GRAPH AND SOLVE QUADRATIC INEQUALITIES WORKSHEET
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Problem 1 :
Graph and solve for x :
x² - 7x + 6 > 0
Problem 2 :
Graph and solve for x :
-x² + 3x - 2 > 0
Problem 3 :
Graph and solve for x :
4x² - 25 ≥ 0
Problem 4 :
Graph and solve for x :
2x² − 12x + 50 ≤ 0

Solutions
Problem 1 :
Graph and solve for x :
x² - 7x + 6 > 0
Solution :
x² - 7x + 6 > 0
(x - 1)(x - 6) > 0
On equating the factors to zero, we see that x = 1, x = 6 are the roots of the quadratic equation. Plotting these roots on real line and marking positive and negative alternatively from the right most part we obtain the corresponding number line as
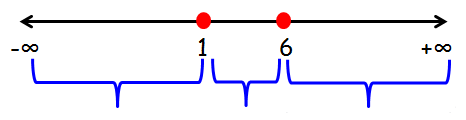
If we plot these points on the number line, we will get intervals (-∞, 1) (1, 6) (6, ∞).
|
From (-∞, 1) let us take -1 |
(-1 − 1) (-1 − 6) > 0 -2(-7) > 0 14 > 0 True |
|
From (1, 6) let us take 4 |
(4 − 1) (4 − 6) > 0 3(-2) > 0 -6 > 0 False |
|
From (6, ∞) let us take 7 |
(7 − 1) (7 − 6) > 0 6(1) > 0 6 > 0 True |
Hence, the solution set is
(− ∞, 1) ∪ (6, ∞)
Problem 2 :
Graph and solve for x :
-x² + 3x - 2 > 0
Solution :
-x² + 3x - 2 > 0
Multiplying by negative sign on both sides
x²- 3x + 2 < 0
(x − 1) (x − 2) < 0
x - 1 = 0 x - 2 = 0
x = 1 and x = 2
On equating the factors to zero, we see that x = 1, x = 2 are the roots of the quadratic equation. Plotting these roots on real line and marking positive and negative alternatively from the right most part we obtain the corresponding number line as
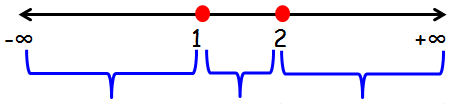
If we plot these points on the number line, we will get intervals (-∞, 1) (1, 2) (2, ∞).
|
From (-∞, 1) let us take -1 |
(x − 1) (x − 2) < 0 (-1 − 1) (-1 − 2) < 0 (-2)(-3) > 0 6 < 0 False |
|
From (1, 2) let us take 1.5 |
(x − 1) (x − 2) < 0 (1.5 − 1) (1.5 − 2) < 0 (-0.5)(-0.5) > 0 0.25 < 0 True |
|
From (2, ∞) let us take 7 |
(7 − 1) (7 − 6) > 0 6(1) > 0 6 > 0 False |
Hence, the solution set is
(1, 2)
Problem 3 :
Graph and solve for x :
4x² - 25 ≥ 0
Solution :
4x² - 25 ≥ 0
(2x)² - 5² ≥ 0
(2x - 5) (2x + 5) ≥ 0
2x - 5 ≥ 0 (or) 2x + 5 ≥ 0
x = 5/2 (or) x = -5/2
On equating the factors to zero, we see that x = 5/2, x = -5/2 are the roots of the quadratic equation. Plotting these roots on real line and marking positive and negative alternatively from the right most part we obtain the corresponding number line as
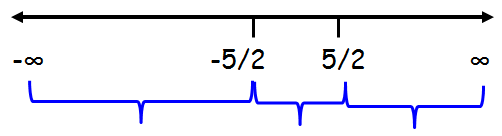
If we plot these points on the number line, we will get intervals (-∞, -5/2) (-5/2, 5/2) (5/2, ∞).Graph solutions to quadratic inequalities
|
From (-∞, -5/2) let us take -3 |
(2x - 5) (2x + 5) ≥ 0 (-6 − 5) (-6 + 5) < 0 (-11)(-1) > 0 11 > 0 True |
|
From (-5/2, 5/2) let us take 0 |
(2x - 5) (2x + 5) ≥ 0 (0− 5) (0 + 5) < 0 (-5)(5) > 0 -25 > 0 False |
|
From (5/2, ∞) let us take 4 |
(2x - 5) (2x + 5) ≥ 0 (8 − 5) (8 + 5) < 0 (3)(13) > 0 39 > 0 True |
Hence, the solution set is
(-∞, -5/2) U (5/2, ∞)
Problem 4 :
Graph and solve for x :
2x² − 12x + 50 ≤ 0
Solution :
2x² − 12x + 50 ≤ 0
2(x²− 6x + 25) ≤ 0
x² − 6x + 25 ≤ 0
(x²− 6x + 9) + 25 − 9 ≤ 0
(x − 3)² + 16 ≤ 0
This is not true for any real value of x.
So, the given quadratic inequality has no solution.
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
SAT Math Problems and Solutions
Feb 14, 26 06:05 AM
SAT Math Problems and Solutions -
SAT Math Practice Questions with Answers
Feb 14, 26 05:47 AM
SAT Math Practice Questions with Answers -
SAT Math Practice Test with Answers
Feb 14, 26 02:30 AM
SAT Math Practice Test with Answers