FIND THE APPROXIMATE VALUE USING LINEAR APPROXIMATION
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Let f : (a,b)→R be a differentiable function and
x0 ∈ (a, b)
We define the linear approximation L of f at x0 by
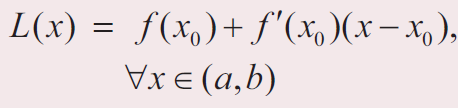
Problem 1 :
Let f (x) = ∛x . Find the linear approximation at x = 27. Use the linear approximation to approximate ∛27.2
L(x) = f(x0) + f'(x0) (x-x0)
Solution :
f(x) = ∛x
Let x0 = 27 and x = 27.2
L(x) = f(x0) + f'(x0) (x - x0)
|
f(x) = ∛x f(x0) = ∛27 f(x0) = 3 |
f'(x) = (1/3)x-2/3 f'(x0) = (1/3)(27)-2/3 f'(x0) = (1/3)(1/9) f'(x0) = 1/27 |
L(27.2) = 3 + (1/27) (27.2-27)
L(27.2) = 3 + (1/27) (0.2)
L(27.2) = 3 + 0.0074
L(27.2) = 3.0074 (approximately)
Problem 2 :
Use the linear approximation to find approximate values of
(i) (123)2/3
Solution :
f(x) = (x)2/3
Let x = 123 and x0 = 125 (the nearest whole number)
|
f(x) = (x)2/3 f(125) = (125)2/3 f(125) = (53)2/3 f(125) = 25 |
f'(x) = (2/3)x2/3 - 1 f'(x) = (2/3)x-1/3 f'(125) = (2/3)(125)-1/3 f'(125) = (2/3)(53)-1/3 f'(125) = (2/3)(5-1) f'(125) = 2/15 |
L(x) = f(x0) + f'(x0) (x - x0)
L(123) = 25 + (2/15) (123-125)
L(123) = 25 + (2/15) (-2)
L(123) = 25 - (4/15)
L(123) = 25 - 0.2667
L(123) = 24.733
So, the approximate value of (123)2/3 is 24.733.
(ii) (15)1/4
Solution :
L(x) = f(x0) + f'(x0)(x-x0)
Let x0 = 16 and x = 15
L(15) = f(16) + f'(16)(x-x0) ----(1)
|
f(x) = x1/4 f(16) = 161/4 f(16) = (24)1/4 f(16) = 2 |
f'(x) = (1/4) x1/4 - 1 f'(x) = (1/4) x-3/4 f'(16) = (1/4) (16)-3/4 f'(16) = (1/4) (2-3) f'(16) = (1/32) |
L(15) = f(16) + f'(16)(x-x0) ----(1)
By applying the values in (1), we get
L(15) = 2 + (1/32)(15-16)
L(15) = 2 + (1/32)(-1)
L(15) = 2 - 0.03125
L(15) = 1.968 (approximately)
So, the approximate value of (15)1/4 is 1.968.
(iii) ∛26
Solution :
Let f(x) = ∛x
Let x = 26 and x0 = 27
L(x) = f(x0) + f'(x0) (x-x0)
L(26) = f(27) + f'(27) (x-x0) ----(1)
|
f(x) = ∛x f(27) = ∛27 f(27) = 3 |
f'(x) = (1/3) x1/3-1 f'(x) = (1/3) x-2/3 f'(27) = (1/3) 27-2/3 f'(27) = (1/3) (1/9) f'(27) = 1/27 |
By applying these value in (1), we get
L(26) = 3 + (1/27) (27-26)
L(26) = 3 + (1/27) (1)
L(26) = 3 + 0.0370
L(26) = 3.0370
So, the approximate value of ∛26 is 3.0370.
Problem 3 :
Consider the implicit function defined by 3(x2 + y2)2 = 100xy . Use a tangent line approximation at the point (3,1) to estimate the value of y when x = 3.1.
Solution :
Even though y is defined implicitly as a function of x here, the tangent line to the graph of 3(x2 + y2)2 = 100xy at (3, 1) can easily be found and used to estimate y for x near 3.
First, find y. Differentiating both sides of 3(x2 + y2)2 = 100xy with respect to x gives
6(x2 + y2)(2x + 2 yy') = 100y + 100xy'
Now substitute (x, y) = (3, 1)
6(9 + 1)(6 + 2y') = 100 + 300 y'
60(6 + 2y') = 100 + 300 y'
360 + 120y'= 100 + 300y'
360 - 100 = 300y'- 120y'
260 = 180y'
y' = 260 / 180
y' = 13/9
which yields y' = 13/9. Thus the equation of the tangent line is
y − 1 = (13/9) (x−3)
y - 1 = (13x/9) - (13/3)
y = (13x/9) - (13/3) + 1
y = (13x/9) + (-13 + 3)/3
y = (13x/9) - (10/3)
Thus, for points (x,y) on the graph of 3(x2 + y2)2 = 100xy with x near 3,
y ≈ (13x/9) − (30/9)
Setting x = 3.1 in this last equation gives
y ≈ 103/90
= 1.14 to two decimals.
Problem 4 :
Finding a local linear approximation at a given point is finding the equation of the tangent line at that point.
a) Find the local linear approximation of f(x) = x3 - 2x + 3 at the point where x = 2.
b) Use your approximation to estimate f(2.1), f(1.9) and f(1.99).
Solution :
f(x) = x3 - 2x + 3
Let x0 = 2
f'(x) = 3x2 - 2(1) + 0
f'(x) = 3x2 - 2
f'(x0) = 3(2)2 - 2
= 12 - 2
f'(x0) = 10
L(x) = f(x0) + f'(x0) (x-x0)
L(2) = f(2) + f'(2) (x-2)
Finding the value of f(2),
f(2) = 23 - 2(2) + 3
= 8 - 4 + 3
= 7
L(2) = 7 + 10 (x - 2)
= 7 + 10x - 20
L(2) = 10x - 13
Using the result above, finding the linear approximation for f(2.1), f(1.9) and f(1.99).
L(2.1) = 10(2.1) - 13
= 21 - 13
= 8
L(1.9) = 10(1.9) - 13
= 19 - 13
= 6
L(1.99) = 10(1.99) - 13
= 19.9 - 13
= 6.9
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
SAT Math Practice Questions with Answers
Feb 02, 26 05:50 AM
SAT Math Practice Questions with Answers -
Mastering the SAT Math
Feb 02, 26 05:34 AM
Mastering the SAT Math -
SAT Math Practice Test with Answers
Feb 02, 26 05:26 AM
SAT Math Practice Test with Answers