HOW TO CALCULATE LENGTH OF CHORD IN CIRCLE
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Perpendicular drawn from the center to a chord will bisect it. Using the perpendicular drawn from the center to the chord, radius and one half of the chord, a right triangle can be formed. We can use Pythagorean theorem in the right triangle and find the length of chord.
Example 1 :
A chord is 8 cm away from the center of a circle of radius 17 cm. Find the length of the chord.
Solution :
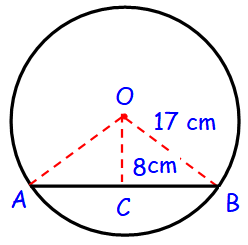
Here the line OC is perpendicular to AB, which divides the chord of equal lengths.
In Δ OCB,
OB2 = OC2 + BC2
172 = 82 + BC2
BC2 = 172 - 82
BC = √(172 - 82)
BC = √289 - 64
BC = √225
BC = √(15 ⋅ 15)
BC = 15 cm
Length of chord = AB = 2 (Length of BC)
= 2 (15)
= 30 cm
Hence the length of chord is 30 cm.
Example 2 :
Find the length of a chord which is at a distance of 15 cm from the center of a circle of radius 25 cm.
Solution :
Distance of chord from center of the circle = 15 cm
Radius of the circle = 25 cm
Length of chord = AB
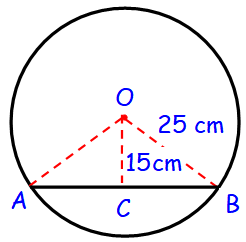
Here the line OC is perpendicular to AB, which divides the chord of equal lengths.
In Δ OCB,
OB2 = OC2 + BC2
252 = 152 + BC2
BC2 = 252 - 152
BC = √(252 - 152)
BC = √625 - 225
BC = √400
BC = √(20 ⋅ 20)
BC = 20 cm
Length of chord = AB = 2 (Length of BC)
= 2 (20)
= 40 cm
Hence the length of chord is 40 cm.
Example 3 :
A chord of length 20 cm is drawn at a distance of 24 cm from the center of a circle. Find the radius of the circle.
Solution :
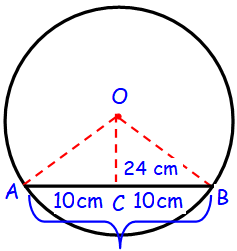
Here the line OC is perpendicular to AB, which divides the chord of equal lengths.
In Δ OCB,
OB2 = OC2 + BC2
OB2 = 242 + 102
BC2 = 576 + 100
BC2 = 676
BC = √676
BC = √(26 ⋅ 26)
BC = 26 cm
Hence the radius of the circle is 26 cm.
Example 4 :
A line which is perpendicular to the radius of the circle through the point of contact is called a ___
(a) tangent (b) chord (c) normal (d) segment
Solution :
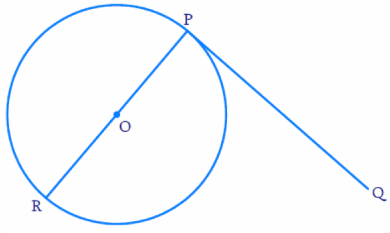
Here the line OP is perpendicular ot PQ. So, the answer is tangent.
Solve for x. Assume that lines which appear tangent are tangent.
Example 5 :
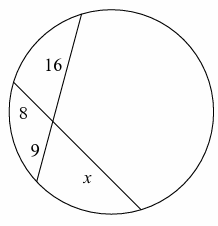
Solution :
When chords are intersecting inside the circle,
8⋅x = 9⋅16
x = (9 ⋅16)/8
x = 9⋅2
x = 18
So, the value of x is 18.
Example 6 :
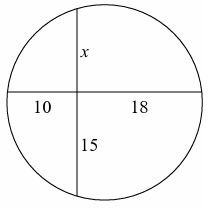
Solution :
When chords are intersecting inside the circle,
10 ⋅ 18 = x ⋅ 15
x = (10 ⋅ 18)/15
x = 180/15
x = 12
So, the value of x is 12
Find the segment length indicated. Assume that lines which appear to be tangent are tangent.
