x2+3
Solution :
As per the procedure first let us find the first derivative
y = f(x) = 4x-x2+3
f'(x) = 4-2 x
set f'(x) = 0
4-2x = 0
x = 2
Therefore the critical number is x = 2.
Now plug the value of x in the original function y = f(x)
f(x) = 4x-x2+3
f(2) = 4(2)-22+3
f(2) = 8-4+3
f(2) = 11-4
f(2) = 7
Therefore the stationary point is (2, 7).
Example 2 :
Find the critical numbers and stationary points of the given function
y = 2x3+3x2-36x+1
Solution :
As per the procedure first let us find the first derivative
y = f(x) = 2x3+3x2-36x+1
f'(x) = 6x2+6x-36
6x2+6x-36 = 0
÷ by 6 ⇒ x2+ x-6 = 0
(x-2) (x+3 ) = 0
x - 2 = 0 x + 3 = 0
x = 2 x = -3
Therefore the critical number x = 2 and x = -3
Now plug the values of x in the original function y = f (x)
f (x) = 2x3+3x2-36x+1
substitute x = 2
f(2) = 2 (2)3 + 3 (2)2-36(2)+1
f(2) = 2(8)+3(4)-72+1
f(2) = 16+12-72+1
f(2) = 28+1-72
f(2) = 29 - 72
f(2) = -43
substitute x = -3
f(-3) = 2(-3)3+3(-3)2-36(-3)+1
f(-3) = 2(-27)+3(9)+108+1
f(-3) = -54+27+108+1
f(-3) = -54+136
f(-3) = 82
Therefore stationary points are (2, -43) and (-3, 42).
Example 3 :
Find the critical points of the function
f(x) = sin2x−cosx
on the interval (0,2π).
Solution :
f(x) = sin2x−cosx
f'(x) = 2 sinx cos x + sinx
f'(x) = sinx(2cos x + sin x)
f'(x) = 0
sin x (2cos x + 1) = 0
sin x = 0 (or) 2cos x + 1 = 0
|
sin x = 0 x = nπ |
2cos x + 1 = 0 cos x = -1/2 x = cos-1(-1/2) x = 2π/3 + 2nπ |
So, the critical points are π and 2π/3.
Example 4 :
The first derivative of the function 𝑓 is given by
𝑓'(𝑥) = sin2x/x - (2/9)
How many critical values does 𝑓 have on the open interval (0, 10) ?
A) One (B) Two (C) Three (D) Four (E) Six
Solution :
Critical number for the function f(x) will be f'(x) = 0
That is, the number of zeroes we get. Here the function f'(x) is having the highest exponent of 2, we will receive two solutions. So total number of critical values for the function f will be Two. Option B is correct.
Example 5 :
If 𝑓 is a continuous, decreasing function on [0, 10] with a critical point at (4, 2) , which of the following statements must be false?
(A) 𝑓 (10) is an absolute minimum of f on [0, 10].
(B) 𝑓 (4) is neither a relative maximum nor a relative minimum.
(C) 𝑓 ′(4) does not exist (D) 𝑓 ′ (4) = 0 (E) 𝑓' (4) < 0
Solution :
In the interval [0, 10] the function is decreasing, it must have minimum value in the interval. So, option A and B will be correct.
Since the function f(x) has critical number in the interval (4, 2), the function may be does not exist or 0. So, option E is incorrect statement.
Example 6 :
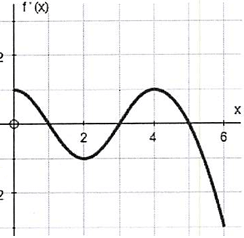
Use the graph of f'(x) defined on [0, 6] provided below to estimate the following.
a) When is f increasing ? when is f decreasing, justify
b) Determine the x-coordinate of all local extrema
Solution :
While observing the graph of f'(x), in the intervals (0, 1) (3, 5) the function is above the x-axis.
In the intervals (1, 3) and (5, 6) the function is below the x-axis.
a)
- On (0, 1) and (3, 5), the function f is increasing since f'(x) is positive.
- On (1, 3) and (5, 6) the function f is decreasing, since f'(x) is negative.
b)
- At x = 1 the function f has local maximum, because f ' changes from + to -.
- At x = 3, the function f has local minimum. Because f' changes from - to +.
- At x = 5, the function f has local maximum. Because f' changes from + to -.
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 23)
Feb 27, 26 04:01 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 23) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 22)
Feb 26, 26 08:43 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 22) -
10 Tricky SAT Math Questions with Answers
Feb 25, 26 08:07 AM
10 Tricky SAT Math Questions with Answers