FIND THE EQUATIONS OF THE TANGENT AND NORMAL TO THE GIVEN CURVE AT THE INDICATED POINT
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Tangent :
The tangent line (or simply tangent) to a plane curve at a given point is the straight line that just touches the curve at that point.
Equation of tangent :
(y-y1) = m(x-x1)
Normal :
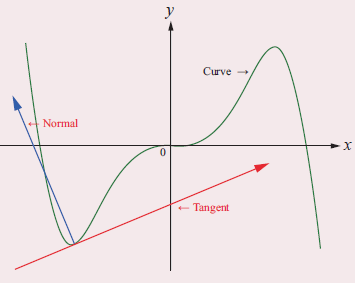
The normal at a point on the curve is the straight line which is perpendicular to the tangent at that point. The tangent and the normal of a curve at a point are illustrated in the adjoining figure.
Equation of normal :
(y-y1) = (-1/m)(x-x1)
Problem 1 :
Find the tangent and normal to the following curves at the given points on the curve.
(i) y = x2 - x4 at (1, 0)
Solution :
y = x2 - x4
Differentiating with respect to x, we get
dy/dx = 2x-4x3
Slope at (1, 0)
dy/dx = 2(1)-4(1)3
dy/dx = -2
Slope of tangent = -2
Slope of normal = 1/2
Equation of tangent :
(y-y1) = m(x-x1)
(y-0) = -2(x-1)
y = -2x+2
2x+y-2 = 0
So, the equation of tangent is 2x+y-2 = 0.
Equation of normal :
(y-y1) = (-1/m)(x-x1)
(y-0) = (1/2)(x-1)
2y = x-1
x-2y-1 = 0
So, equation of normal is x-2y-1 = 0.
(ii) y = x4+2ex at (0, 2)
Solution :
dy/dx = 4x3 + 2ex
Slope at (0, 2)
dy/dx = 4(0)3 + 2e0
dy/dx = 2
Slope of the tangent = 2
Slope of the normal = -1/2
Equation of tangent :
(y-2) = 2(x-0)
y-2 = 2x
2x-y+2 = 0
Equation of normal :
(y-2) = (-1/2)(x-0)
2(y-2) = -x
2y-4 = -x
x+2y-4 = 0
So, equation of tangent is 2x-y+2 = 0 and equation of normal is x+2y-4 = 0.
(iii) y = x sin x at (π/2, π/2)
Solution :
y = x sin x
dy/dx = x cos x + sin x (1)
dy/dx = x cos x + sin x
dy/dx at (π/2, π/2)
dy/dx = π/2 cos π/2 + sin π/2
dy/dx = π/2 (0) + 1
dy/dx = 1
Slope of tangent = 1
Slope of normal = -1
Equation of tangent :
(y - π/2) = 1(x - π/2)
y - π/2 = x - π/2
x-y = 0
Equation of normal :
(y - π/2) = -1(x - π/2)
y - π/2 = -x + π/2
x+y-π = 0
(iv) x = cost, y = 2 sin2t at t = π/3
Solution :
|
x = cost dx/dt = -sin t |
y = 2 sin2t dy/dt = 4 sin t cost |
dy/dx = (dy/dt) / (dx/dt)
dy/dx = 4 sin t cost / (-sin t)
dy/dx = -4 cost
dy/dx at t = π/3 = -4cos (π/3)
= -4(1/2)
= -2
Slope of tangent = -2
Slope of normal = -1/(-2) ==> 1/2
|
x = cost x = cos ( π/3) x = 1/2 |
y = 2 sin2t y = 2 sin2(π/3) y = 2 (3/4) y = 3/2 |
Equation of tangent :
(y-(3/2)) = -2(x-(1/2))
(2y-3) = -2(2x-1)
2y-3 = -4x+2
4x+2y-5 = 0
Equation of normal :
(y-(3/2)) = (1/2)(x-(1/2))
2(2y-3) = (2x-1)
4y-6 = 2x-1
2x-4y-1+6 = 0
2x-4y+5 = 0
Problem 2 :
Find the tangent and normal to the curve x3 + y3 = 2xy at (1, 1).
Solution :
x3 + y3 = 2xy
Differentiate with respect to x, we get
3x2 + 3xy2(dy/dx) = 2[x(dy/dx) + y(1)]
3xy2(dy/dx) - 2x(dy/dx) = 2y - 3x2
(dy/dx)(3xy2 - 2x) = 2y - 3x2
(dy/dx) = (2y - 3x2) / (3xy2 - 2x)
Slope of the tangent at (1, 1) :
dy/dx = (2 - 3) / (3 - 2)
= -1
Slope of normal :
= -1/m
= -1/(-1)
= 1
Equation of tangent :
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y - 1 = -1(x - 1)
y - 1 = -x + 1
x + y - 1 - 1 = 0
x + y = 2
Equation of normal :
y - y1 = -1/m(x - x1)
y - 1 = 1(x - 1)
y - 1 = x - 1
x - y - 1 + 1 = 0
x - y = 0
Problem 3 :
Consider the curve defined by 2y3 + 6x2 y - 12x2 + 6y = 1
i) Find dy/dx
ii) Write an equation of each horizontal tangent line to the curve.
iii) The line through the origin with slope -1 is tangent to the curve at point P. Find the x and y coordinate of P.
Solution :
2y3 + 6x2 y - 12x2 + 6y = 1
i)
2(3y2 dy/dx) + 6[2x y + x2 (dy/dx)] - 12(2x) + 6(dy/dx) = 0
(6y2 dy/dx) + 12x y + 6x2 (dy/dx) - 24x + 6(dy/dx) = 0
dy/dx(6y2 + 6x2 + 6) = - 12xy + 24x
dy/dx = (- 12xy + 24x) / (6y2 + 6x2 + 6)
dy/dx = 6(- 2xy + 4x) / 6(y2 + x2 + 1)
dy/dx = (- 2xy + 4x) / (y2 + x2 + 1)
ii) Equation of horizontal tangent :
For horizontal tangent, the slope = 0
(- 2xy + 4x) / (y2 + x2 + 1) = 0
-2xy + 4x = 0
-2x(y - 2) = 0
x = 0 and y = 2
When x = 0,
2y3 + 6(0)2 y - 12(0)2 - 6y = 1
2y3 - 6y = 1
When y = 2
2(2)3 + 6x2 (2) - 12x2 + 6(2) = 1
16 + 12x2 - 12x2 + 12 = 1
There are no points on the curve where y = 2.
iii) The line passes through origin will be y = x
Since it has the slope -1, it must be falling line and the required line will be y = -x
(- 2xy + 4x) / (y2 + x2 + 1) = -1
Applying y = -x, we get
(2x2 + 4x) / (x2 + x2 + 1) = -1
2x2 + 4x = -x2 - x2 - 1
2x2 + 4x = -2x2 - 1
4x2 + 4x + 1 = 0
(2x + 1)2 = 0
2x + 1 = 0
2x = -1
and x = -1/2
y = 1/2
So, the required point is (-1/2, 1/2).
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
Mastering the SAT Math
Feb 12, 26 07:16 AM
Mastering the SAT Math -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 1)
Feb 12, 26 06:31 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 1) -
Simplifying Square Roots Worksheet
Feb 10, 26 07:29 AM
Simplifying Square Roots Worksheet