FIND INVERSE FUNCTION FROM THE GIVEN FUNCTION
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
To find inverse function of the given function, we follow the steps given below.
Step 1 :
Let the given function be f(x). The given function will be defined in terms of x. Replace f(x) by y.
Step 2 :
In the given function interchange y and x.
Step 3 :
Derive the new equation for y.
Step 4 :
y can be replaced by f-1(x)
For each of the following functions :
Example 1 :
a) f(x) = 2x+5 b) f(x) = (3-2x)/4 c) f(x) = x+3
(i) Find f-1(x)
(ii) sketch y = f(x), y = f-1(x) and y = x on the same axes.
Solution :
a) f(x) = 2x+5
(i)
Step 1 :
Let, y = f(x)
y = 2x+5
Step 2 :
By interchanging x and y, we get
x = 2y+5
2y = x-5
y = (x-5)/2
Step 3 :
So, the required inverse function is
f-1(x) = (x-5)/2
(ii) By applying some random values of x in the function
y = 2x+5
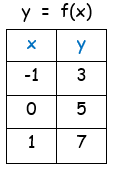 |
By joining the points (-1, 3), (0, 5) and (1, 7), we will get the graph of original function. So, the required coordinates of inverse function are (3,-1) (5, 0) and (7, 1). |
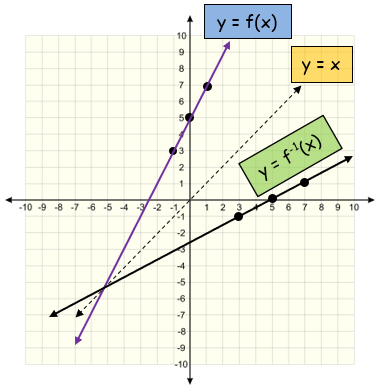
We draw the graph of inverse function be reflecting the graph of original function about y = x.
b) f(x) = (3-2x)/4
Solution :
(i) Let, y = f(x)
y = (3-2x)/4
By interchanging x and y, we get
x = (3-2y)/4
4x = 3-2y
2y = 3-4x
y
= (3-4x)/2
y = -2x+(3/2)
We express f-1 as a function of x in terms of y
f-1(x) = -2x+(3/2)
(ii) For graphing, by applying some random values of x in the function
y = -2x+(3/2)
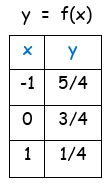 |
By joining the points (-1, 5/4), (0, 3/4) and (1, 1/4), we will get the graph of original function. So, the required coordinates of inverse function are (5/4, -1), (3/4, 0) and (1/4, 1) |
By plotting the points, we get graph of the given function and inverse function.

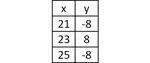
c) f(x) = x+3
Solution :
(i) Let, y = f(x)
y = x+3
By interchanging x and y, we get
x = y+3
y = x-3
We express f-1 as a function of x in terms of y
f-1(x) = x-3
(ii)
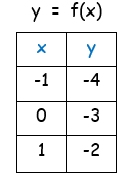 |
Coordinates of given function : (-1, -4) (0, -3) and (1, -2) Coordinates of inverse function : (-4, -1) (-3, 0) and (-2, 1) |
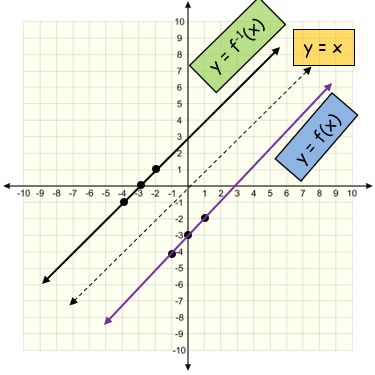
Example 2 :
If f(x) = 2x + 7, find :
a) f-1(x) b) f(f-1(x)) c) f-1(f(x))
Solution :
a.
Given, f(x) = 2x + 7
Let y = 2x+7
By interchanging x and y, we get
x = 2y+7
2y = x-7
y
= (x-7)/2
We express f-1 as a function of x in terms of y
f-1(x) = (x-7)/2
b)
We have, f-1(x) = (x-7)/2
Then,
f(f-1(x)) = f((x-7)/2)
= 2x+7
= 2[(x-7)/2] + 7
= x–7+7
f(f-1(x)) = x ----(1)
c)
we have, f-1(x) = (x-7)/2
f-1(f(x)) = (f(x) - 7)/2
= (2x+7-7)/2
= 2x/2
f-1(f(x)) = x ----(2)
Example 3 :
If f(x) = (2x + 1)/(x + 3), find :
a) f-1(x) b) f(f-1(x)) c) f-1(f(x))
Solution :
a)
Given, f(x) = (2x+1)/(x+3)
Let y = (2x+1)/(x+3)
By interchanging x and y, we get
x = (2y+1)/(y+3)
x(y+3) = 2y+1
xy+3x = 2y+1
-2y+xy = -3x+1
y(-2+x) = -3x+1
y = (-3x+1)/(x-2)
y = (1-3x)/(x-2)
We express f-1 as a function of x in terms of y
f-1(x) = (1-3x)/(x-2)
b) f(f-1(x)) = f((1-3x)/(x-2))
By using x in terms of f(x), we get
f(x) = (2x+1)/(x+3)
= [2[(1-3x)/(x-2)]+1]/[(1-3x)/(x-2)+3]
= [(2-6x+x-2)/(x-2)]/[(1-3x+3x-6)/(x-2)]
= (-5x)/(-5)
= x
f(f-1(x)) = x ------(1)
c) we have, f-1(x) = (1-3x)/(x-2)
By using f(x) in terms of f-1(x), we get
f-1(f(x)) = (1-3f(x))/(f(x)-2)
simplifying the terms,
= [1-3(2x+1)/(x+3)]/[(2x+1)/(x+3)-2)
= [(x+3) – 3(2x+1)/(x+3)]/[(2x+1) – 2(x+3)/(x+3)]
= [x+3–6x–3]/[2x+1–2x–6]
= (-5x)/(-5)
= x
f-1(f(x)) = x ------(2)
Example 4 :
You need a total of 50 pounds of two types of ground beef costing $1.25 and $1.60 per pound, respectively. A model for the total cost of the two types of beef is
y = 1.25x + 1.60(50 - x)
where is the number of pounds of the less expensive ground beef.
(a) Find the inverse function of the cost function. What does each variable represent in the inverse function?
(b) Determine the number of pounds of the less expensive ground beef purchased when the total cost is $73.
Solution :
a)
y = 1.25x + 1.60(50 - x)
y = 1.25x + 80 - 1.60x
y = -0.35x + 80
Solving for x, we get
0.35x = 80 - y
x = (80 - y)/0.35
f-1(x) = (80 - x)/0.35
b) y = 1.25x + 1.60(50 - x)
y = 73
73 = 1.25x + 80 - 1.60x
73 = -0.35x + 80
73 - 80 = -0.35x
-7 = -0.35x
x = 7/0.35
x = 20
So, 20 pounds is the answer.
Example 5 :
The function given by
f(x) = k(2 - x - x2)
has an inverse function f-1(3) = -2, find k.
Solution :
Domain of function f(x) is range of inverse function.
Instead of finding inverse of given function, we apply -2 in the original function f(x) to get the value of f-1(3).
When input x = -2, output = 3
f(2) = k(2 - 2 - 22)
3 = k(-4)
k = -3/4
So, the required value of k is -3/4.
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part -27)
Feb 28, 26 07:46 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part -27) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 26)
Feb 28, 26 06:28 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 26) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 25)
Feb 28, 26 07:21 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 25)