Example 7 :
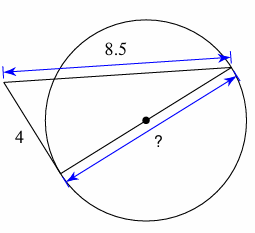
Solution :
The line which touches the circle is the tangent and it make the right angle with the diameter of the circle.
Let x be the diameter of the circle.
Using Pythagorean theorem,
8.52 = 42 + x2
72.25 = 16 + x2
x2 = 72.25 - 16
x2 = 56.25
x = √56.25
x = 7.5
So, the diameter of the circle is 7.5 cm.
Example 8 :
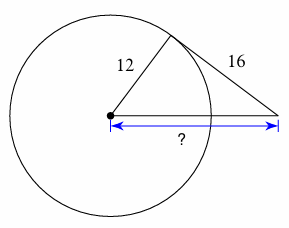
Solution :
The line which touches the circle is the tangent and it make the right angle with the diameter of the circle.
Let x be the length of the chord of circle.
Using Pythagorean theorem,
x2 = 122 + 162
= 144 + 256
= 400
x = √400
x = 20
Example 9 :
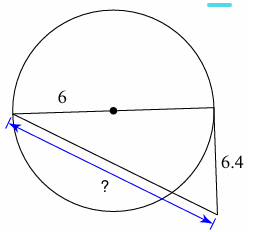
Solution :
Radius = 6 units
Diameter = 12
Let x be the missing side.
x2 = 122 + (6.4)2
x2 = 144 + 40.96
x2 = 184.96
x = √184.96
= 13.6
So, the measure of the missing side is 13.6 units.
Example 10 :
PQ is a chord of length 8 cm of a circle of radius 5 cm. The tangents at P & Q intersect at a point T. Find the length of TP.
Solution :
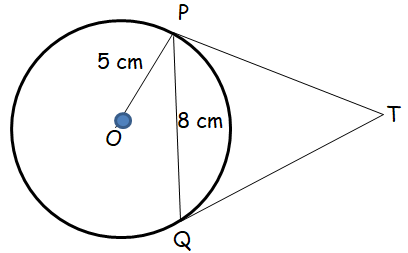
We draw a line from center to T.
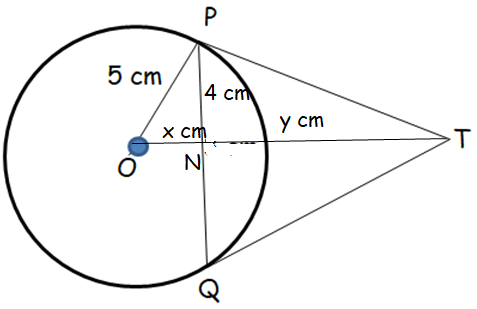
In the triangle PON,
OP2 = ON2 + PN2
52 = x2 + 42
25 - 16 = x2
x2 = 9
x = 3 cm
Then ON is 3 cm.
In triangle POT,
OT2 = OP2 + PT2
(3 + y)2 = 52 + PT2
PT2 = (3 + y)2 - 25 ----(1)
In triangle PNT,
PT2 = PN2 + NT2
PT2 = 42 + y2 ----(2)
(3 + y)2 - 25 = 42 + y2
9 + 6y + y2- 25 = 16 + y2
6y - 16 = 16
6y = 16 + 16
6y = 32
y = 32/6
y = 5.33 cm
Applying the value of y in (2), we get
PT2 = 42 + 5.32
= 16 + 28.09
= 44.09
PT = √44.09
PT = 6.64
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Questions and Answers
Mar 11, 26 11:40 AM
Digital SAT Math Questions and Answers -
Digital SAT Math Practice Test with Answers
Mar 11, 26 11:35 AM
Digital SAT Math Practice Test with Answers -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 50)
Mar 06, 26 07:48 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 50)